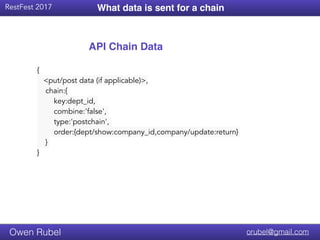
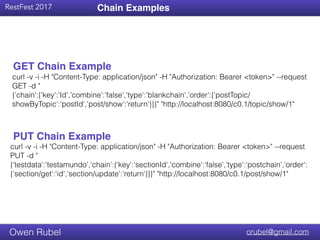
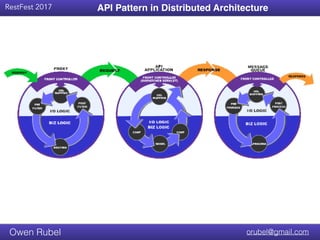
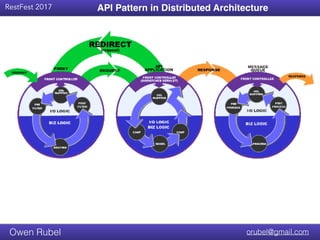
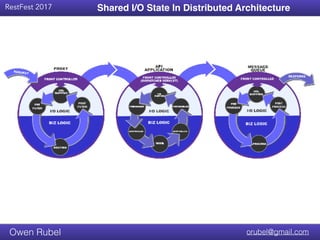
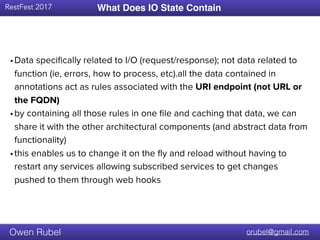
The document discusses API chaining, a method that streamlines multiple API calls into one request/response process, emphasizing separation of concerns between business logic and communication logic. It highlights the importance of shared I/O state in distributed architectures, enabling synchronization without affecting overall functionality, and introduces new API patterns that improve efficiency and reduce code duplication. Additionally, it provides examples of API chaining in practice, showcasing its flexibility and operational benefits.







![Title Text
RestFest 2017
orubel@gmail.comOwen Rubel
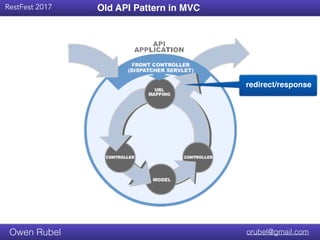
“Cross-cutting concerns can be directly responsible for tangling,
or system inter-dependencies, within a program. Because
procedural and functional language constructs consist entirely of
procedure calling, there is no semantic through where two
goals (the capability to be implemented and the related cross-
cutting concern) can be addressed simultaneously.[3] As a
result, the code addressing the cross-cutting concern must be
scattered, or duplicated, across the various related locations,
resulting in a loss of modularity.[2]”
- Source : Cross Cutting Concern, Wikipedia
What is a Cross Cutting Concern?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apichaining-170914144558/85/Api-chaining-tm-12-320.jpg)












![Title Text
RestFest 2017
orubel@gmail.comOwen Rubel
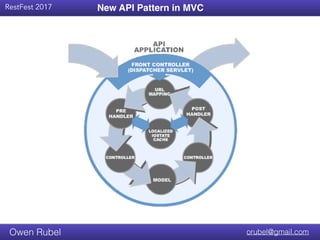
Code Reduction (1 of 2)
Controller : Mixed Concerns (Duplication)
@Secured(['ROLE_ADMIN', ‘ROLE_USER'])
@RequestMapping(value="/create", method=RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public ModelAndView createAddress(){
List authorities = springSecurityService.getPrincipal().getAuthorities()
User user
if(authorities.contains(‘ROLE_ADMIN’)){
if(params.id){
user = User.get(params.id.toLong())
}else{
render(status:HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST)
}
}else if(authorities.contains(‘ROLE_USER’)){
user = User.get(principal.id)
}
Address address = new Address(params)
…
address.user = user
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apichaining-170914144558/85/Api-chaining-tm-30-320.jpg)