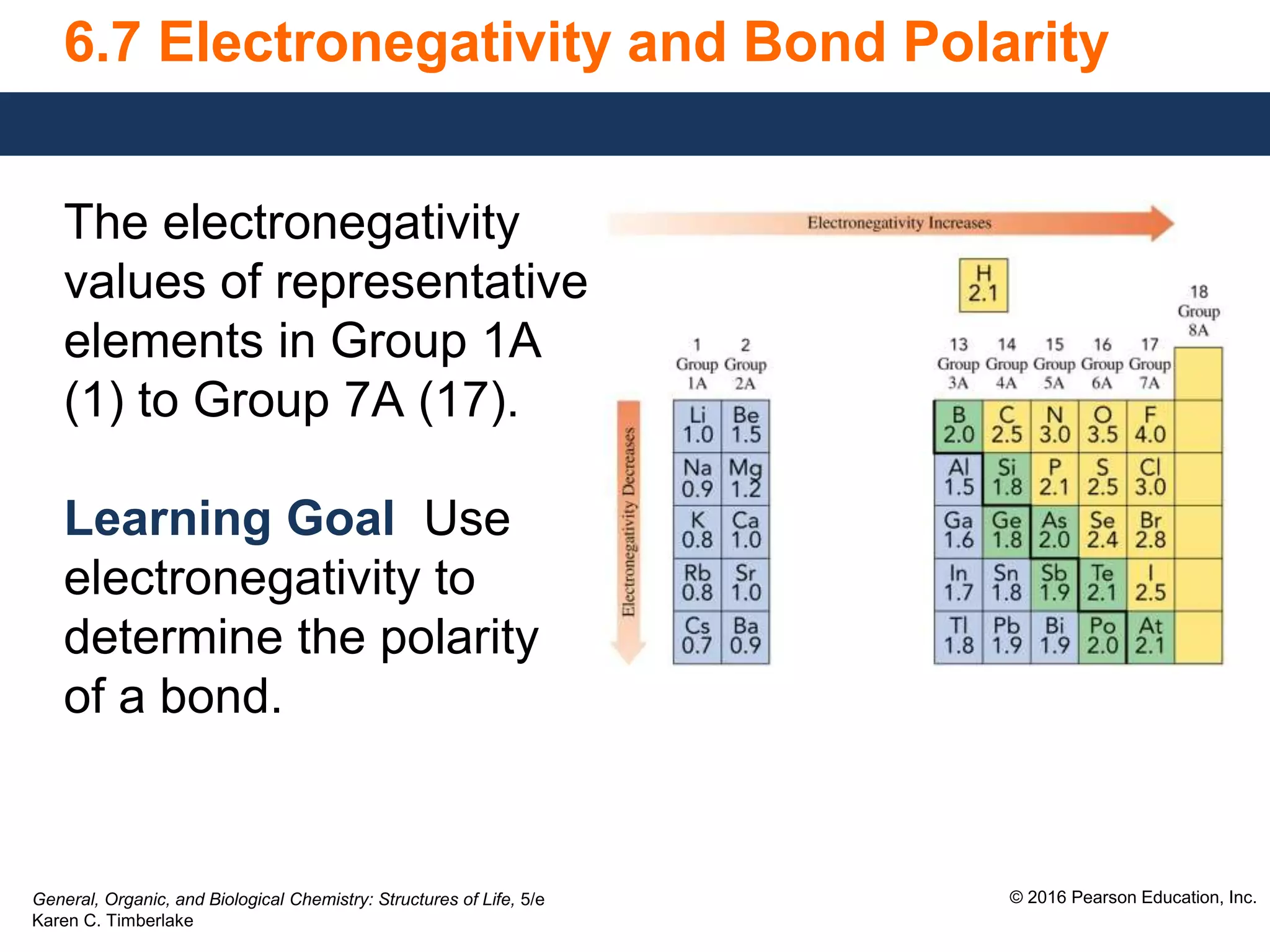
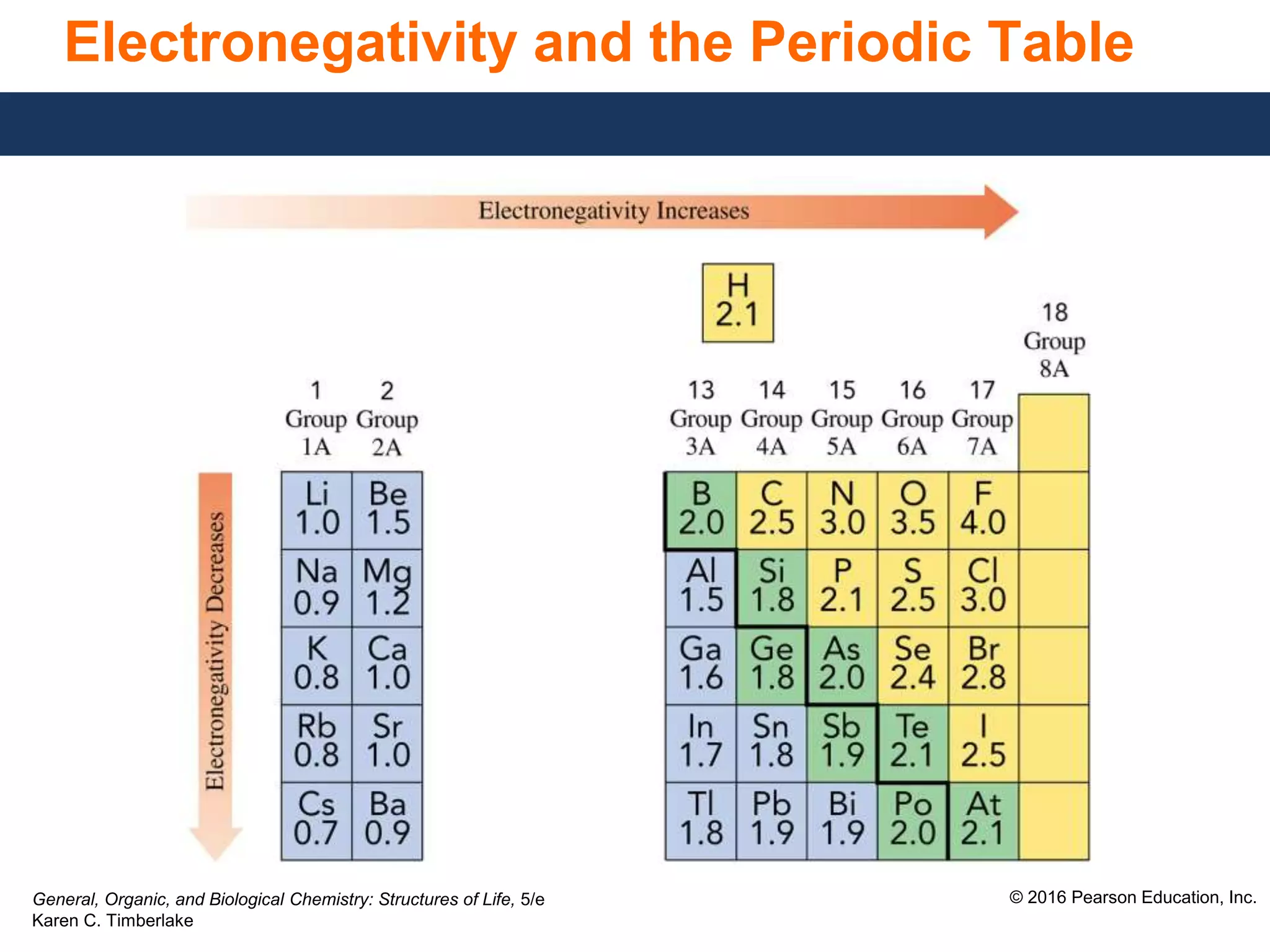
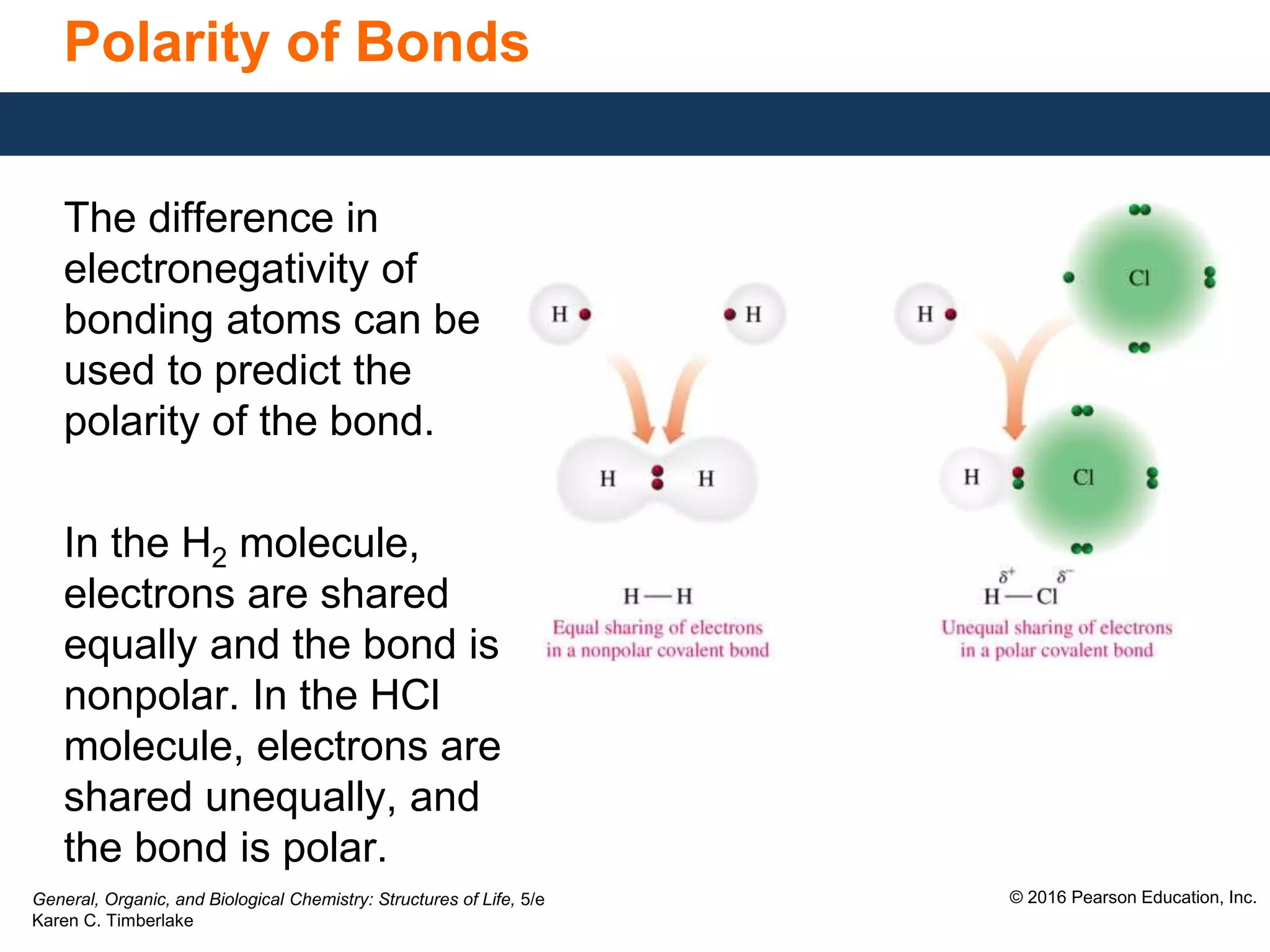
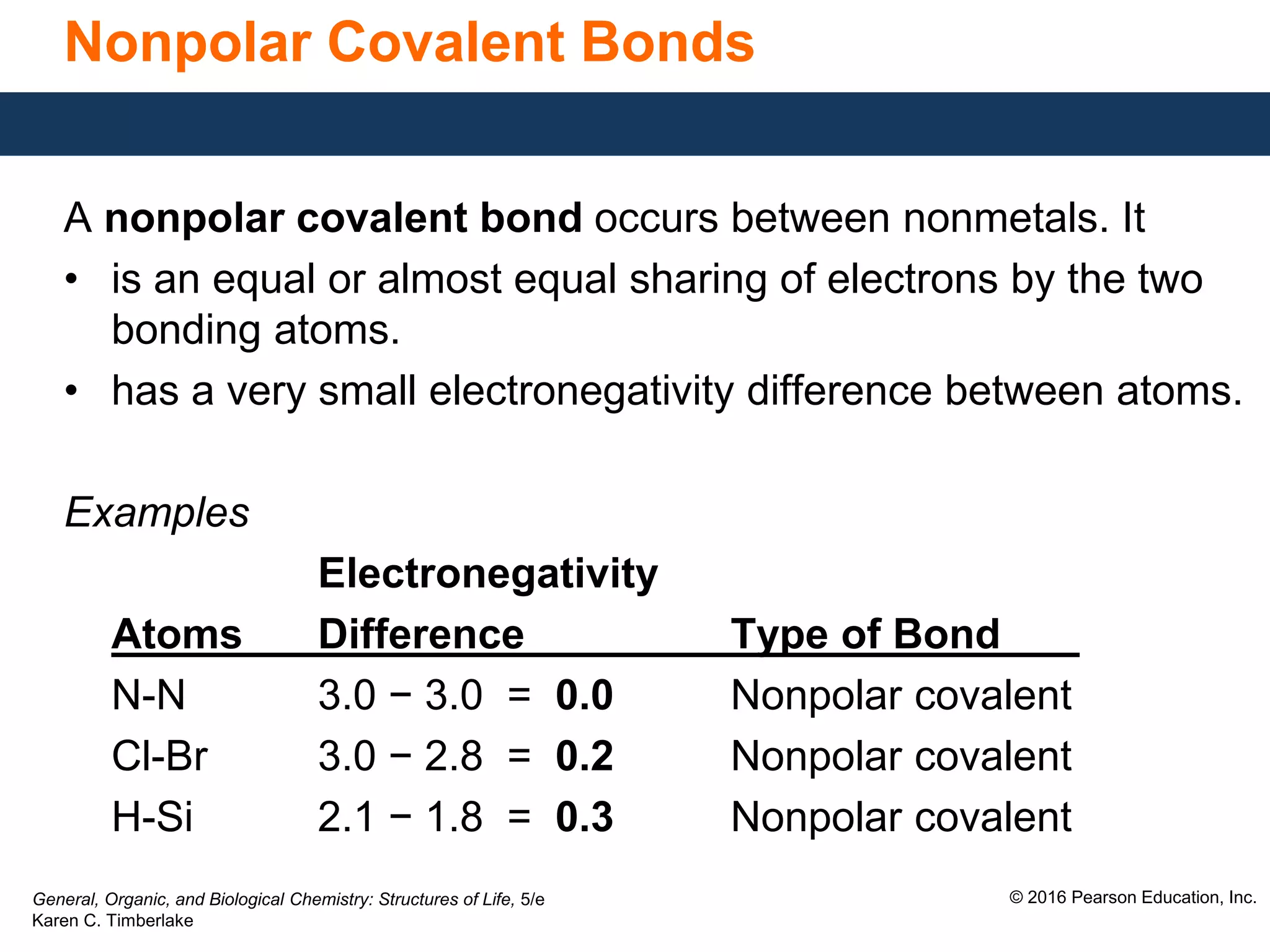
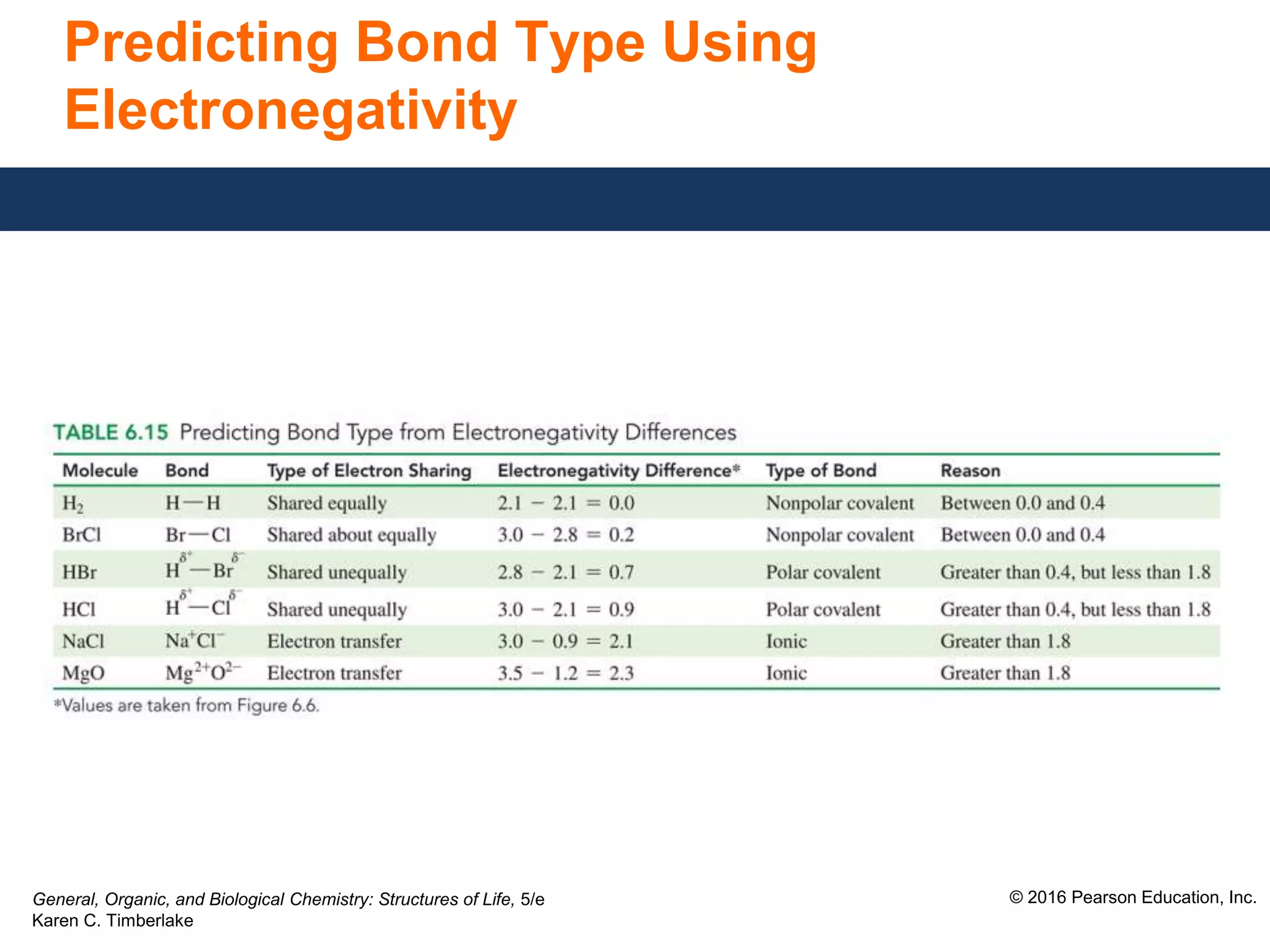
This document discusses electronegativity and how it can be used to predict bond polarity. It explains that electronegativity increases across periods and up groups in the periodic table. Bond polarity is determined by the difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms - a small difference leads to nonpolar covalent bonds, a moderate difference leads to polar covalent bonds, and a large difference leads to ionic bonds through electron transfer. Examples are given of different bond types classified by their electronegativity differences.


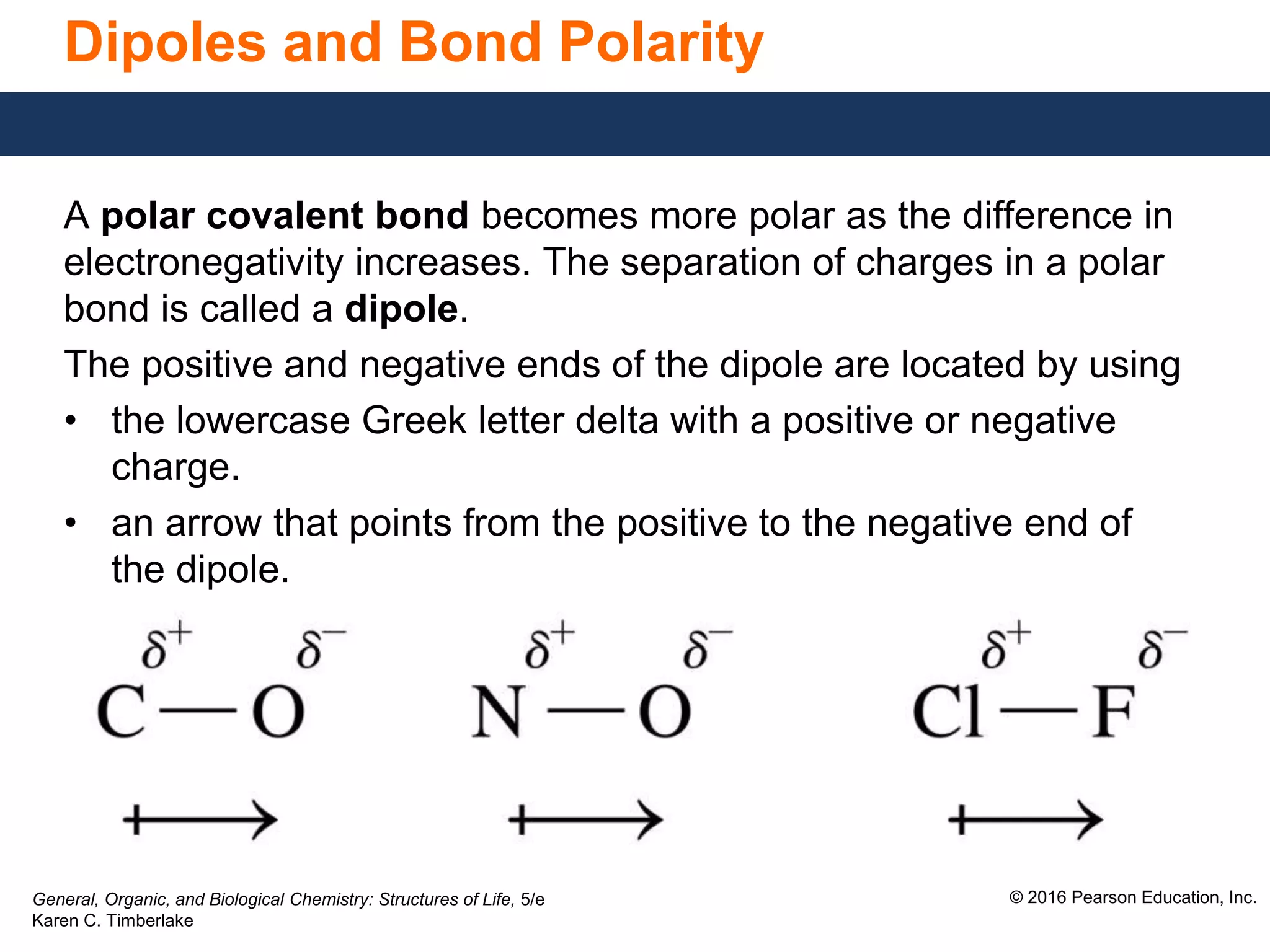
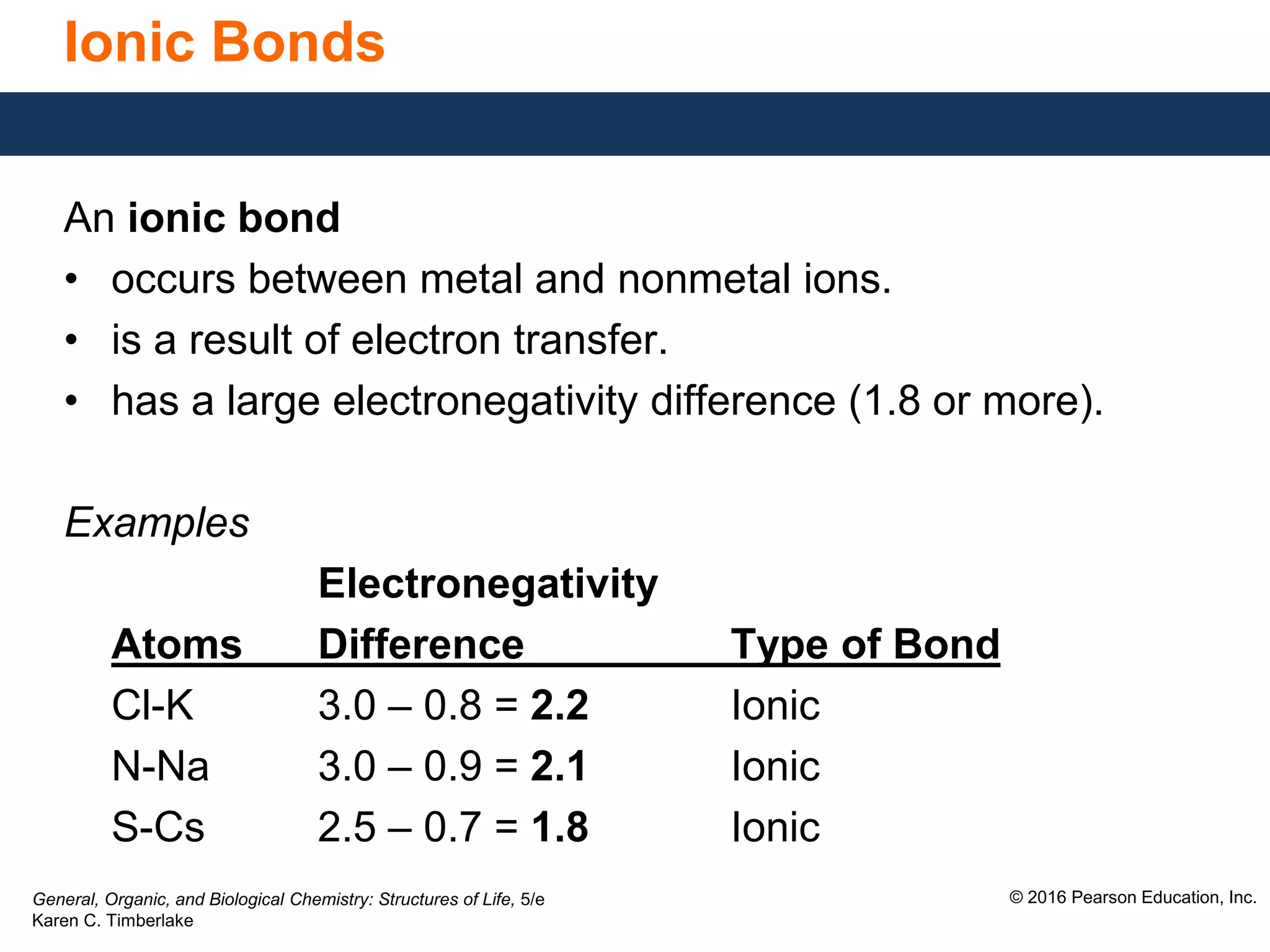
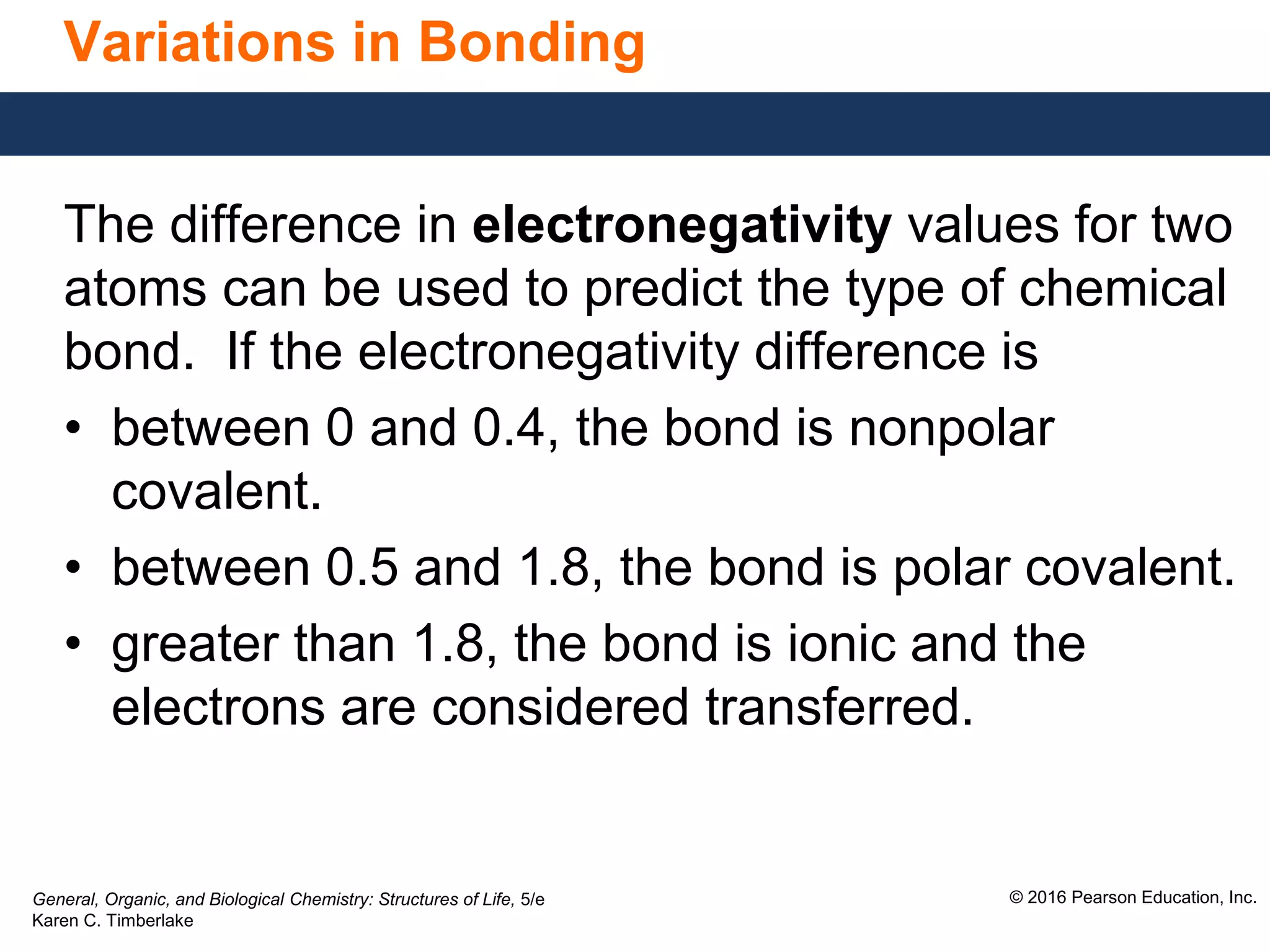
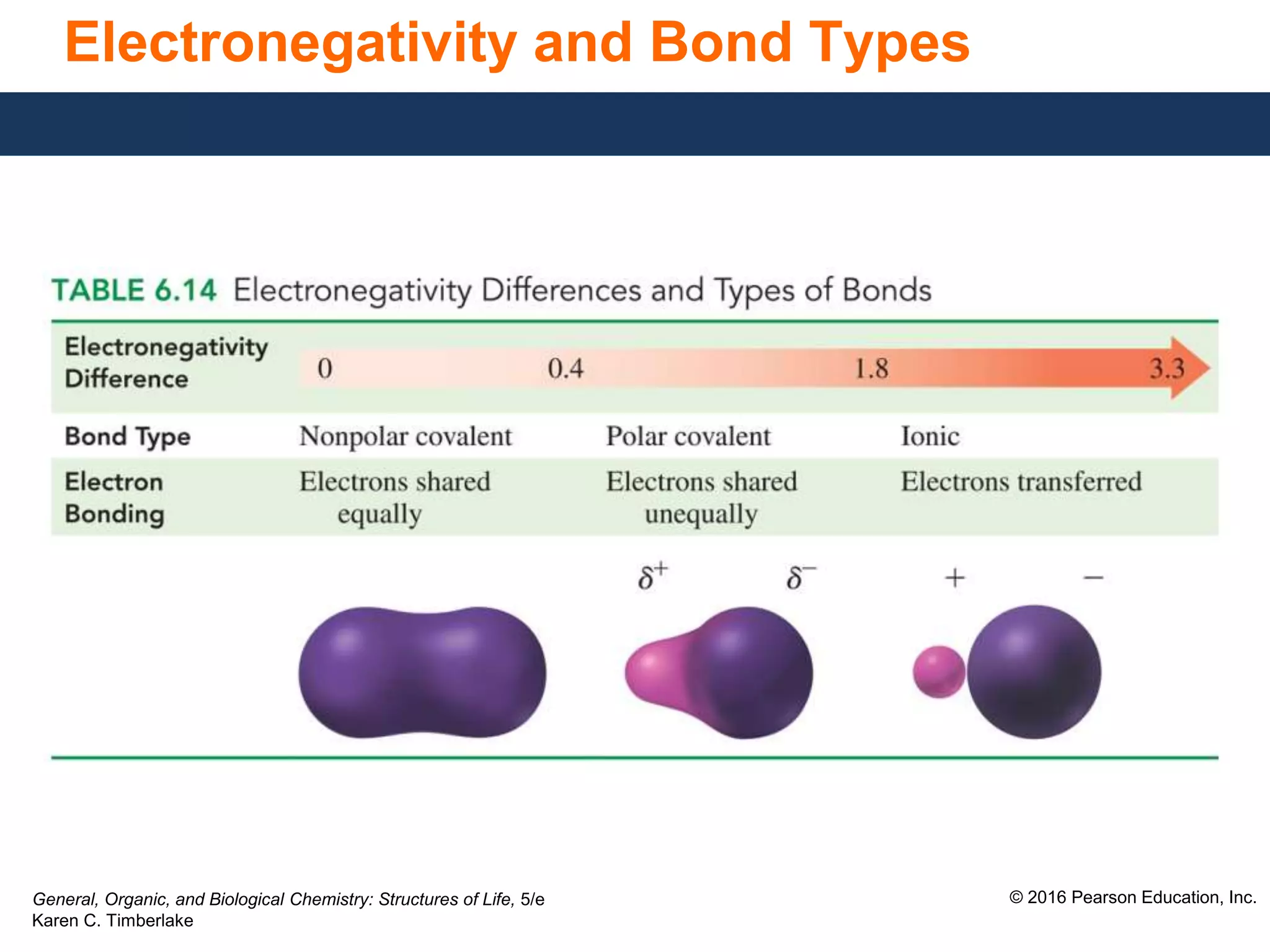
![General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e
Karen C. Timberlake
© 2016 Pearson Education, Inc.
Study Check
Use the electronegativity difference to identify
the type of bond (nonpolar covalent [NP], polar
covalent [P], or ionic [I]) between the following:
A. K—N
B. N—O
C.Cl—Cl
D.H—Cl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-230305113354-901e7a7f/75/Electronegativity-pptx-12-2048.jpg)
![General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e
Karen C. Timberlake
© 2016 Pearson Education, Inc.
Solution
Use the electronegativity difference to identify
the type of bond (nonpolar covalent [NP], polar
covalent [P], or ionic [I]) between the following:
Difference Type of bond
A. K—N 2.2 ionic (I)
B. N—O 0.5 polar covalent (P)
C.Cl—Cl 0.0 nonpolar covalent (NP)
D.H—Cl 0.9 polar covalent (P)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-230305113354-901e7a7f/75/Electronegativity-pptx-13-2048.jpg)