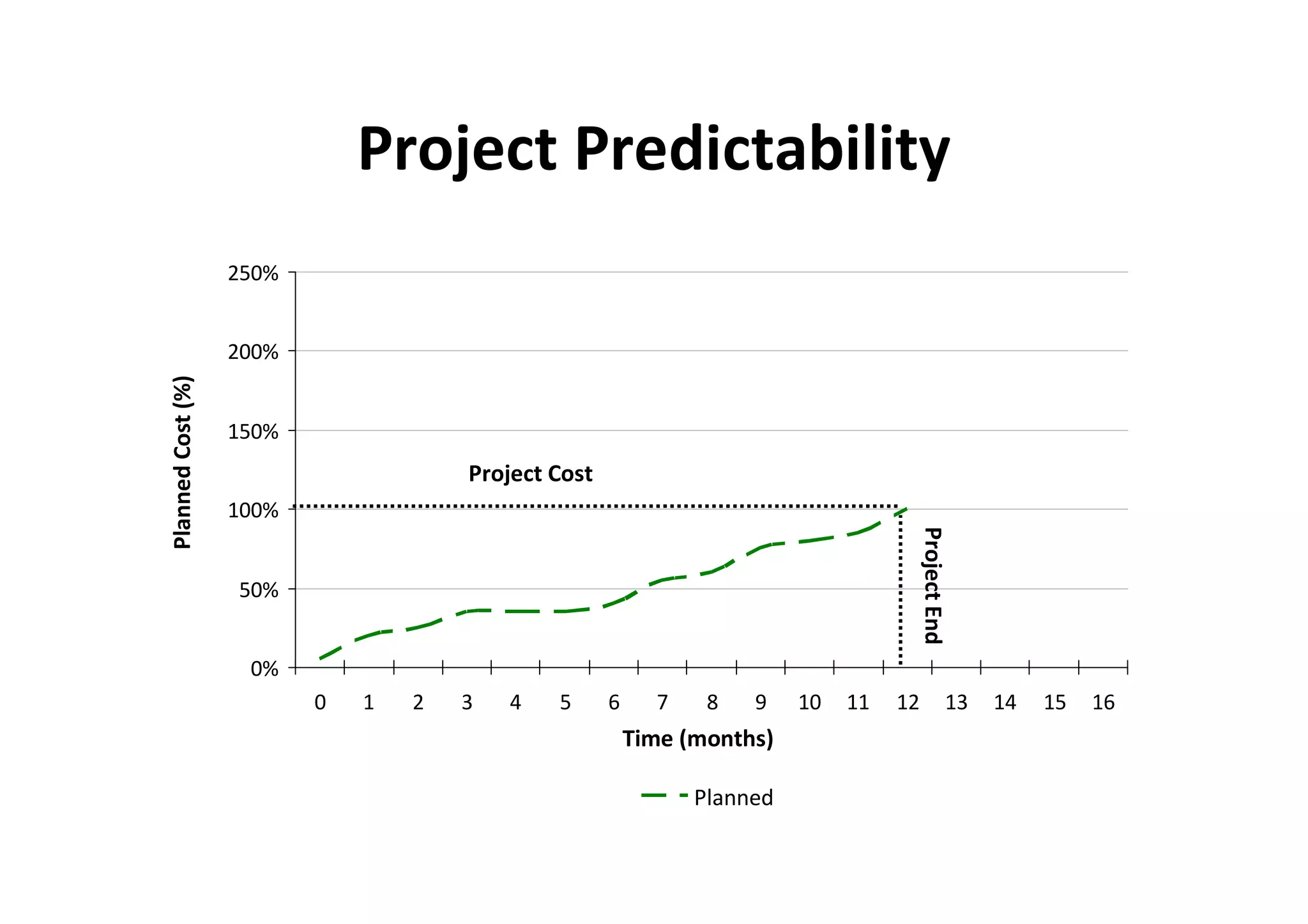
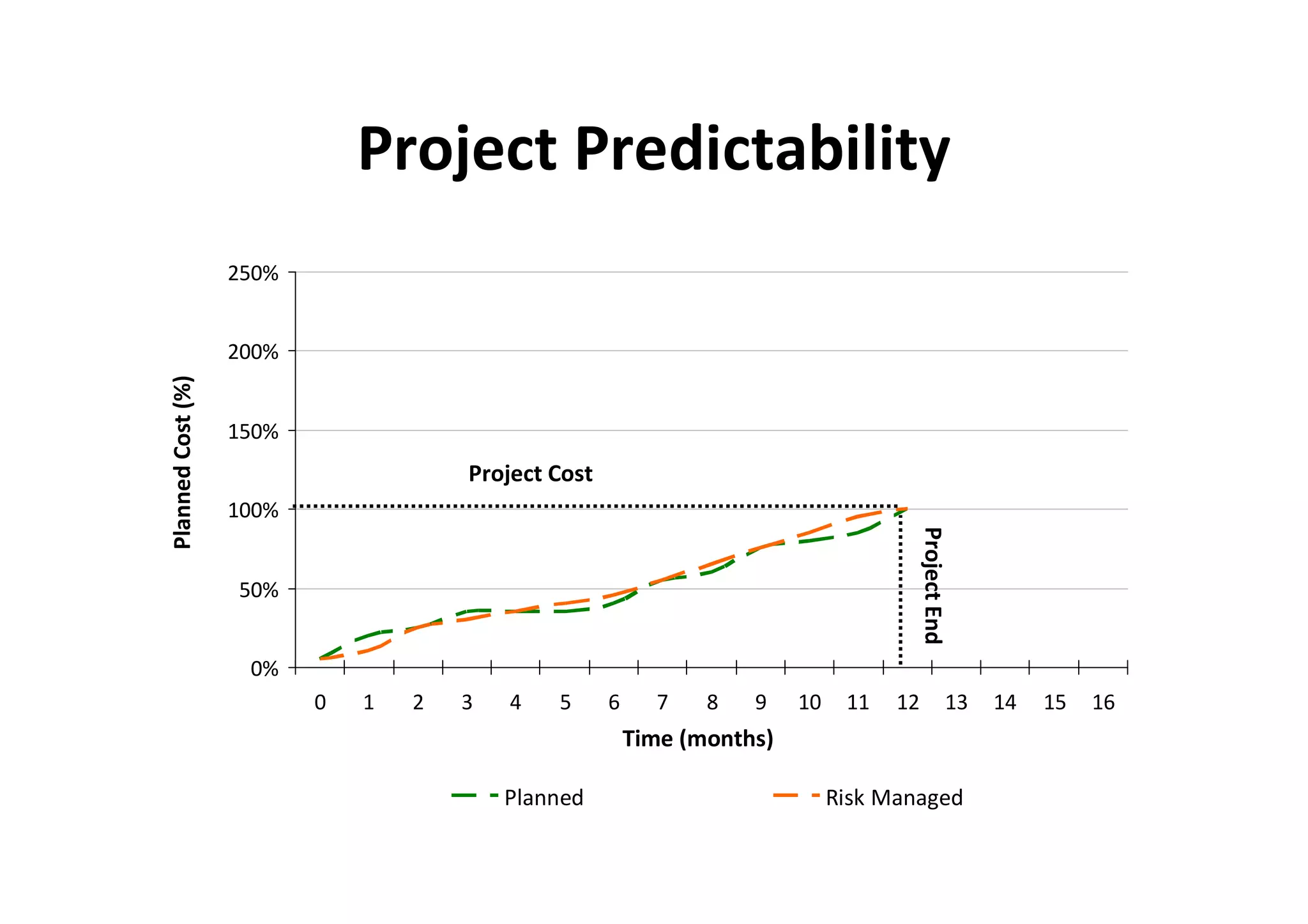
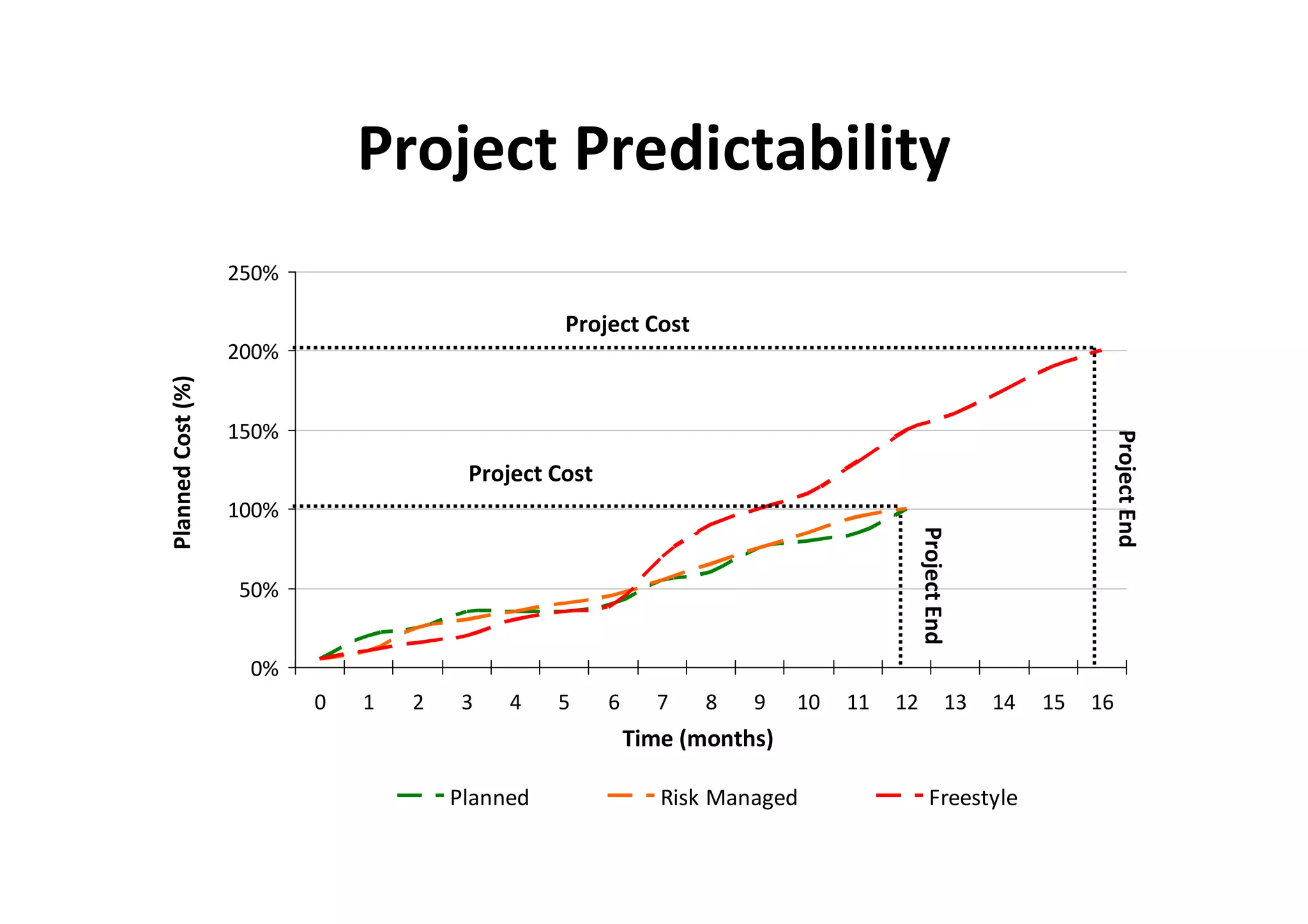
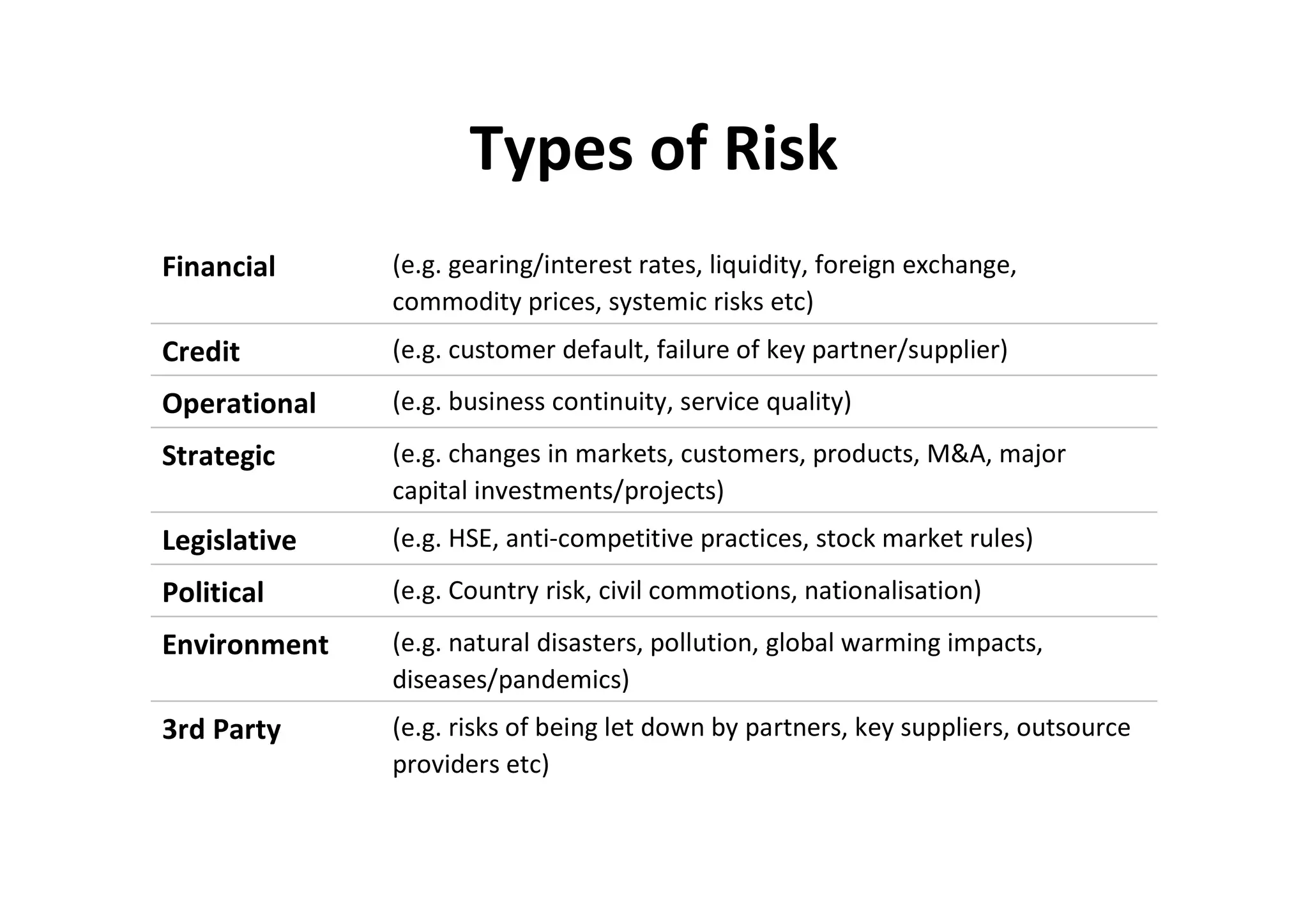
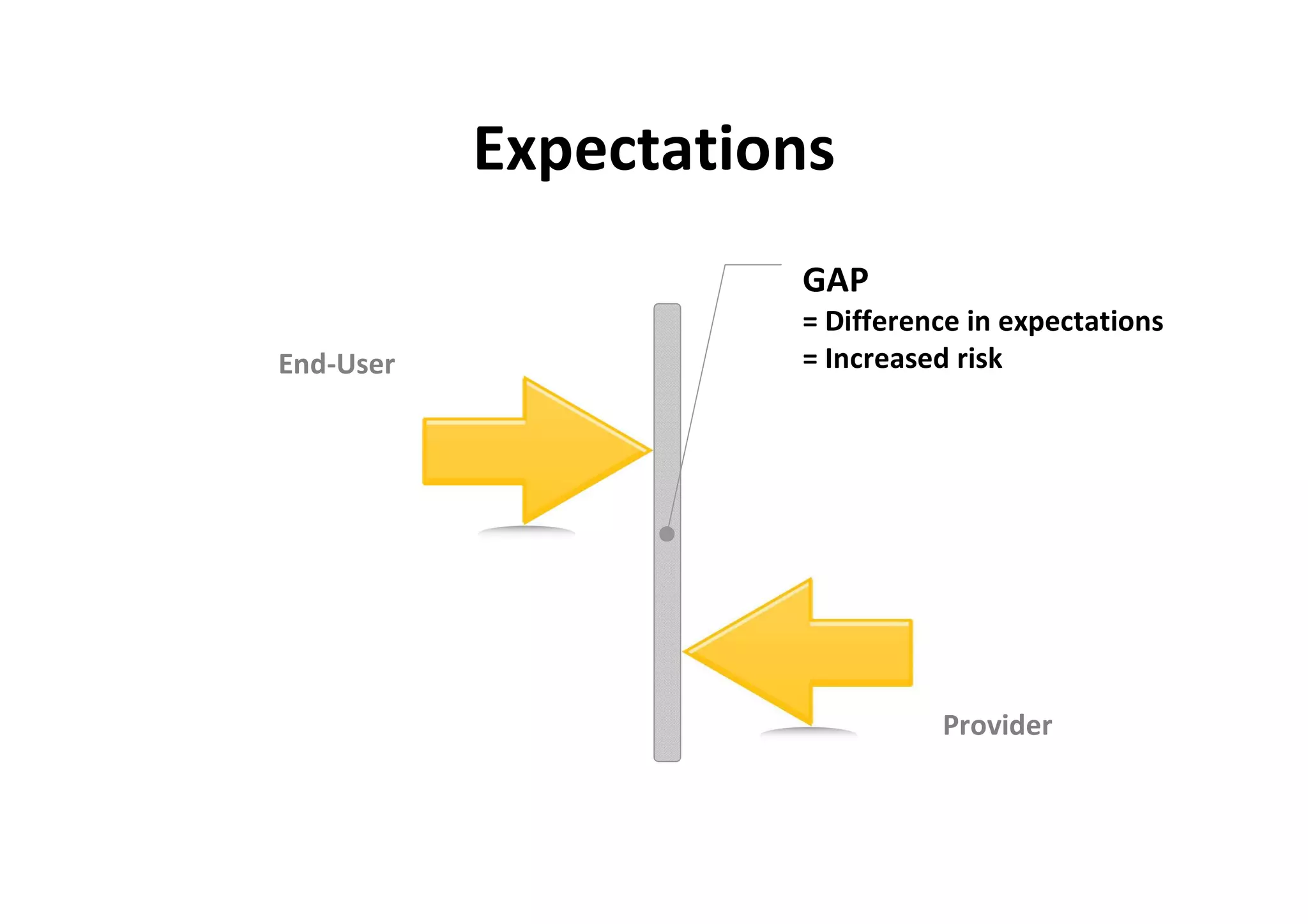
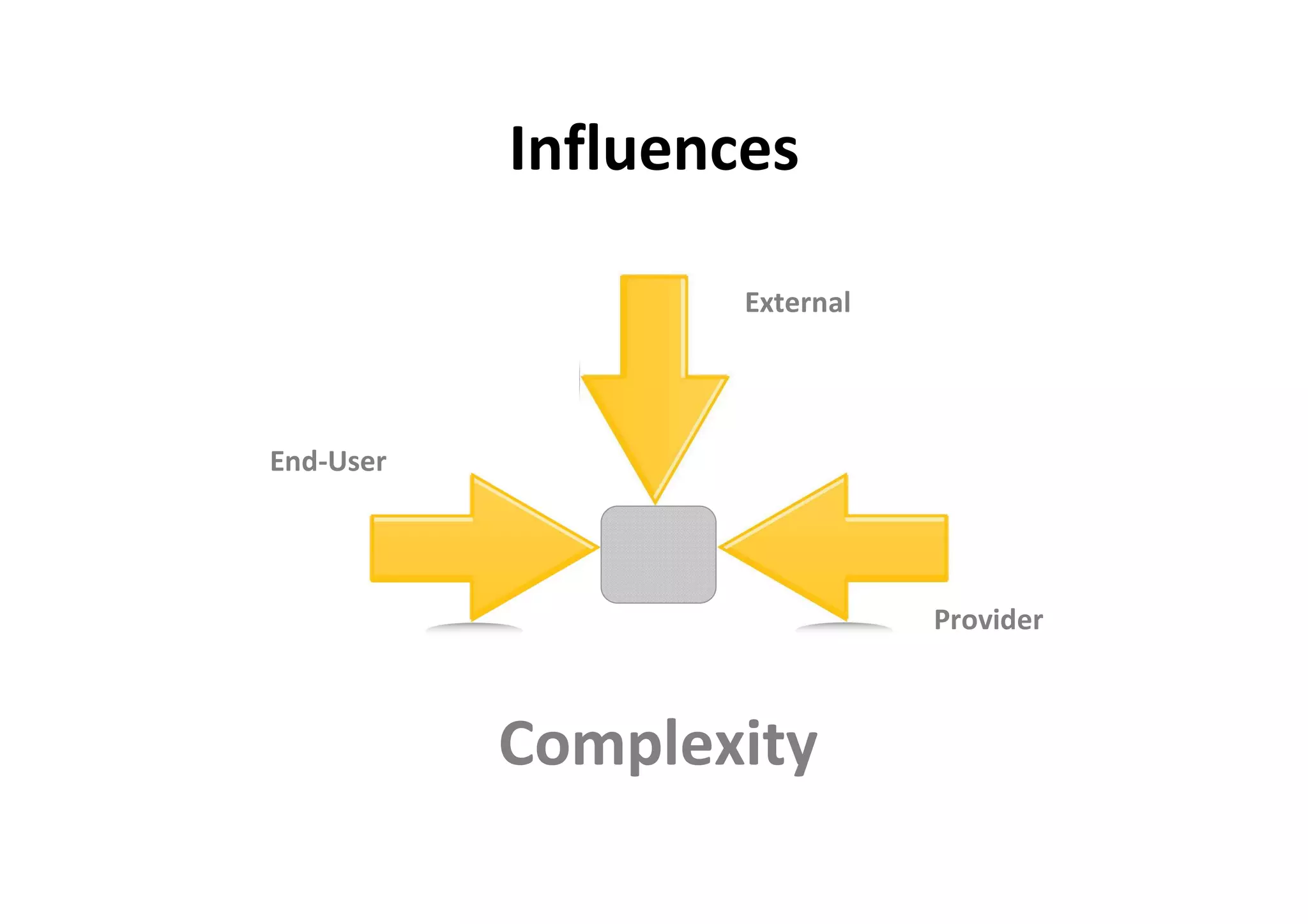
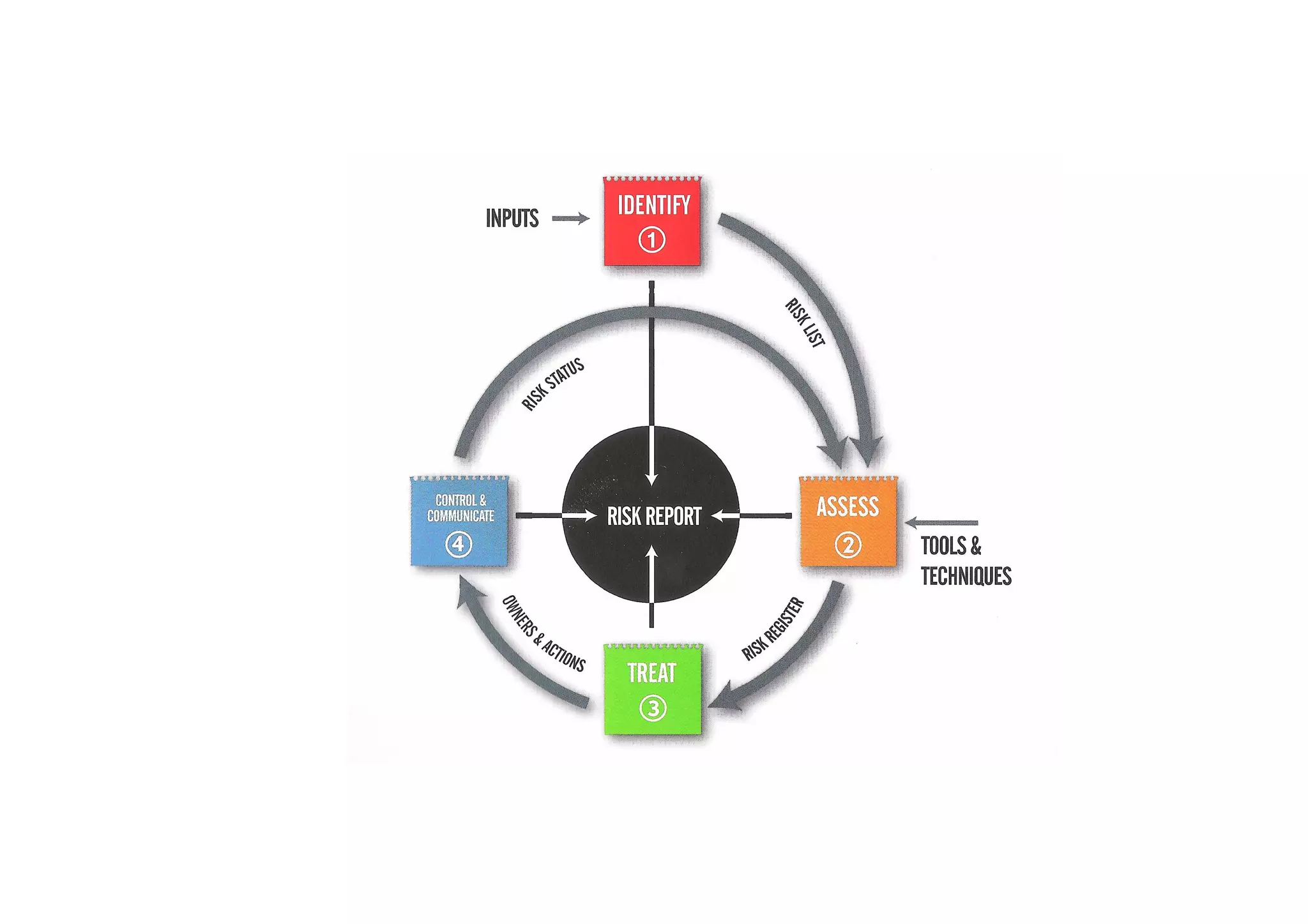
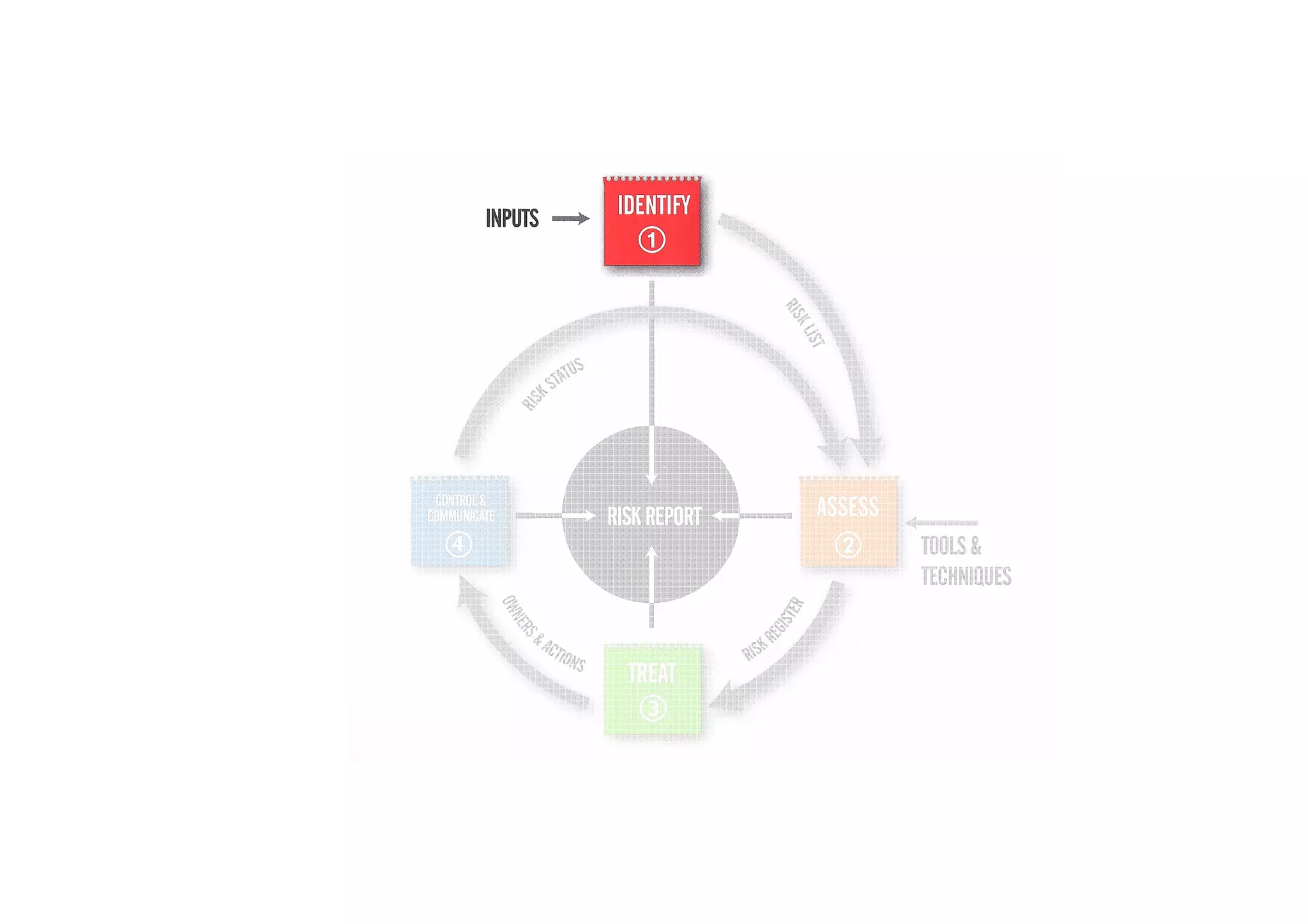
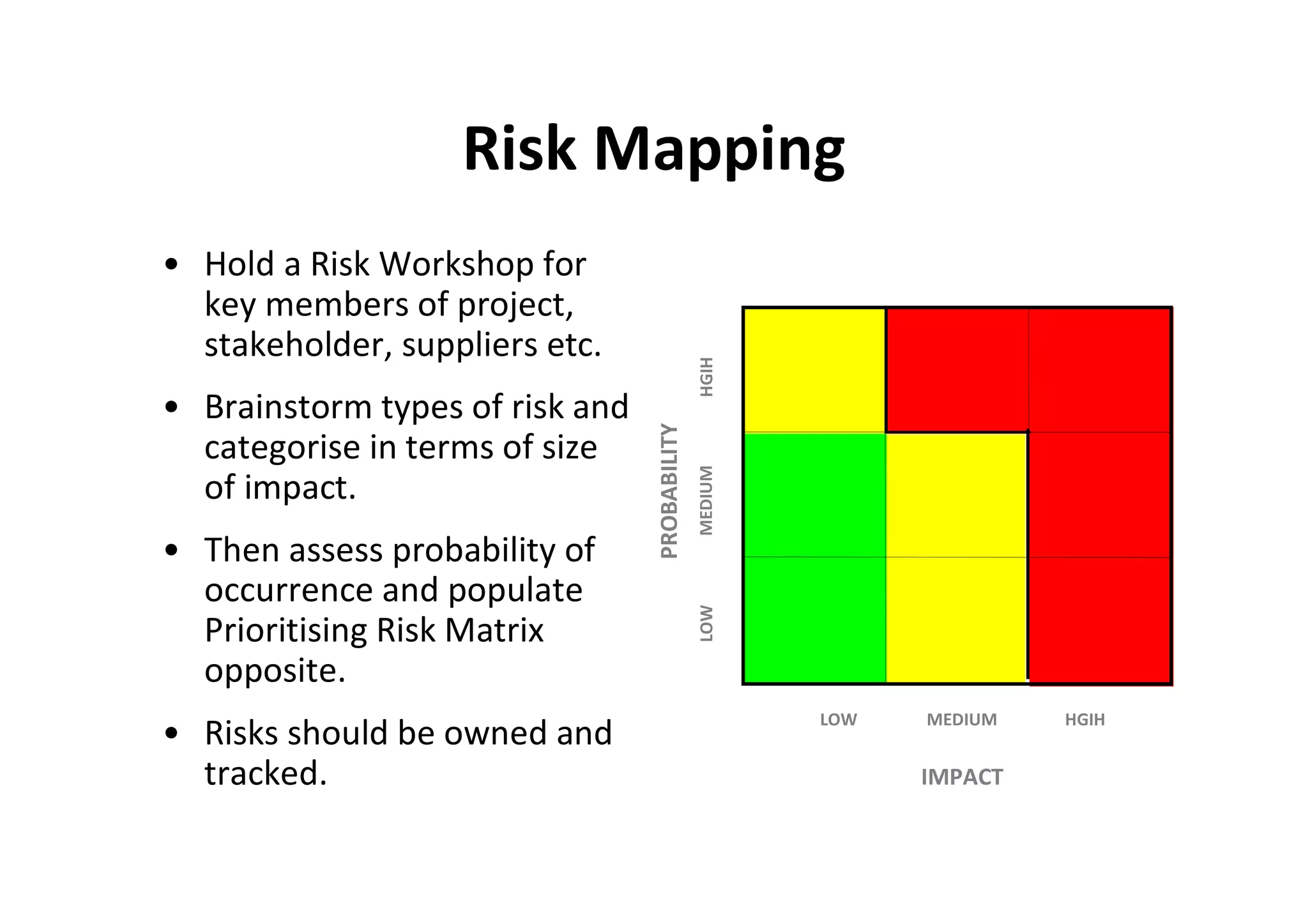
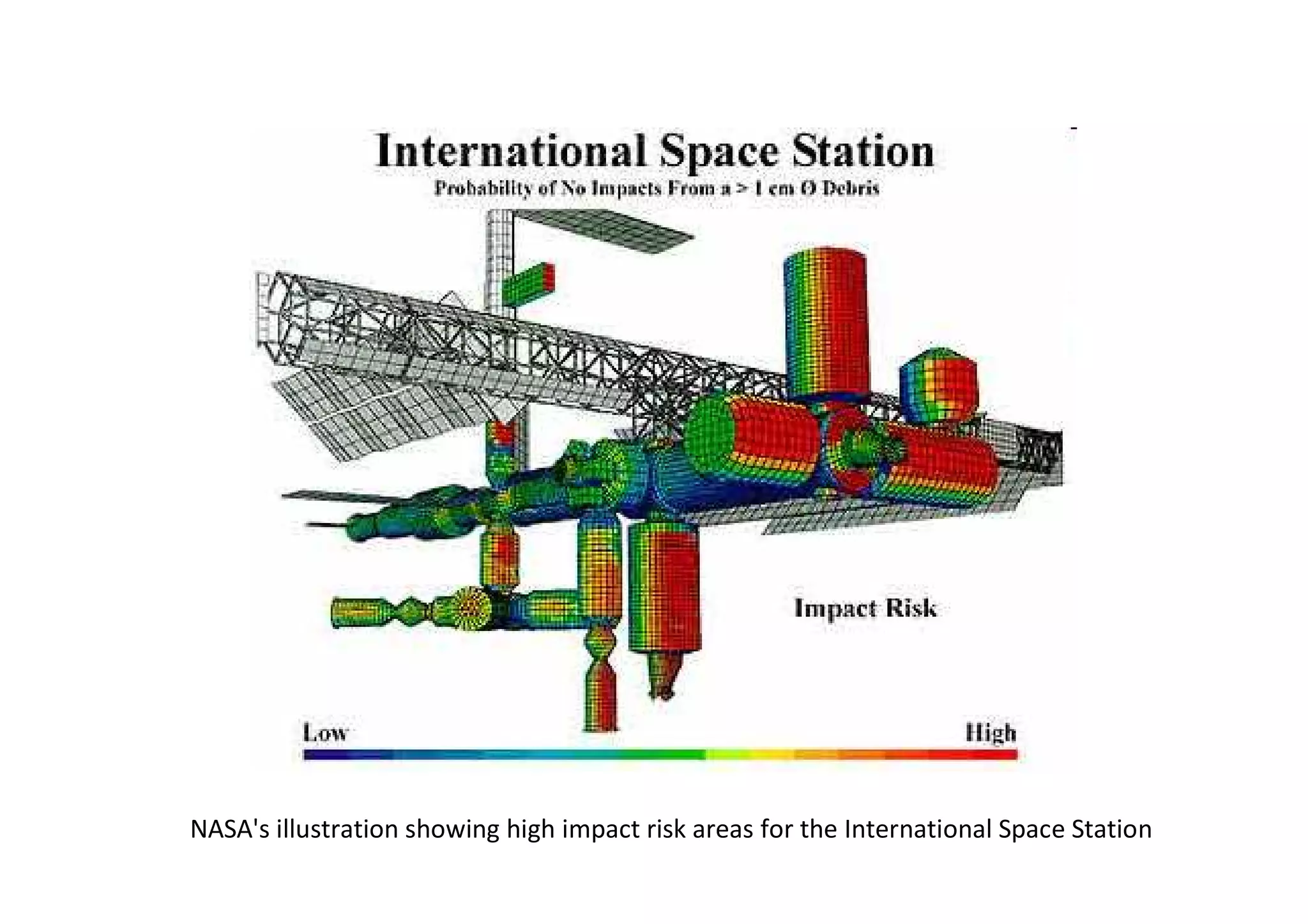
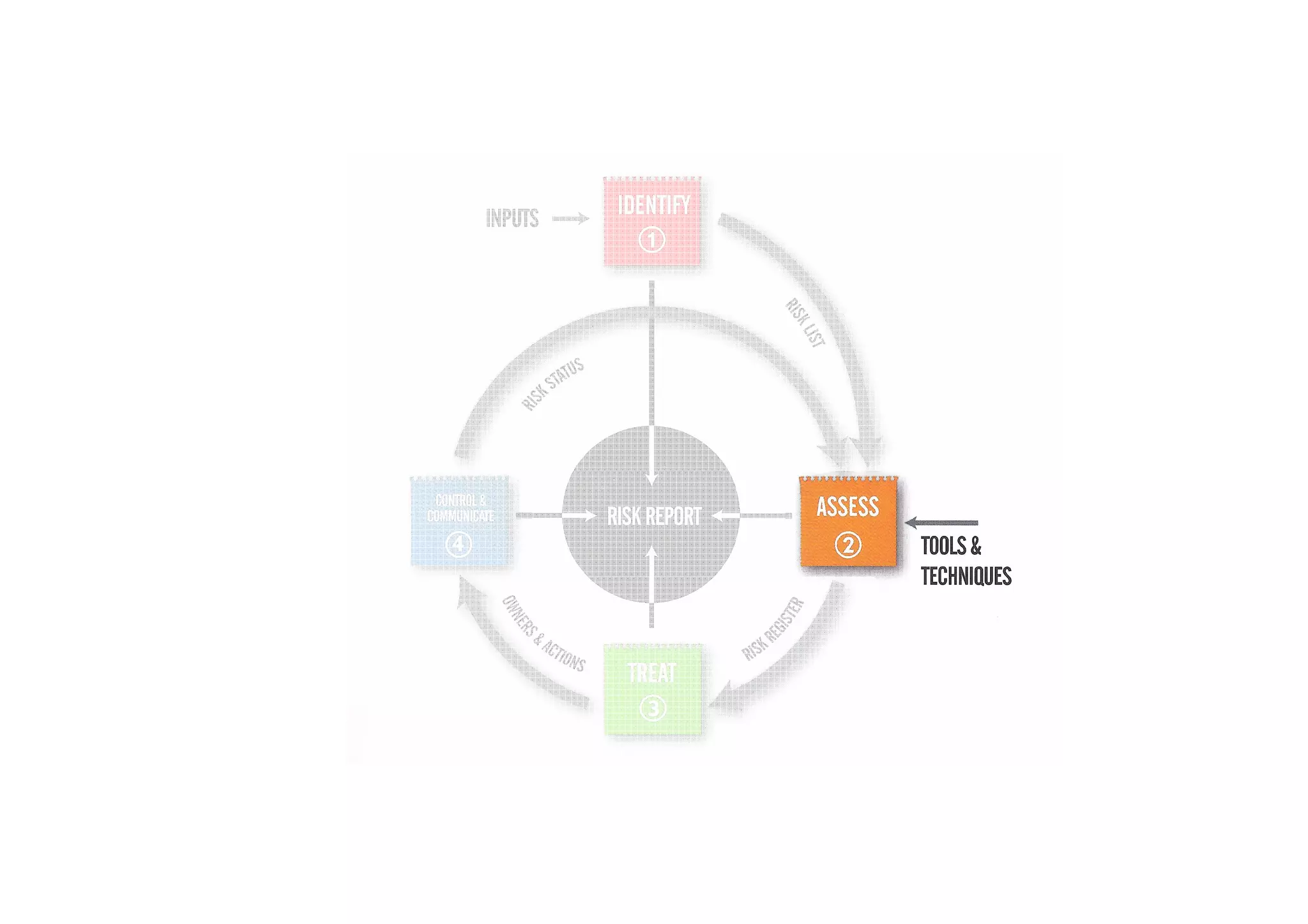
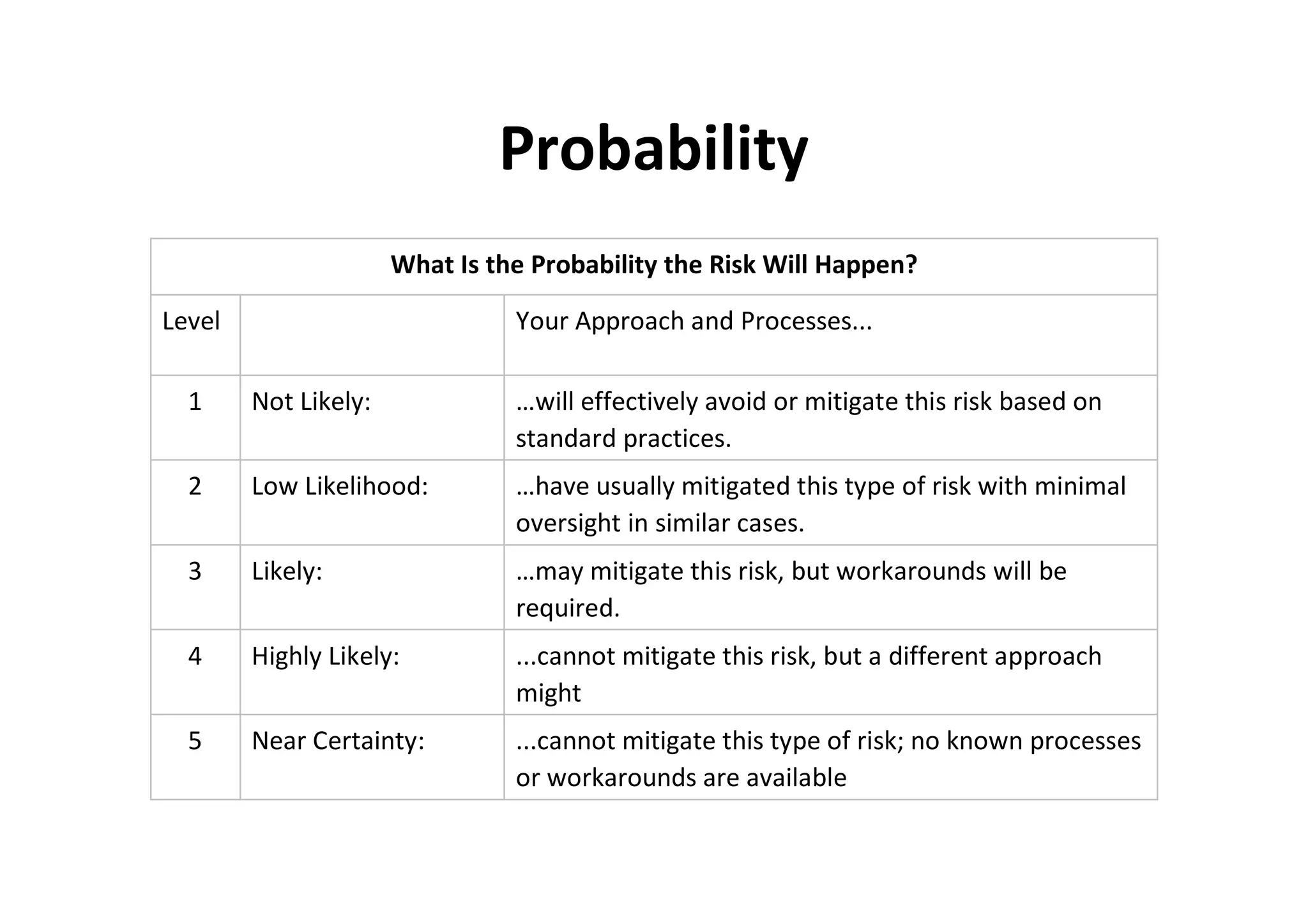
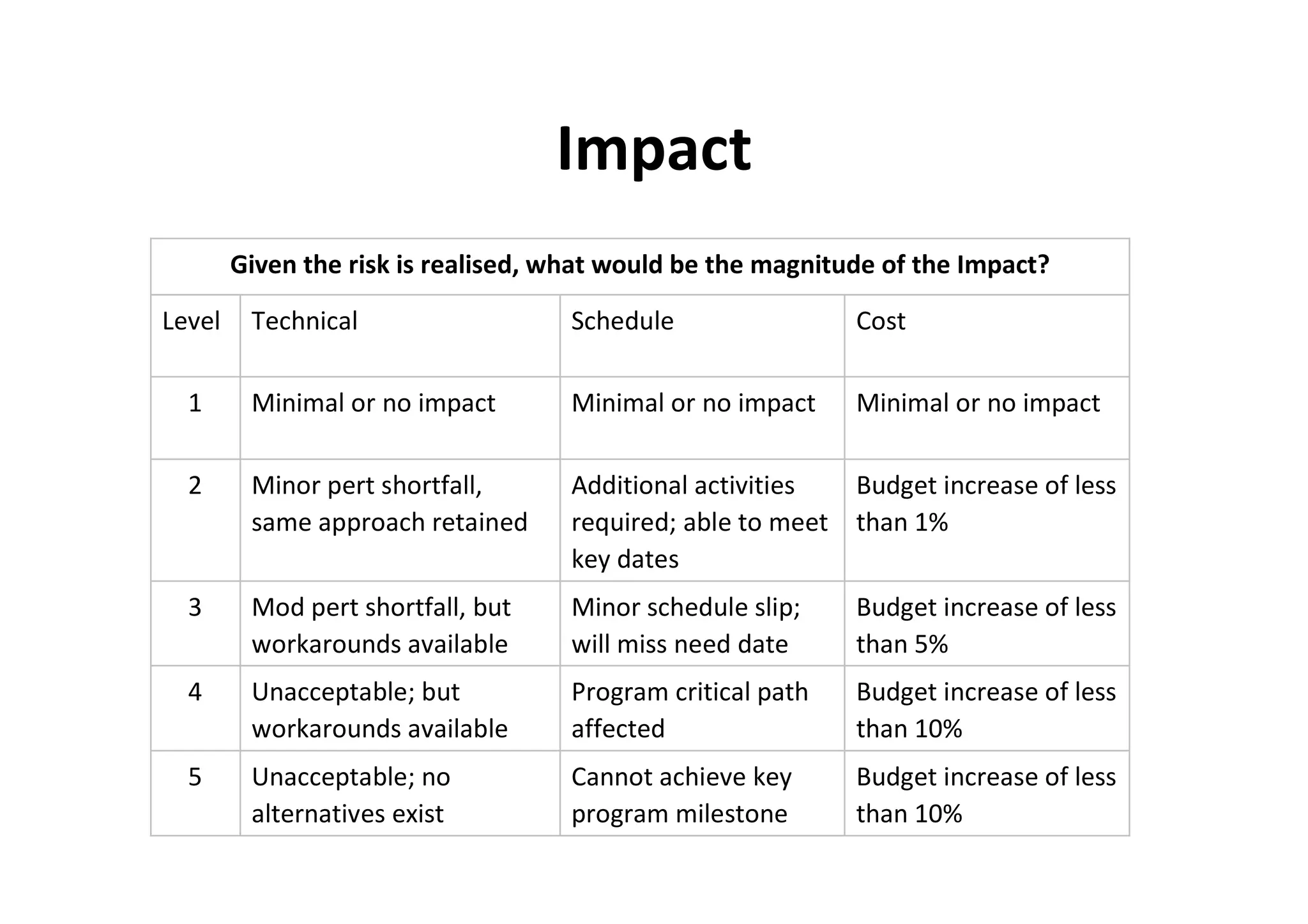
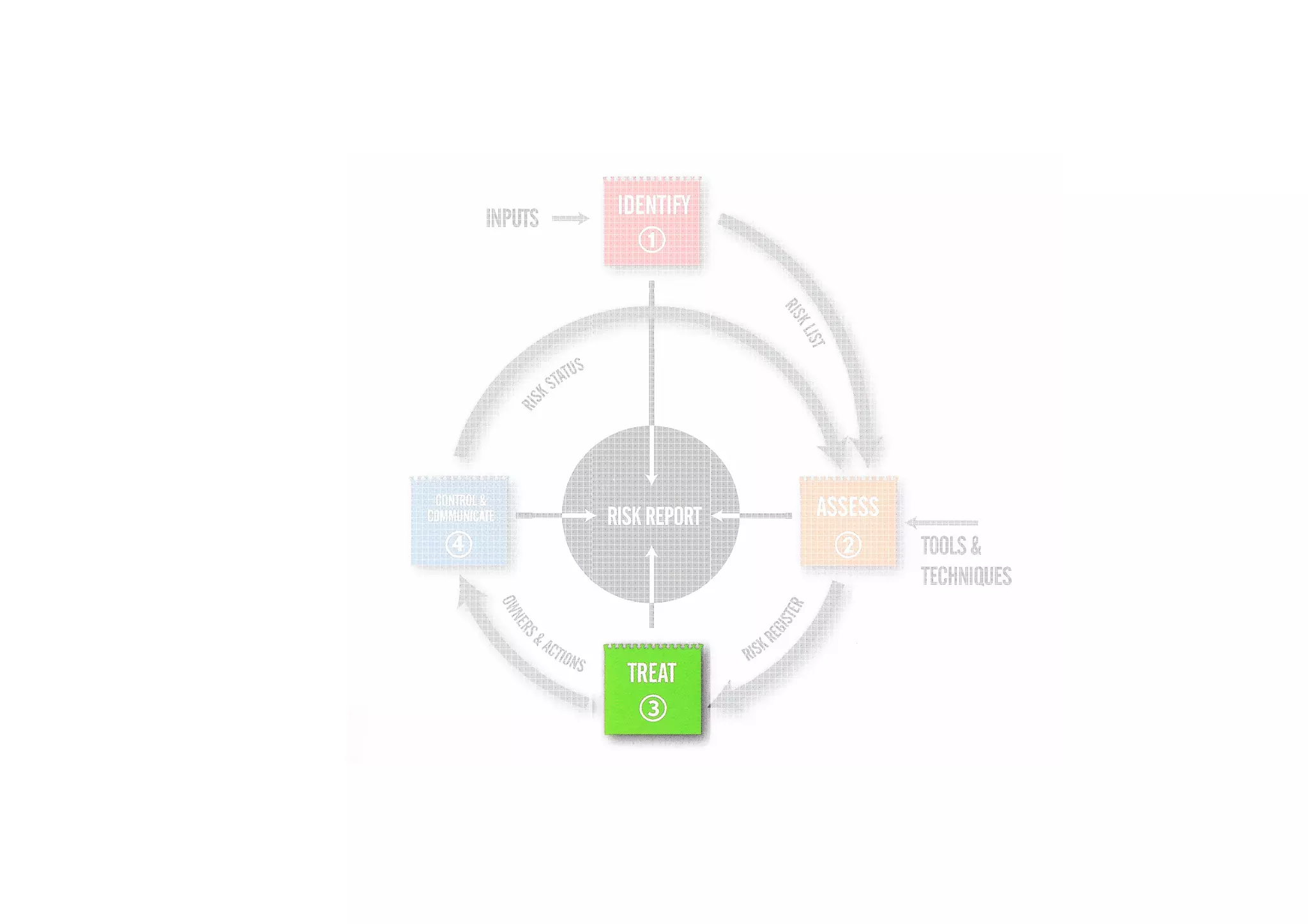
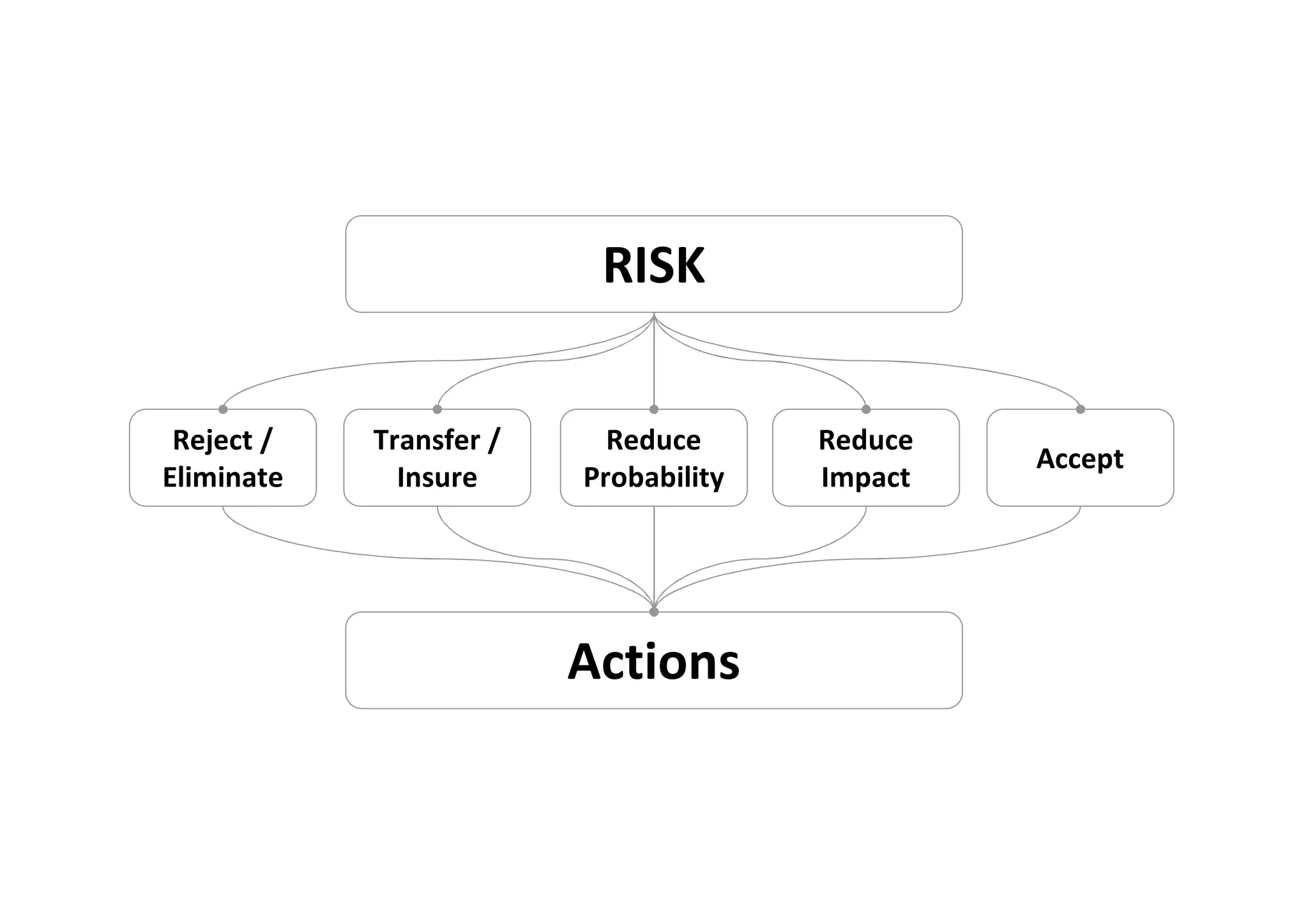
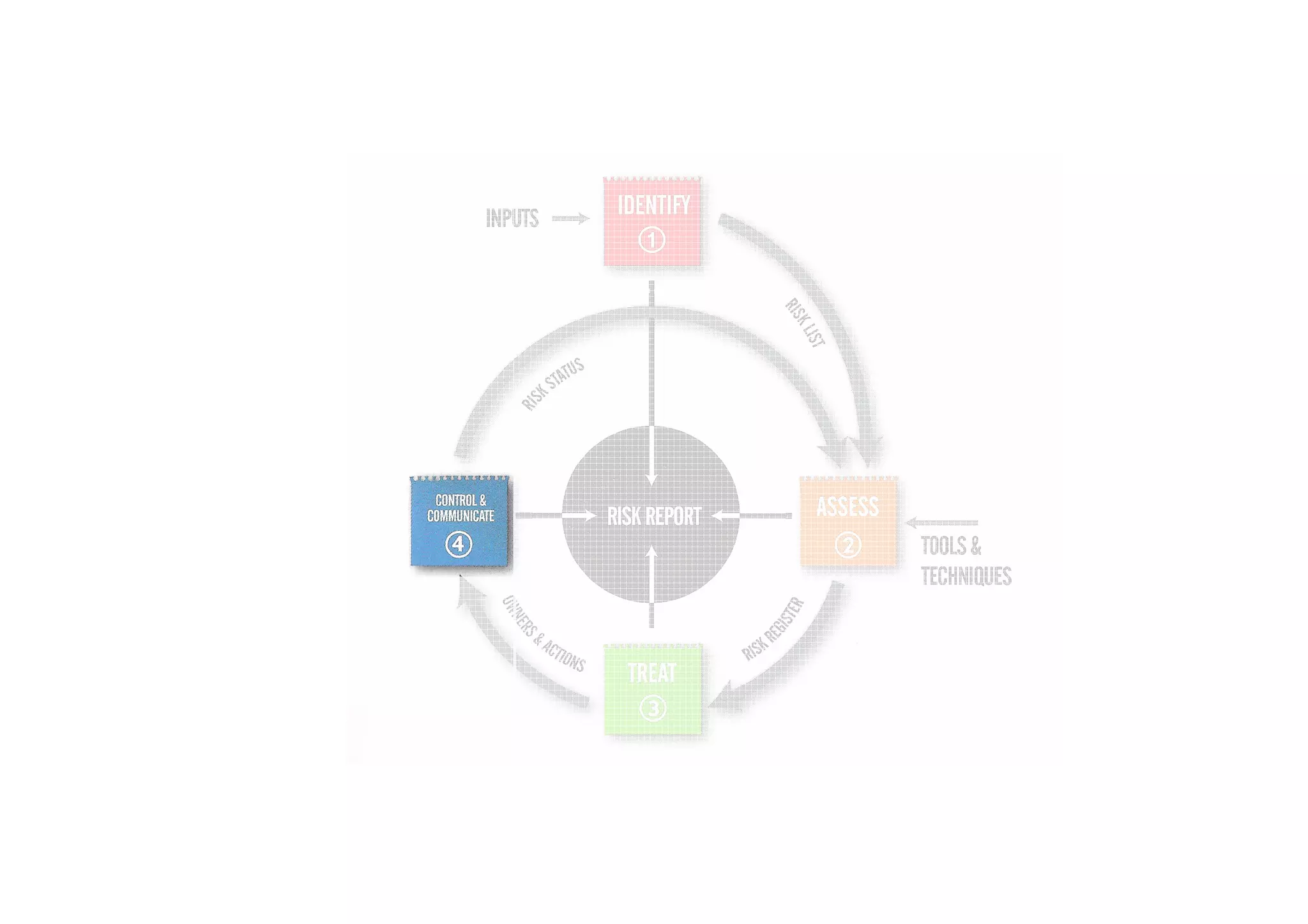
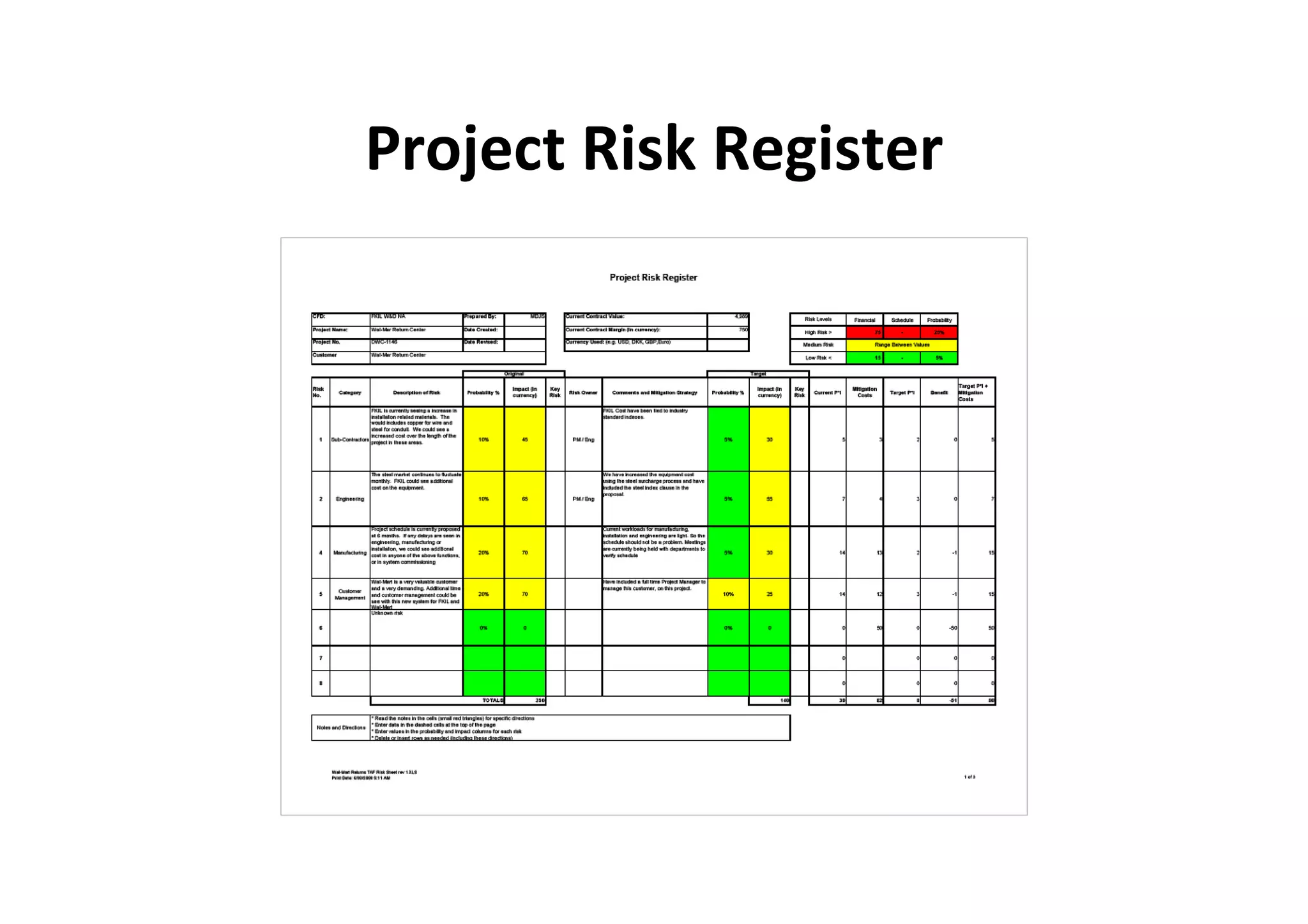
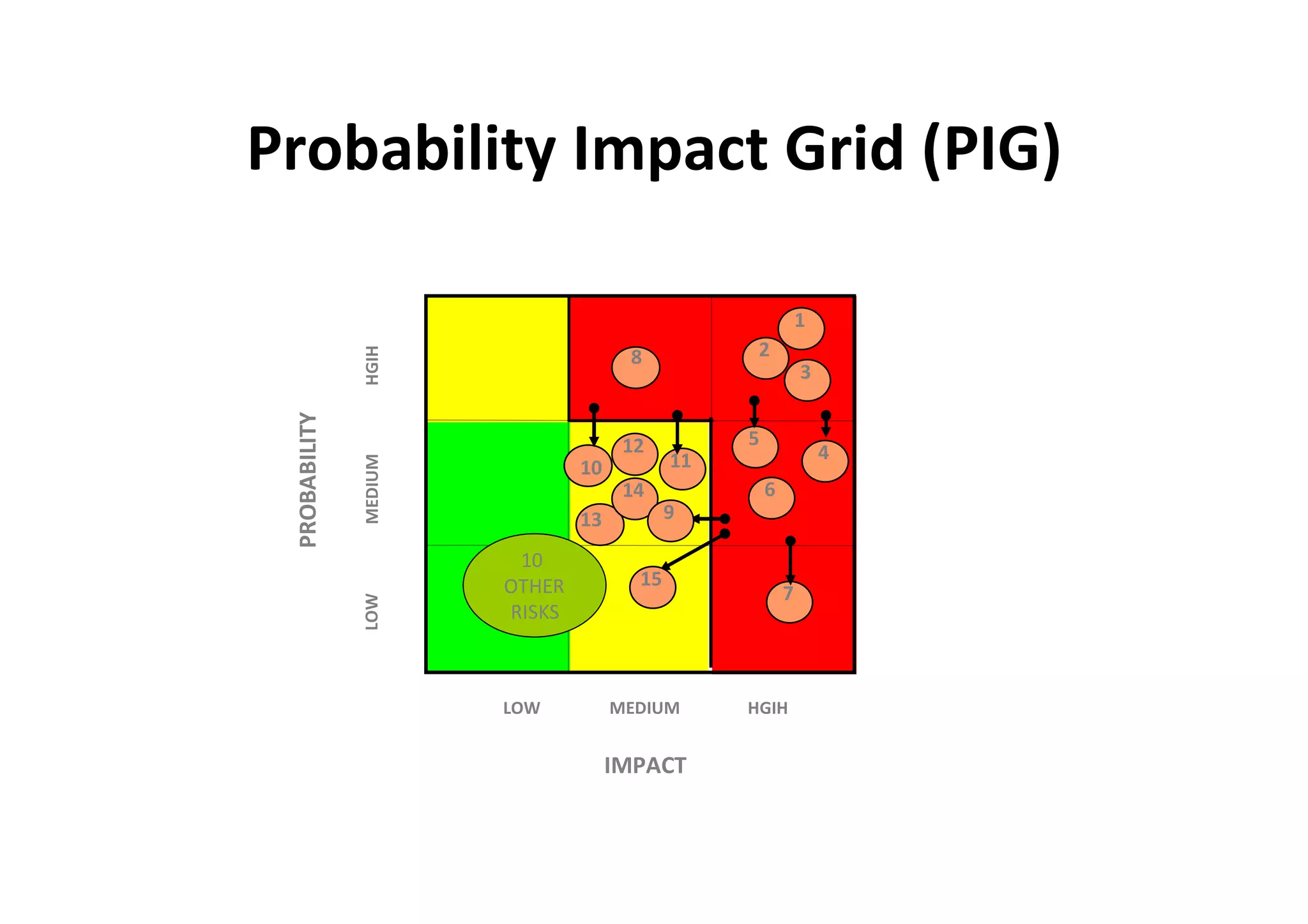
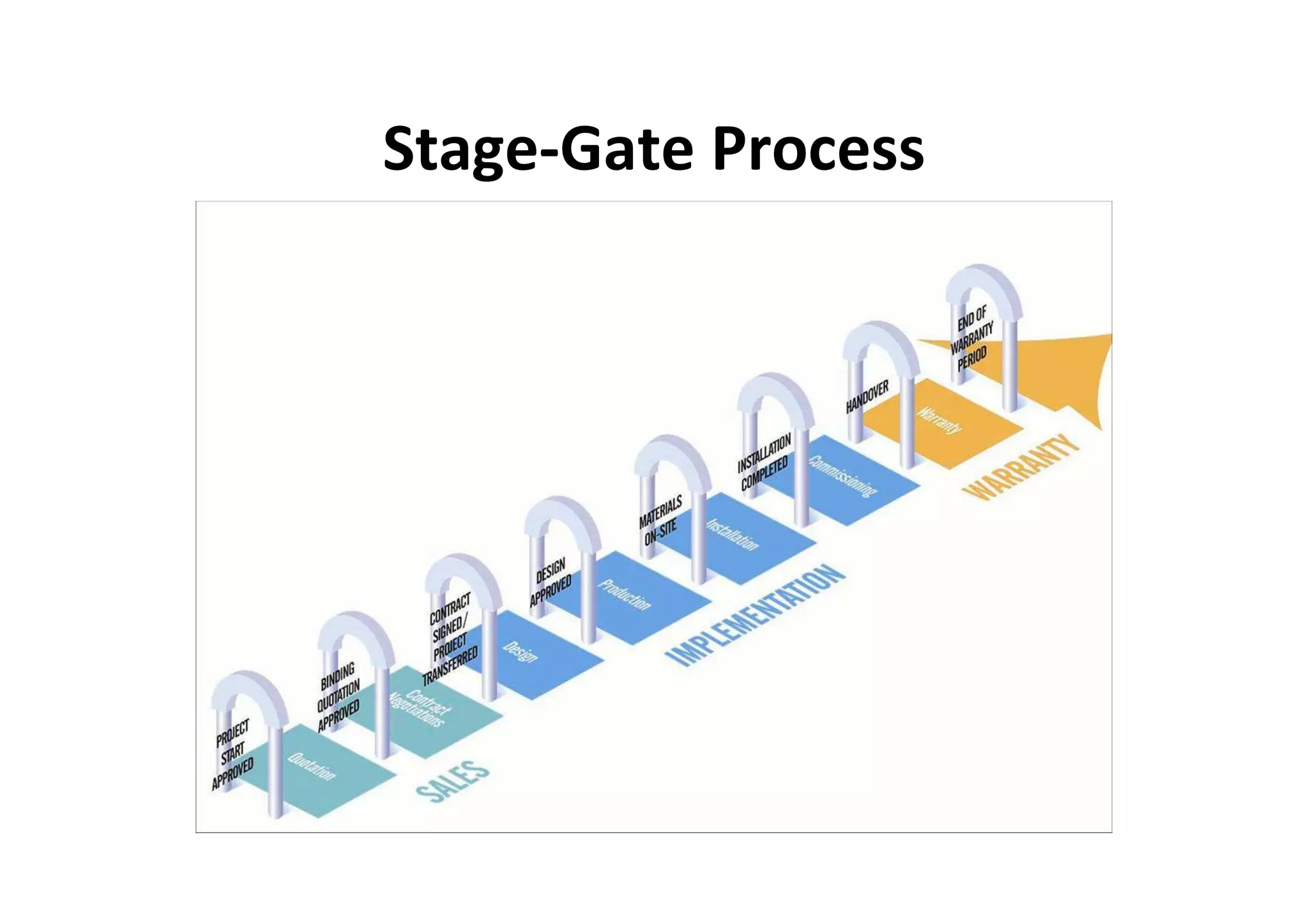
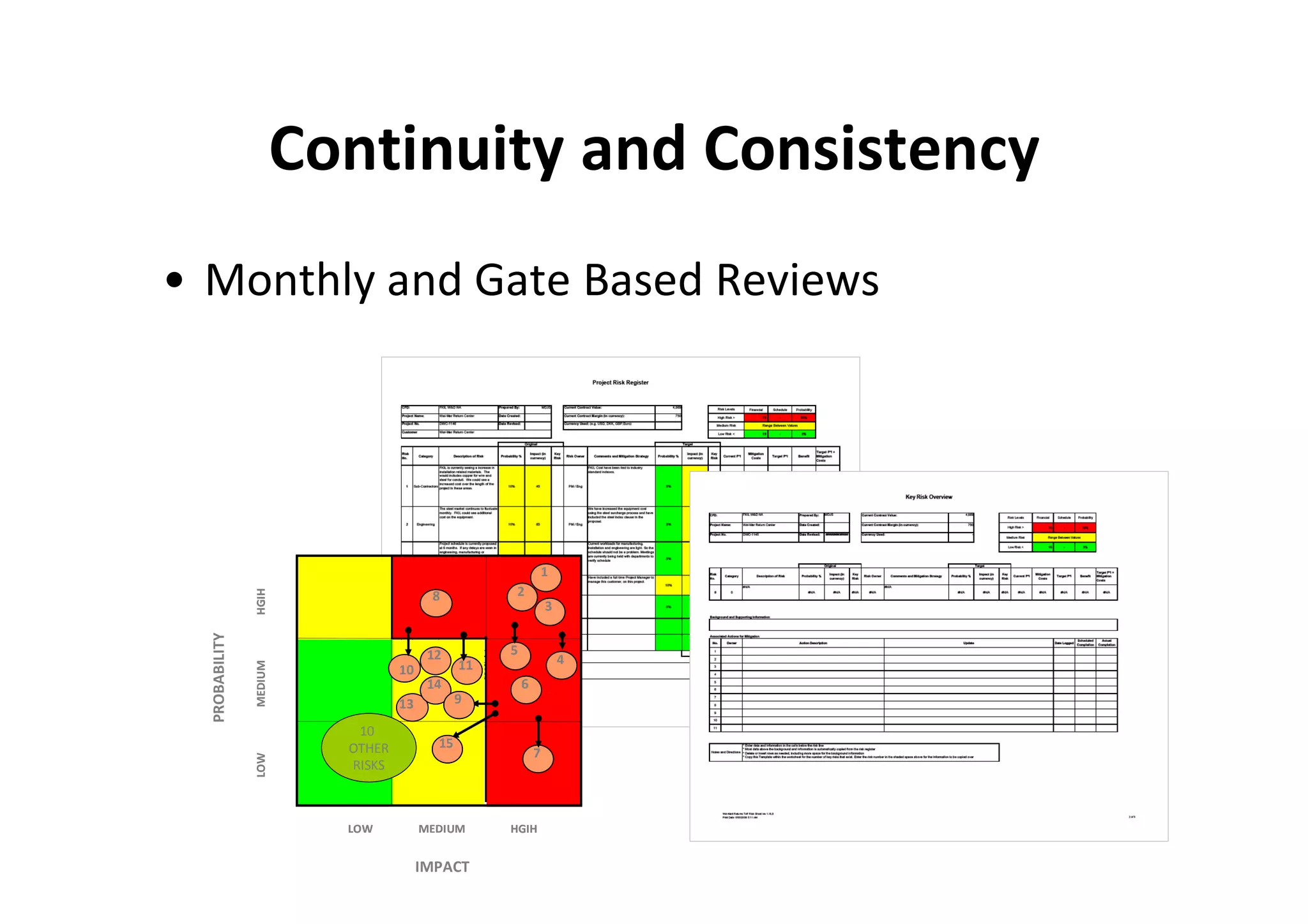
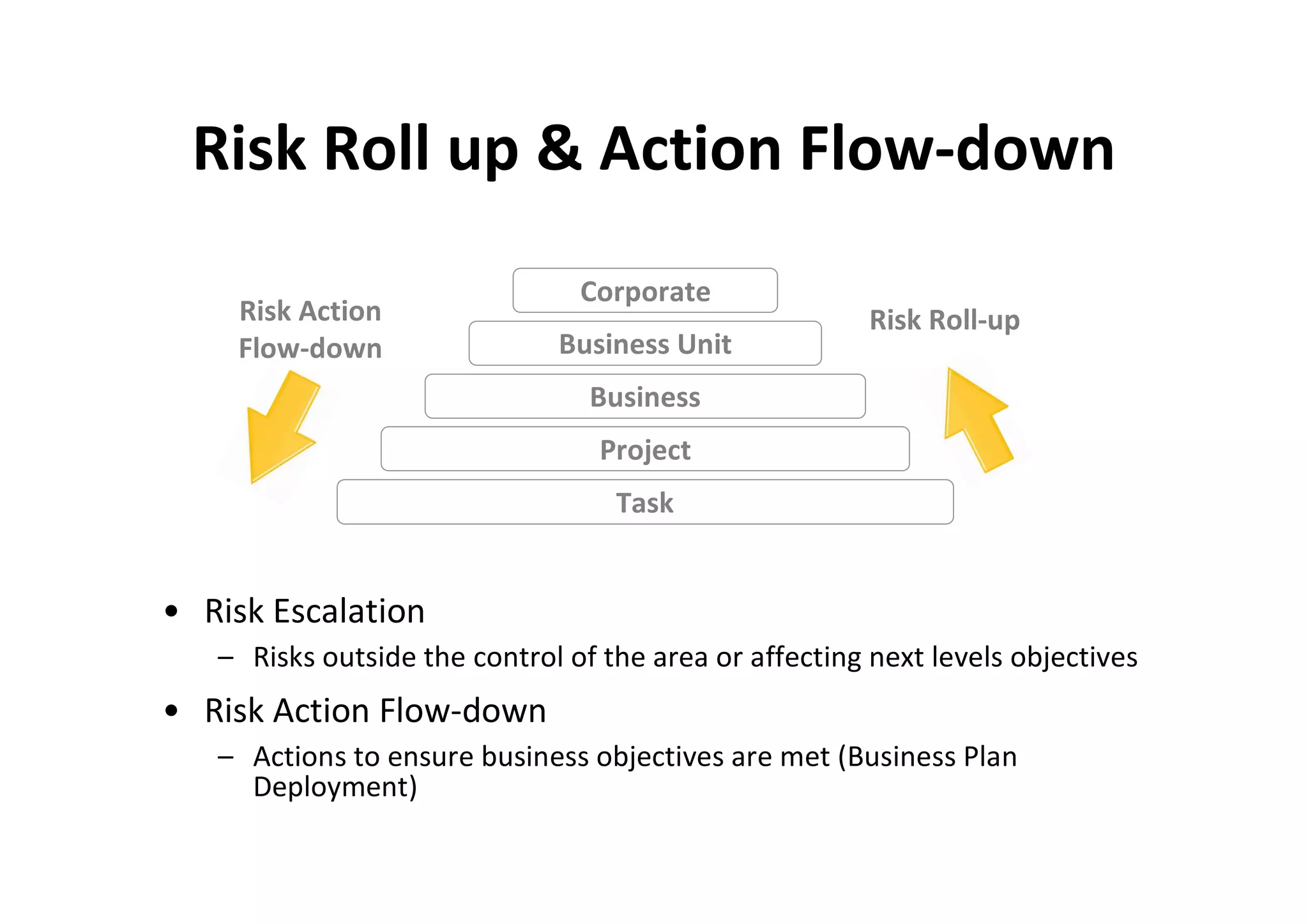
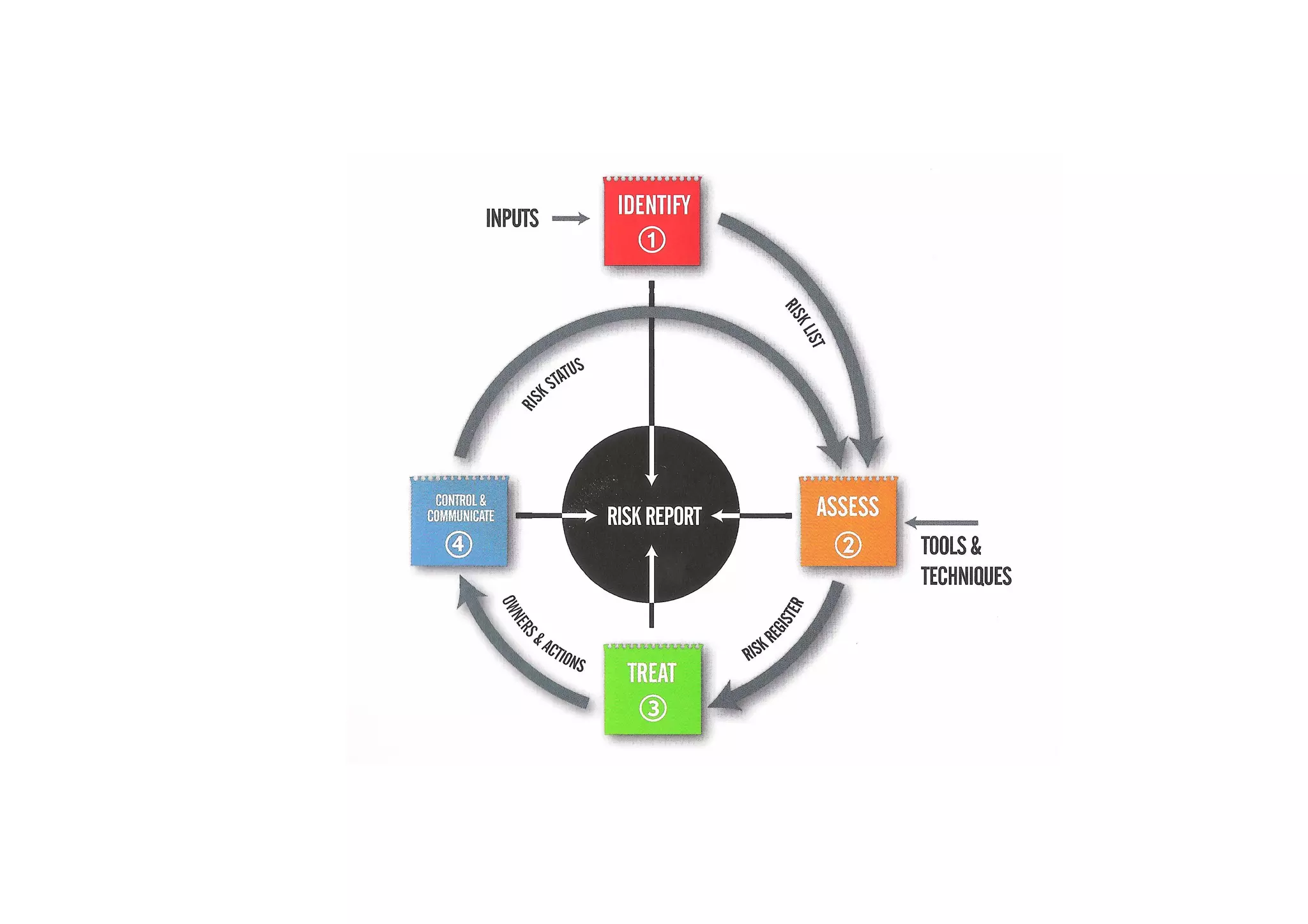
The document discusses understanding and managing risk within complex supply chain projects. It outlines different types of risks that can occur, such as financial, operational, strategic and political risks. It also discusses identifying and evaluating risks through methods like risk mapping, workshops and prioritizing risks based on probability and impact. Finally, it discusses implementing risk processes and governance through tools like risk registers, probability impact grids, stage-gate processes, and defining roles for risk management.