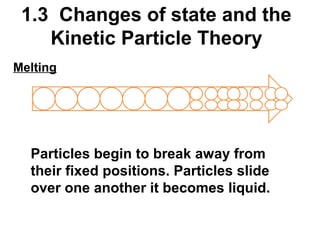
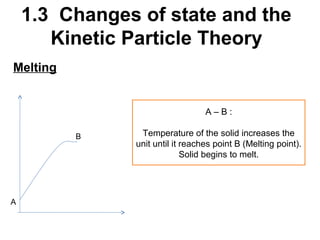
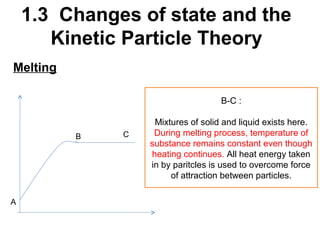
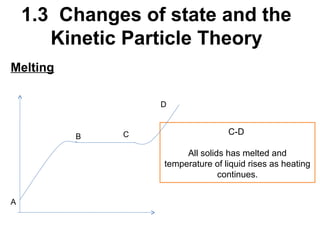
1. The kinetic particle theory describes the three states of matter (solid, liquid, gas) based on how closely particles are packed and how they move. In solids, particles vibrate in fixed positions; in liquids, they slide over each other; and in gases, they are far apart and move rapidly.
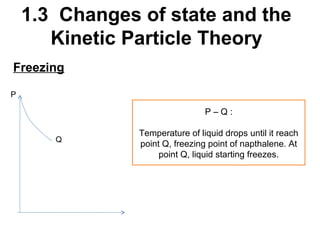
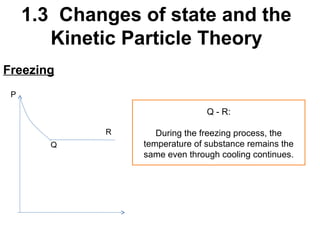
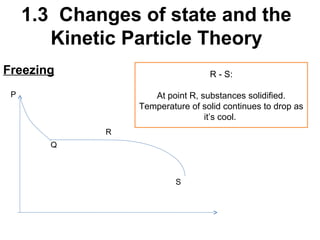
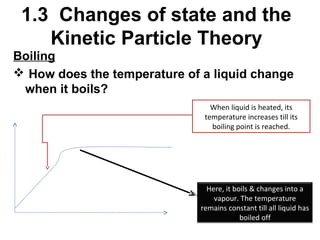
2. Changes of state like melting, freezing, boiling, and condensation occur when particles gain or lose enough kinetic energy to overcome the forces between them. Melting and boiling happen when particles break away from fixed positions and spread out. Freezing and condensation occur when particles slow down and settle into fixed positions.
3. Evaporation and sublimation are also changes of state: evap