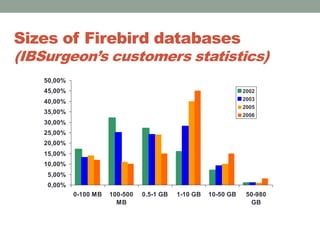
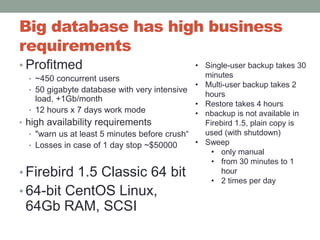
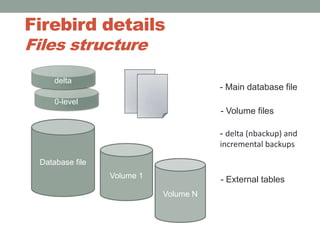
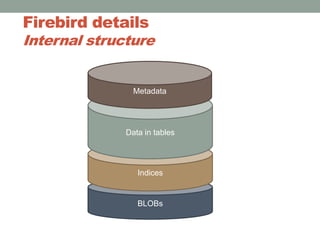
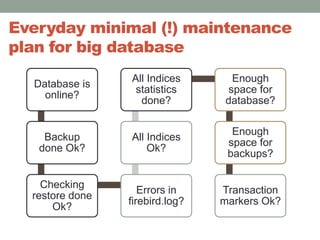
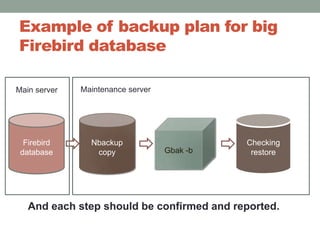
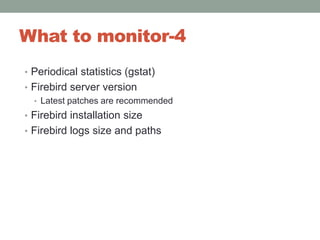
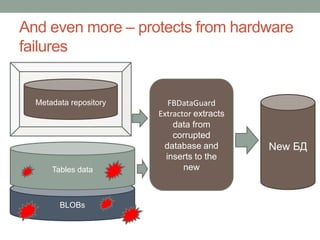
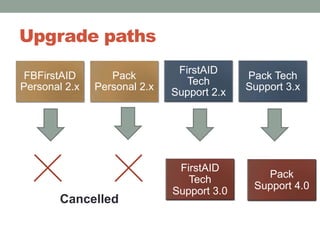
The document addresses the challenges and peculiarities of managing large Firebird databases, defining 'big' as databases reaching or exceeding 1 terabyte and discussing real-world examples. It emphasizes the need for individualized maintenance, including backup and restoration strategies, and the importance of monitoring various database parameters to ensure operational integrity. Additionally, it introduces fbdataguard, a tool designed to automate and oversee maintenance tasks to safeguard against data corruption and hardware failures.