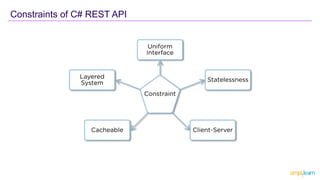
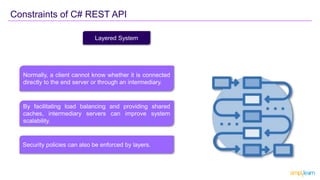
The document provides an overview of REST API, its principles, and how it operates using HTTP methods (verbs) such as POST, GET, PUT, and DELETE, along with HTTP status codes. It highlights constraints specific to C# REST API, including uniform interface, statelessness, client-server separation, cacheability, and layered architecture, which enhance scalability and simplify design. The key takeaway emphasizes that REST API facilitates communication between clients and servers over HTTP, serving as a gateway to access resources.










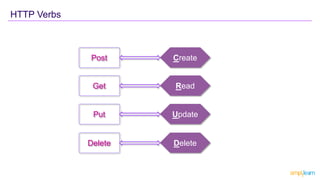
![HTTP Verbs
Create
Post
Read
Get
Update
Put
Delete
Delete
To insert the data into the database, the
method must be defined as a POST method.
To define a Post method, we decorate a
method with [HttpPost].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crestapi-220616200749-367d9f75/85/C-REST-API-15-320.jpg)
![HTTP Verbs
Create
Post
Read
Get
Update
Put
Delete
Delete
Retrieving data or information is possible
through the Get verb. To define a Get method
we decorate a method with [HttpGet].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crestapi-220616200749-367d9f75/85/C-REST-API-16-320.jpg)
![HTTP Verbs
Create
Post
Read
Get
Update
Put
Delete
Delete
To Update or modify the data in the database,
the method must be defined as a PUT method.
To define a Put method we decorate a method
with [HttpPut].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crestapi-220616200749-367d9f75/85/C-REST-API-17-320.jpg)
![HTTP Verbs
Create
Post
Read
Get
Update
Put
Delete
Delete To Delete the data from the database, the
method must be defined as a DELETE
method. To define a Delete method we
decorate a method with [HttpDelete].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crestapi-220616200749-367d9f75/85/C-REST-API-18-320.jpg)