This document provides an overview and revision of topics for a BTEC Creative Digital Media Production Unit 1 exam, including:
1. There are three learning aims focused on digital media sectors, audiences, and how audiences engage with media.
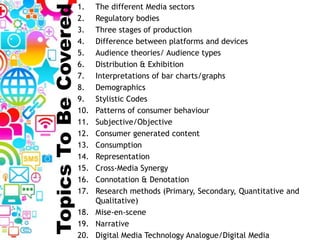
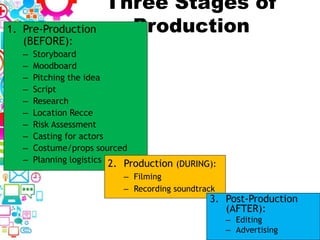
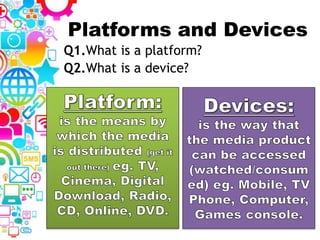
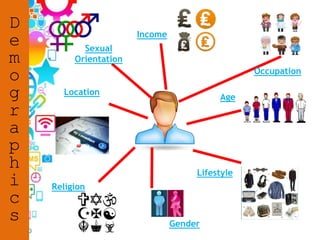
2. Topics to be covered include media sectors, regulatory bodies, production stages, platforms versus devices, audience theories, and research methods.
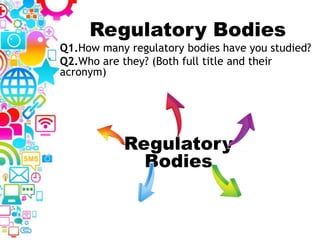
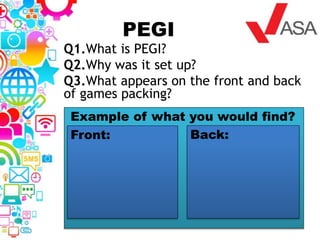
3. A revision placemat provides questions to test understanding of key topics like regulatory bodies, audience theories, distribution, and the difference between analogue and digital media.