Photoreception
•Download as DOCX, PDF•
4 likes•5,269 views
photoreception
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Pattern of nitrogenous waste and phylogenectical development of

Pattern of nitrogenous waste and phylogenectical development of
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (12)
Similar to Photoreception
Similar to Photoreception (20)
More from Aftab Badshah
More from Aftab Badshah (20)
The theory of endosymbiosis says that eukaryote cells have evolved from a sym...

The theory of endosymbiosis says that eukaryote cells have evolved from a sym...
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
High Profile 🔝 8250077686 📞 Call Girls Service in GTB Nagar🍑

High Profile 🔝 8250077686 📞 Call Girls Service in GTB Nagar🍑
chemical bonding Essentials of Physical Chemistry2.pdf

chemical bonding Essentials of Physical Chemistry2.pdf
9999266834 Call Girls In Noida Sector 22 (Delhi) Call Girl Service

9999266834 Call Girls In Noida Sector 22 (Delhi) Call Girl Service
pumpkin fruit fly, water melon fruit fly, cucumber fruit fly

pumpkin fruit fly, water melon fruit fly, cucumber fruit fly
The Mariana Trench remarkable geological features on Earth.pptx

The Mariana Trench remarkable geological features on Earth.pptx
Dubai Call Girls Beauty Face Teen O525547819 Call Girls Dubai Young

Dubai Call Girls Beauty Face Teen O525547819 Call Girls Dubai Young
Pests of mustard_Identification_Management_Dr.UPR.pdf

Pests of mustard_Identification_Management_Dr.UPR.pdf
Thyroid Physiology_Dr.E. Muralinath_ Associate Professor

Thyroid Physiology_Dr.E. Muralinath_ Associate Professor
FAIRSpectra - Enabling the FAIRification of Analytical Science

FAIRSpectra - Enabling the FAIRification of Analytical Science
300003-World Science Day For Peace And Development.pptx

300003-World Science Day For Peace And Development.pptx
Call Girls Ahmedabad +917728919243 call me Independent Escort Service

Call Girls Ahmedabad +917728919243 call me Independent Escort Service
High Class Escorts in Hyderabad ₹7.5k Pick Up & Drop With Cash Payment 969456...

High Class Escorts in Hyderabad ₹7.5k Pick Up & Drop With Cash Payment 969456...
Photoreception
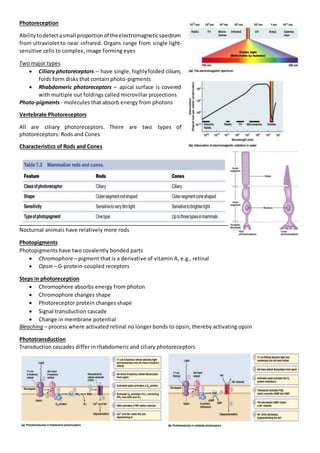
- 1. Photoreception Abilitytodetectasmall proportionof theelectromagneticspectrum from ultraviolet to near infrared. Organs range from single light- sensitive cells to complex, image forming eyes Two major types Ciliary photoreceptors – have single, highlyfolded cilium; folds form disks that contain photo-pigments Rhabdomeric photoreceptors – apical surface is covered with multiple out foldings called microvillar projections Photo-pigments - molecules that absorb energy from photons Vertebrate Photoreceptors All are ciliary photoreceptors. There are two types of photoreceptors: Rods and Cones Characteristics of Rods and Cones Nocturnal animals have relatively more rods Photopigments Photopigments have two covalently bonded parts Chromophore – pigment that is a derivative of vitamin A, e.g., retinal Opsin – G-protein-coupled receptors Steps in photoreception Chromophore absorbs energy from photon Chromophore changes shape Photoreceptor protein changes shape Signal transduction cascade Change in membrane potential Bleaching – process where activated retinal no longer bonds to opsin, thereby activating opsin Phototransduction Transduction cascades differ in rhabdomeric and ciliary photoreceptors
- 2. PLC = Phospho lipase C PIP2 = Phospho tidyel inositol biphosphate DAG = di-acyl glycerol IP3 = inositol tri-phosphate TRP = tryptophan PDE = phosphor di-esterase cGMP = cyclic Gwanosine mono-phosphate The Eye Eyespots are single cells or regions of a cell that contain photosensitive pigment, e.g., protist Euglena Eyes are complex organs Flat-sheet Eyes Provide some sense of light direction and intensity Most often seen in larval forms or as accessory eyes in adults Cup-shaped Eyes Retinal sheet is folded to form a narrow aperture Better discrimination of light direction and intensity Seen in the Nautilus Vesicular Eyes Use a lens in the aperture to improve clarity and intensity Lens refracts light and focuses it onto a single point on the retina Present in most vertebrates Convex Eye Photoreceptors radiate outward forming a convex retina Present in annelids, molluscs, and arthropods Compound Eyes Most complex convex eyes found in arthropods Composed of ommatidia Form images in two ways Apposition compound eyes – ommatidium operate independently; afferent neurons make interconnection to generate an image Superposition compound eyes –ommatidiumworktogether to form an image on the retina The Vertebrate Eye Forms bright, focused images Parts Sclera white of the eye Cornea transparent layer Choroid pigmented layer Tapetum layer in the choroid of nocturnal animals that reflects light
- 3. Iris two layers of pigmented smooth muscle Pupil opening in iris Lens focuses image Ciliary body muscles for changing lens shape Aqueous humor fluid in the anterior chamber Vitreous humor gelatinous mass in the posterior chamber Image Formation Refraction – bending light rays Both the cornea and the lens act as converting lens to focus light on the retina In terrestrial vertebrates,mostof the refractionoccursbetweenthe airandthe cornea Image Accommodation Accommodation- incominglightraysmustconvergeonthe retina to produce a clear image Focal point – point at which light waves converge Focal distance – distance from a lens to its focal point Distantobject:lightraysare parallel whenenteringthe lens Close object: light rays are not parallel when entering the lens and must be refracted more Light rays are focusedonthe retinaby changingthe shape of the lens The Retina Arranged into several layers Rods and cones are are at the back and their tips face backwards Axons of ganglion cells join together to form the optic nerve Optic nerve exits the retina at the optic disk (“blind spot”) The Fovea Small depressioninthe centerof the retinawhere overlyingbipolarand ganglion cells are pushed to the side Contains only cones Provides the sharpest images Signal Processing in the Retina Rods and cones form different images Rods o Principle of convergence– as many as 100 rods synapse with a single bipolar cell many bipolar cells synapse with a ganglion cell o Large visual field o Fuzzy image Cones o One cone synapseswithone bipolar cell whichconnects to one ganglion cell o Small visual field o High resolution image
- 4. Complex “on” and “off” regions of the receptive fields of ganglion cells improve their ability to detect contrasts between light and dark The Brain Processes the Visual Signal Opticnerves opticchiasm optictract lateral geniculatenucleus visual cortex Color Vision Detecting different wavelengths of light Requires multiple types of photoreceptors with different maximal sensitivities Humans: three (trichromatic) Most mammals: two (dichromatic) Some bird, reptiles and fish: three, four, or five (pentachromatic)
