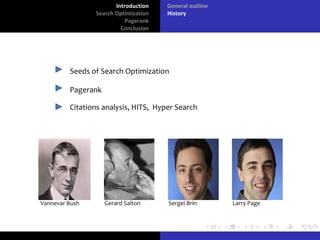
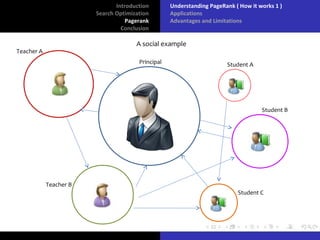
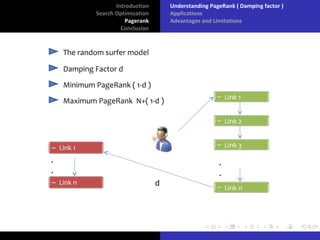
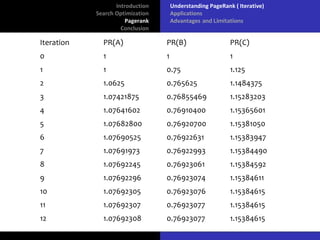
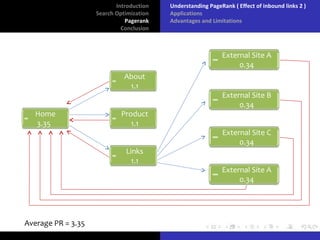
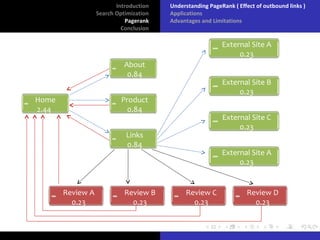
The document discusses search optimization with a focus on the PageRank algorithm, its history, and its applications in various search engines. It covers how PageRank is calculated, including factors like inbound and outbound links, and its advantages and limitations. The document concludes by emphasizing the significance of optimization for webmasters and its impact on the web development industry.