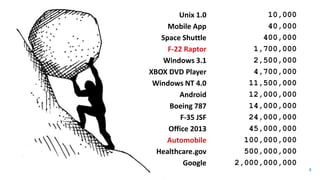
The document discusses Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP) technology, which integrates security controls directly into applications to detect and prevent real-time attacks. It highlights the challenges of implementing RASP, including issues of rejection, usability, accuracy, performance, and reliability, while emphasizing that RASP is not a panacea for security vulnerabilities. The presentation concludes by encouraging organizations to assess their specific needs and challenges when considering RASP solutions.