This Slideshare presentation is a partial preview of the full business document. To view and download the full document, please go here:
http://flevy.com/browse/business-document/itil-v3-service-management-overview-280
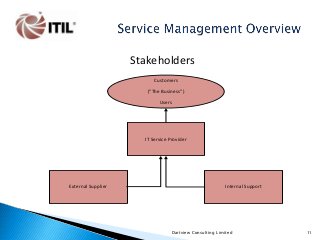
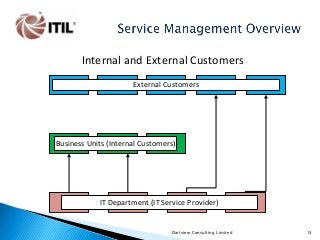
This document is a 129-slide PowerPoint presentation that provides an overview of IT Service Management based on the ITIL V3 Best Practice Framework.
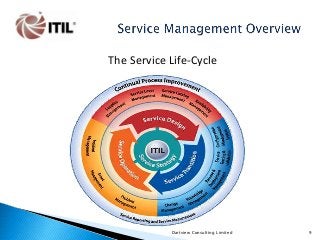
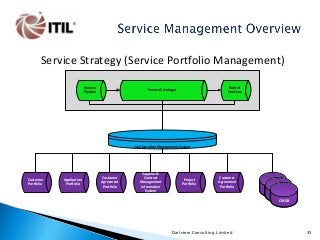
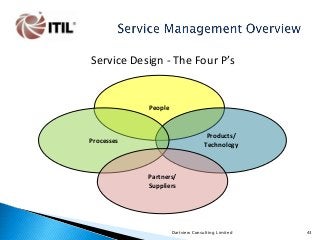
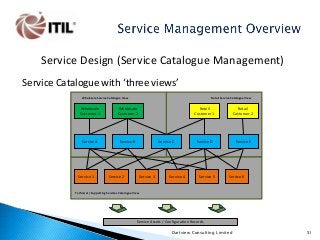
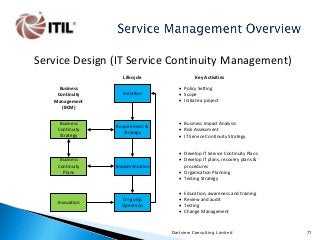
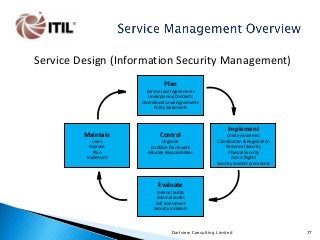
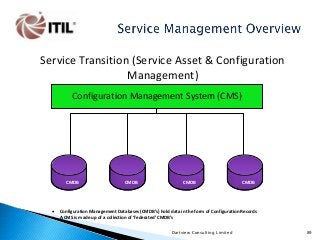
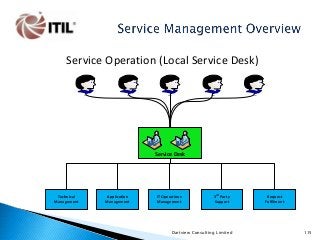
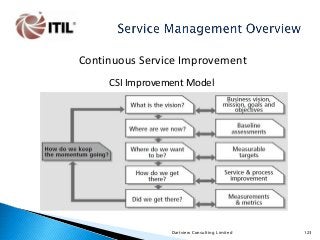
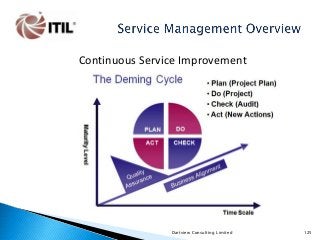
The whole of the Service Lifecycle (Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation and Continual Service Improvement) is covered, with many graphical illustration included.
Very easy to customise!!!!