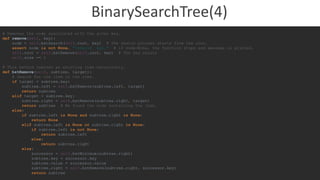
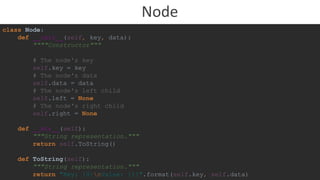
The document discusses the creation and functionality of a binary search tree (BST) compared to a linked list for data organization, emphasizing improved search efficiency with traversal times of O(log n) versus O(n) in the worst case. It includes code for implementing a BST, along with methods for inserting, searching, and deleting nodes, as well as a translator class that utilizes the BST for word lookups and spell-checking functions. Additionally, it provides details on how to handle word suggestions based on similarities, enhancing user interaction with the translation features.


![6
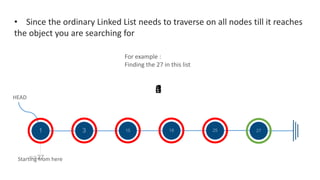
We see that in Linked List it needs to traverse on
all nodes to reach the specific data [27] because
It exists at the last node.
Which means that Linked List
would traverse on (n) of nodes
for the worst case of running time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-170322211107/85/Python-Spell-Checker-4-320.jpg)
![3
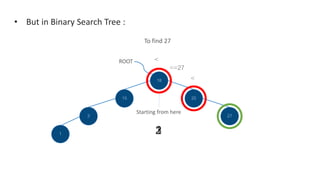
In Binary Search Tree it only traverse on
specific nodes that leads to the specific data [27]
by doing a comparison at each node to determine
the next node.
The Binary Search Tree
would approximately traverse on (log(n)) of nodes
for the worst case of running time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-170322211107/85/Python-Spell-Checker-6-320.jpg)






![Translator(1)
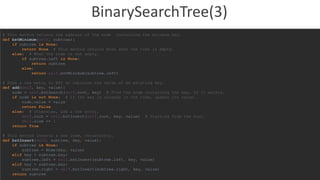
class Translator:
"""AVLTree Implementation"""
def __init__(self):
time1 = datetime.now()
print("Loading Database...")
self.__tree = self.__getDictionary()
self.SpellChecker = self.__makeSpellChecker()
time2 = datetime.now()
print("Loaded in {0}rn".format(time2 - time1))
@staticmethod
def __getDictionary():
words = [line.rstrip('rn') for line in open("UltimateZeroDict.txt", "r", encoding='utf-8')]
avl = AVLTree()
for word in words:
temp = word.lower().split(':')
avl.insert(temp[0], temp[1])
return avl
@staticmethod
def __makeSpellChecker():
words = [line.rstrip('rn') for line in open("UltimateZeroDict.txt", "r", encoding='utf-8')]
english = []
for word in words:
temp = word.lower().split(':')
english.append(temp[0])
return SpellChecker(english)
def hasWord(self, englishWord):
return self.__tree.has_key(englishWord.lower())](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-170322211107/85/Python-Spell-Checker-17-320.jpg)
![Translator(2)
def Translate(self, englishWord):
englishWord = englishWord.lower()
trans = self.__tree.ValueOf(englishWord)
result = Result()
if trans is not None:
result.Value = trans
else:
result.Suggesions = self.SpellChecker.GetSuggestions(englishWord)
return result
def TranslateSentense(self, sentense):
words = sentense.split(' ')
FinalOut = ""
output = []
wrong = "Unable to recognize these words, Here are some Suggestions:rn"
w = False
for word in words:
trans = self.Translate(word)
if not trans.Translated():
wrong += word + " => " + str(trans.Suggesions) + "rn"
w = True
output.append(trans.Value if trans.Translated() else word)
FinalOut += " ".join(output) + "rn"
FinalOut += wrong if w else ""
return FinalOut](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-170322211107/85/Python-Spell-Checker-18-320.jpg)

![SpellChecker(1)
import math
class SpellChecker:
def __init__(self, tree):
self.wordlist = tree
@staticmethod
def __areInRange(num1, num2, Range=1):
for i in range(Range + 1):
if math.fabs(num1 - num2) == i:
return True
return False
@staticmethod
def __LettersInplace(word, Input):
lettersInplace = 0
for i in range(len(Input)):
if (len(word) > i) and (word[i] == Input[i]):
lettersInplace += 1
return lettersInplace
@staticmethod
def __CommonLetters(word, Input):
commonLetters = 0
Inputs = {}
for i in range(len(Input)):
if (Inputs.get(Input[i], False)):
Inputs[Input[i]] += 1
else:
Inputs[Input[i]] = 1
for key, value in Inputs.items():
if word.count(key) == value:
commonLetters += 1
if (Input[len(Input) - 1] == word[len(word) - 1]):
commonLetters += 1
if (len(Input) == len(word)):
commonLetters += 1
if word[0] == Input[0]:
commonLetters += 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-170322211107/85/Python-Spell-Checker-20-320.jpg)
![SpellChecker(2)
@staticmethod
def __LettersInRange(word, Input):
lettersInRange = 0
for i in range(len(Input)):
if (len(word) > i) and (Input[i] in word) and SpellChecker.__areInRange(i, Input.index(word[i]) if (word[i] in Input) else -1):
lettersInRange += 1
return lettersInRange
def IsValid(self, Input):
return Input in self.__tree
def GetSuggestions(self, Input, NumOfSuggestions = 5):
arr = []
for word in self.wordlist:
if SpellChecker.__areInRange(len(word), len(Input), 1):
arr.append(word)
dic = {}
for word in arr:
NumOfSimilarities = 0
NumOfSimilarities += SpellChecker.__CommonLetters(str(word), Input)
NumOfSimilarities += SpellChecker.__LettersInplace(str(word), Input)
NumOfSimilarities += SpellChecker.__LettersInRange(str(word), Input)
dic[str(word)] = NumOfSimilarities
Maxes = []
for i in range(NumOfSuggestions):
if len(dic) > 0:
Max = list(dic.keys())[list(dic.values()).index(max(dic.values()))]
Maxes.append(Max)
del dic[str(Max)]
return Maxes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-170322211107/85/Python-Spell-Checker-21-320.jpg)
