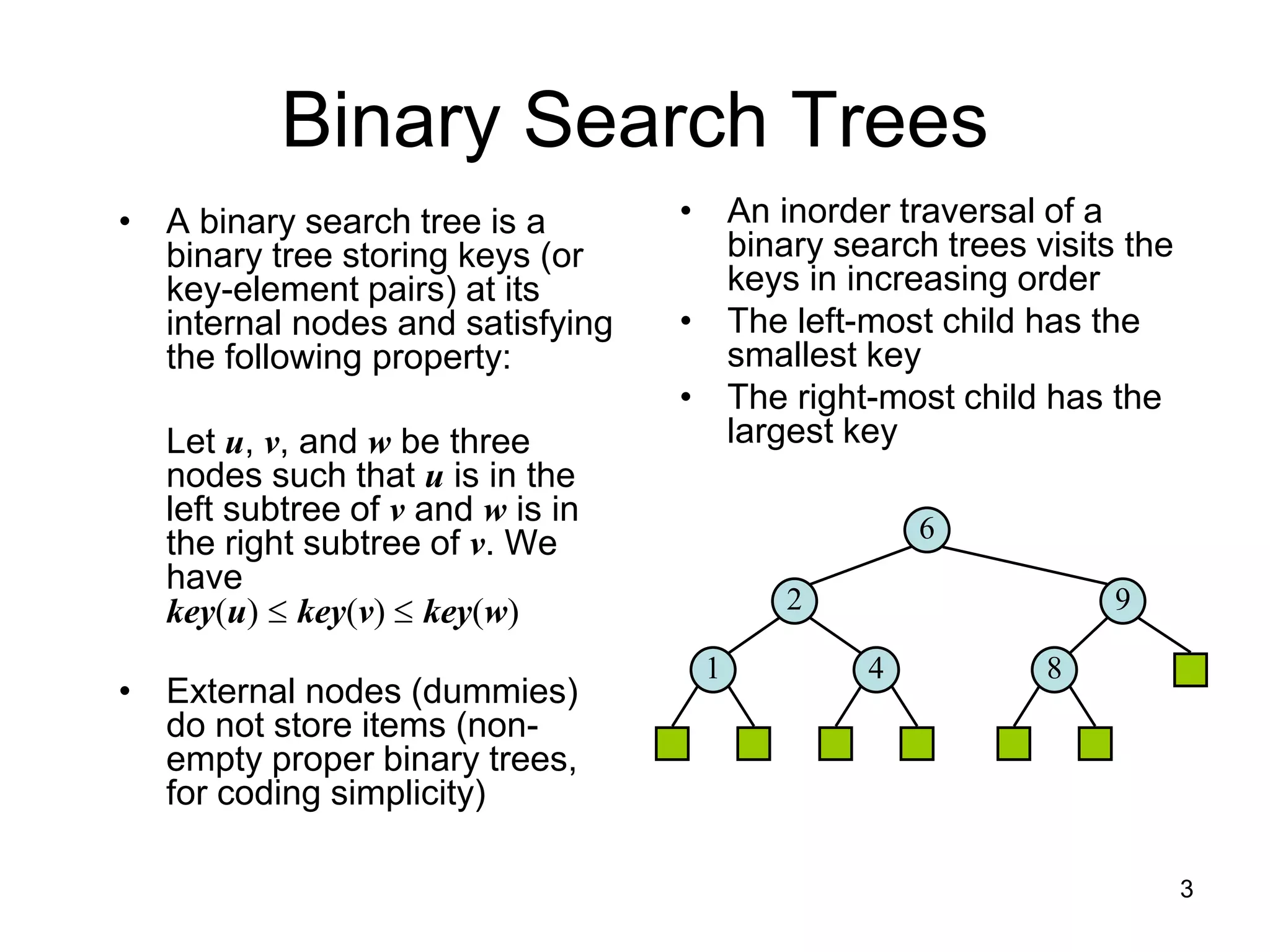
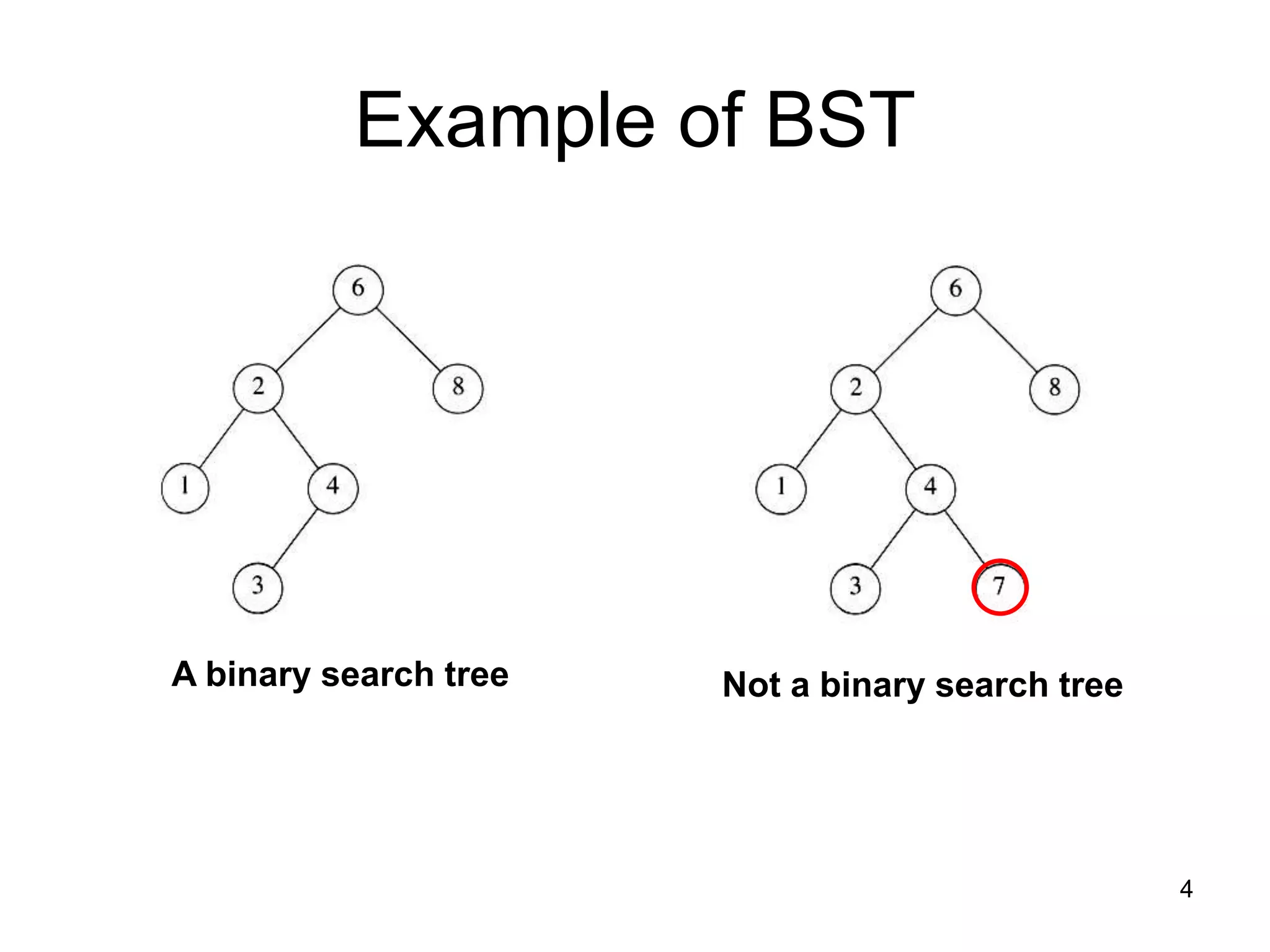
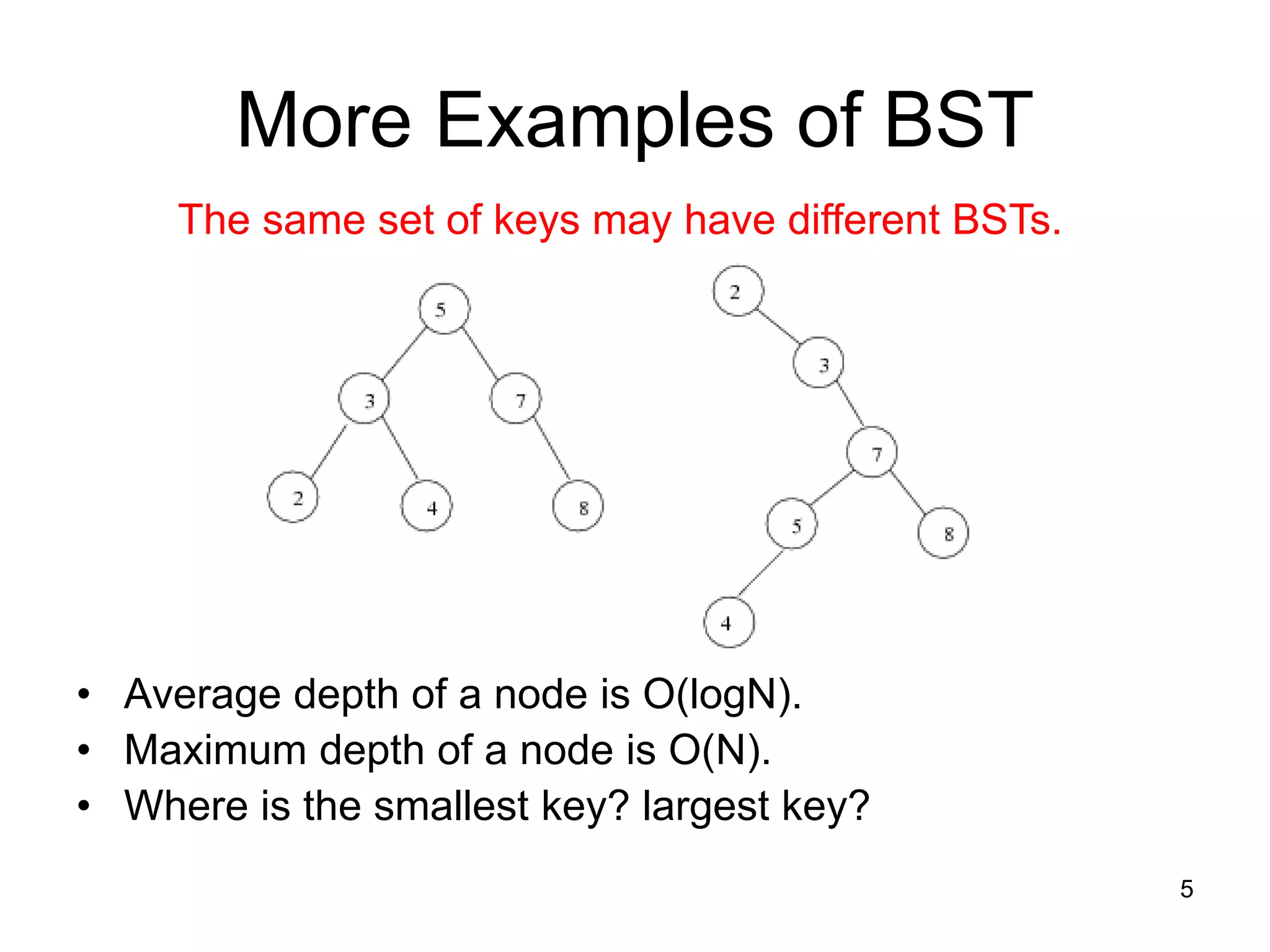
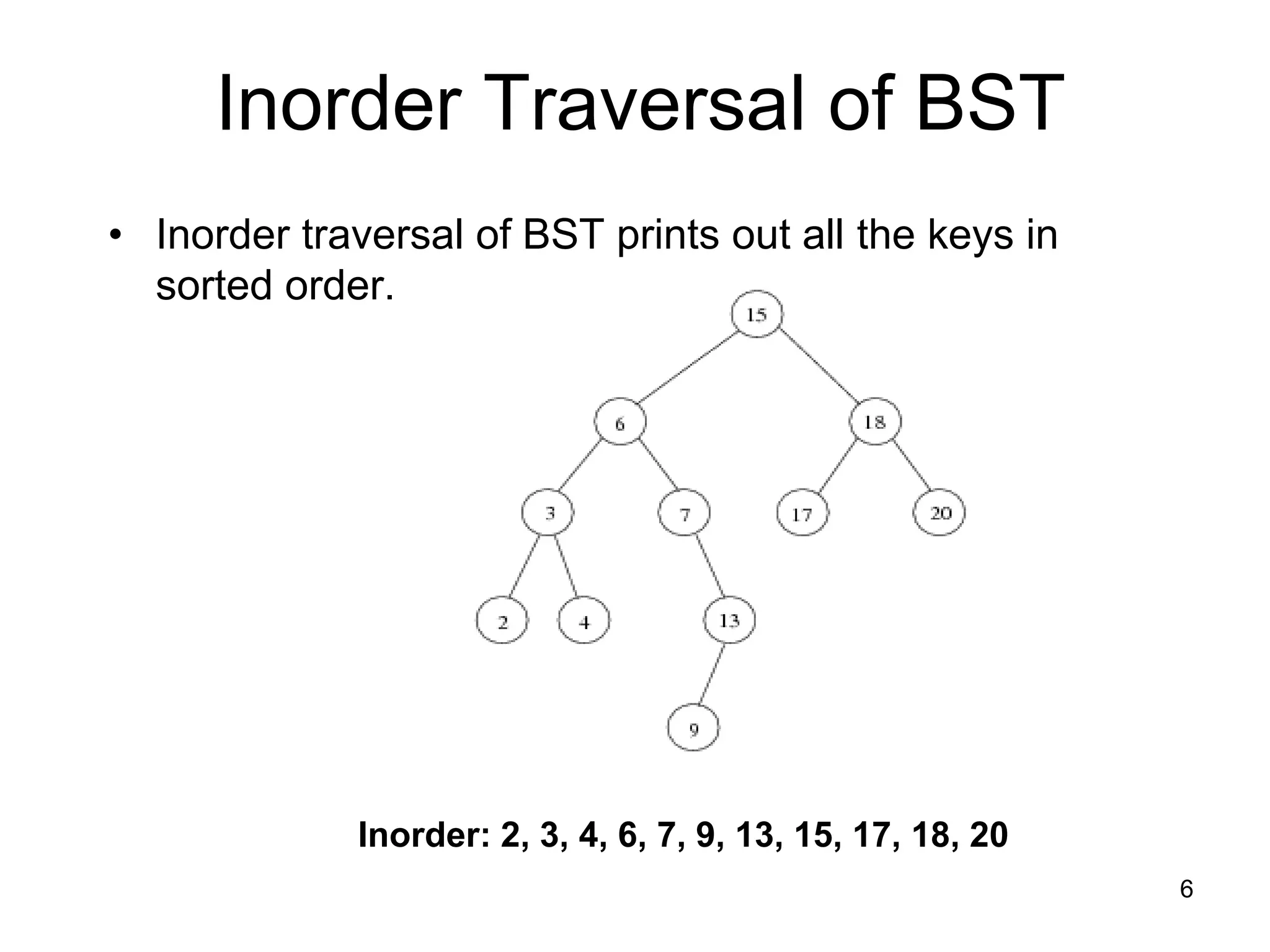
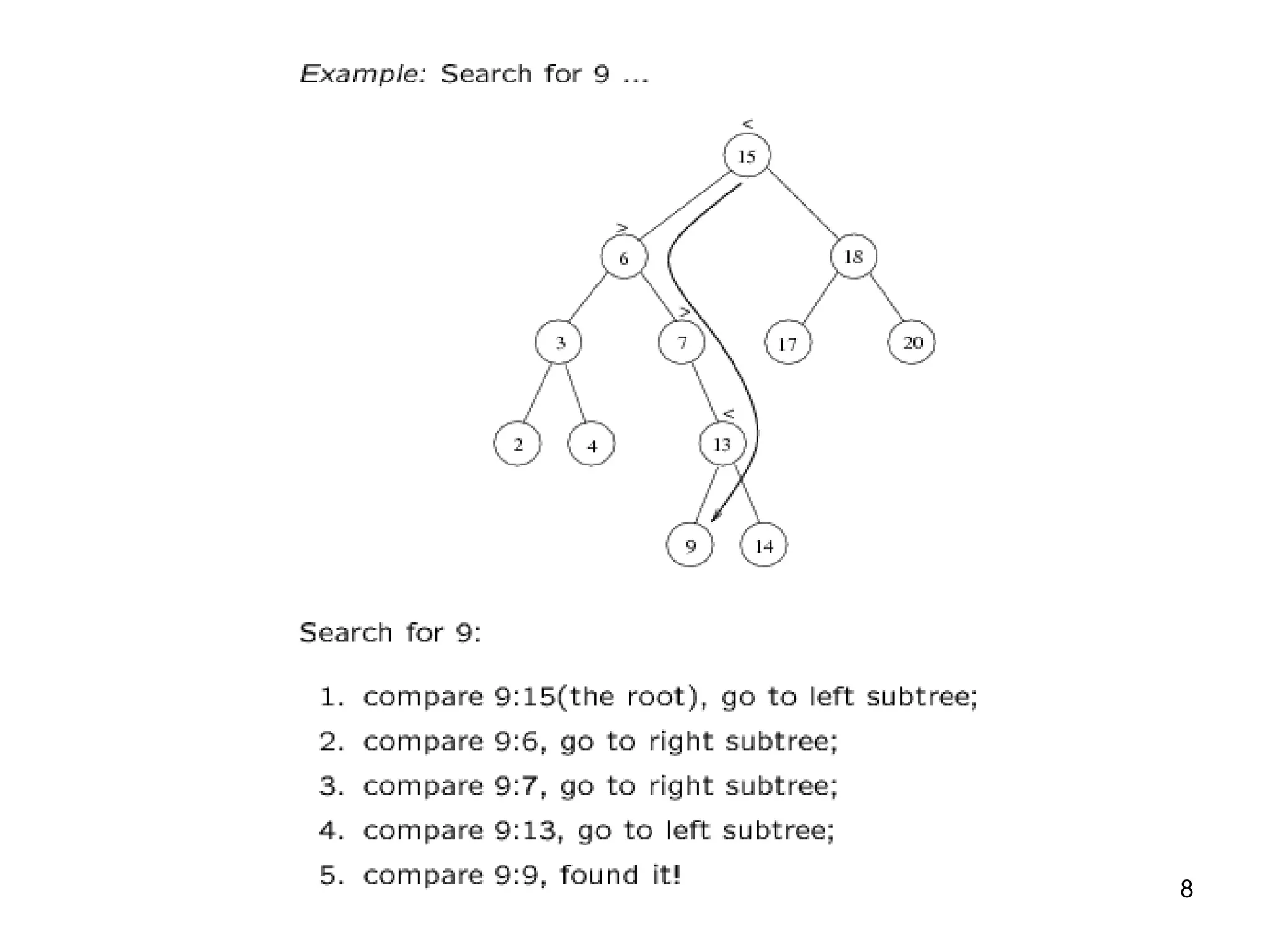
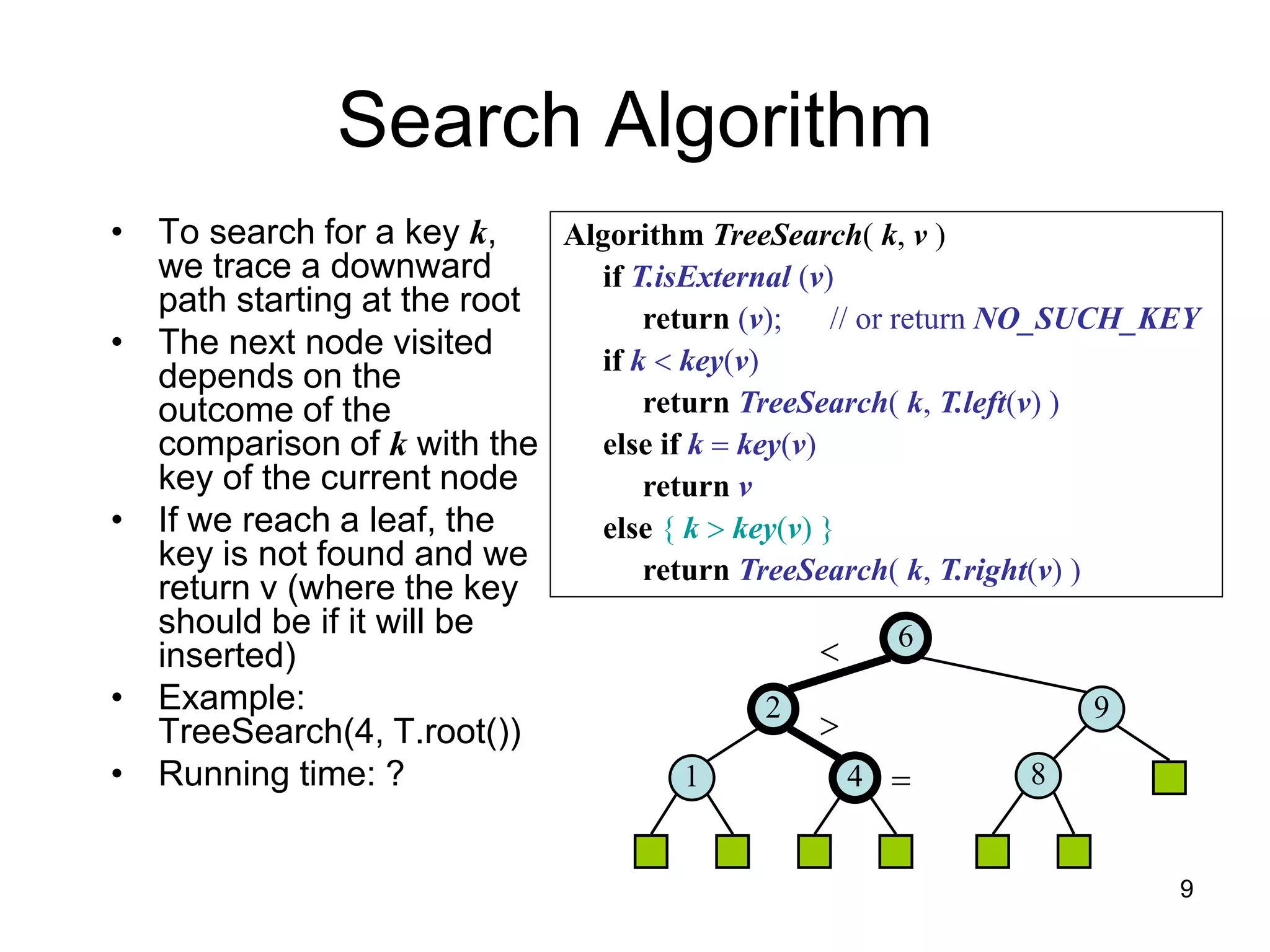
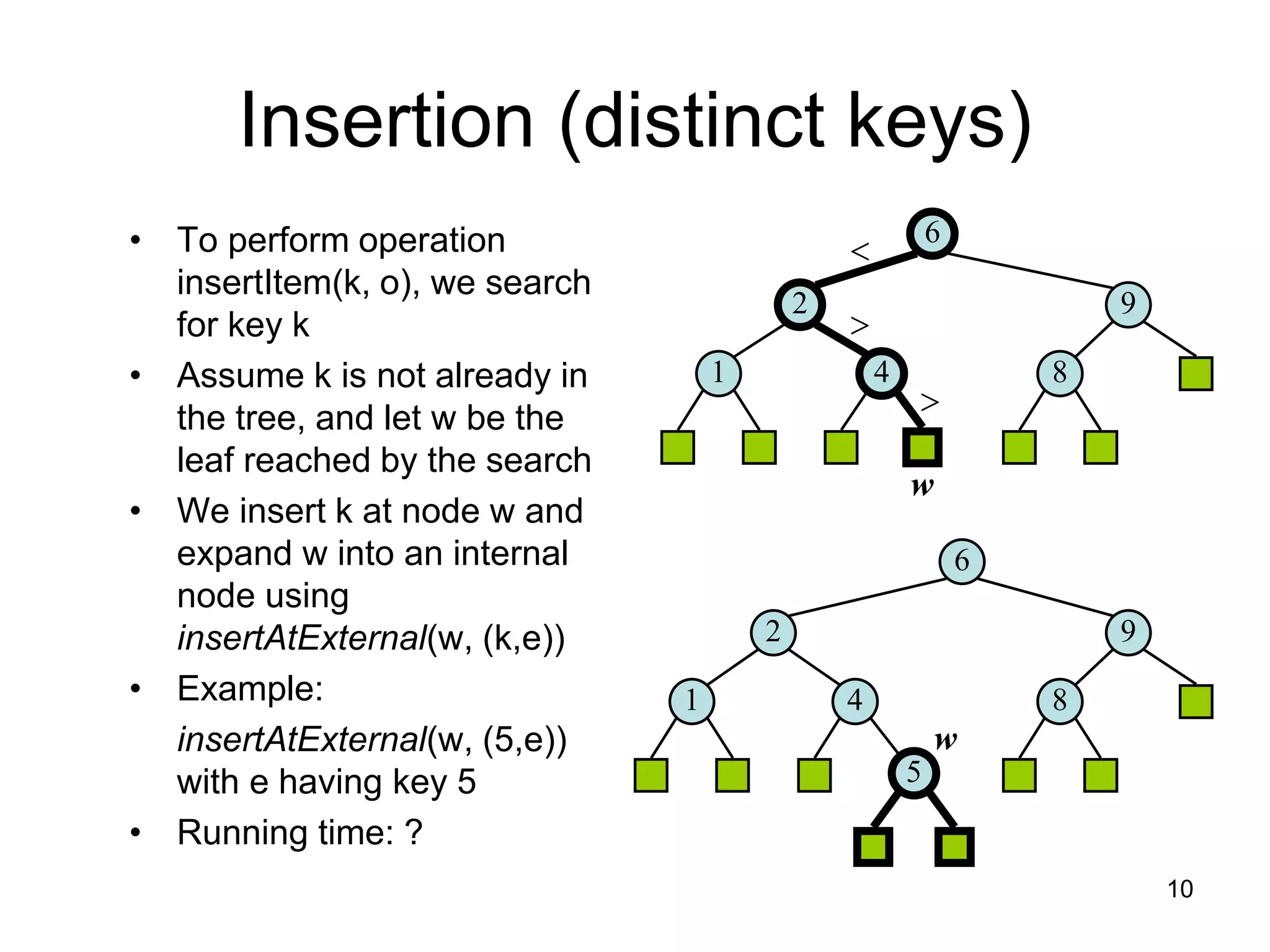
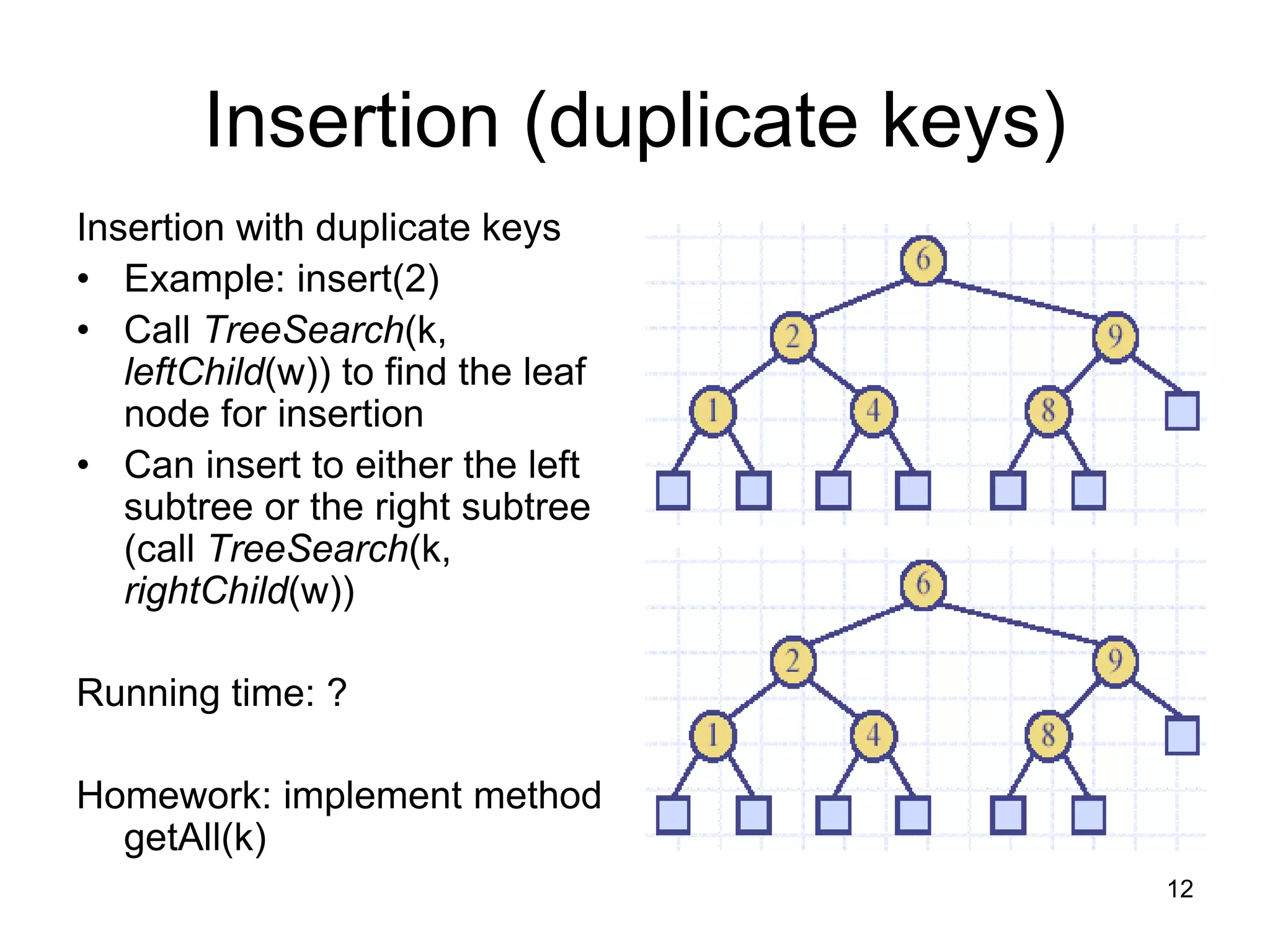
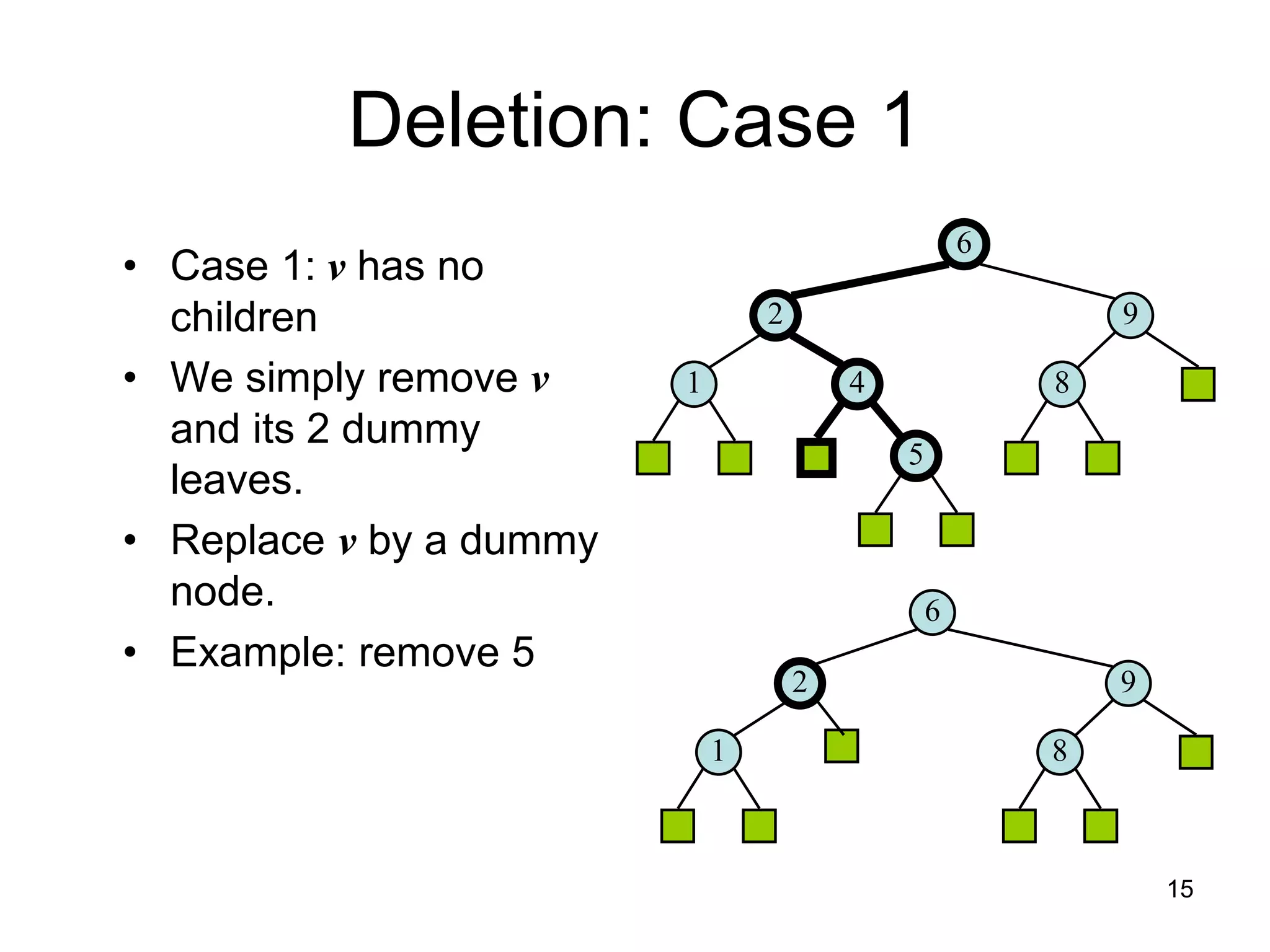
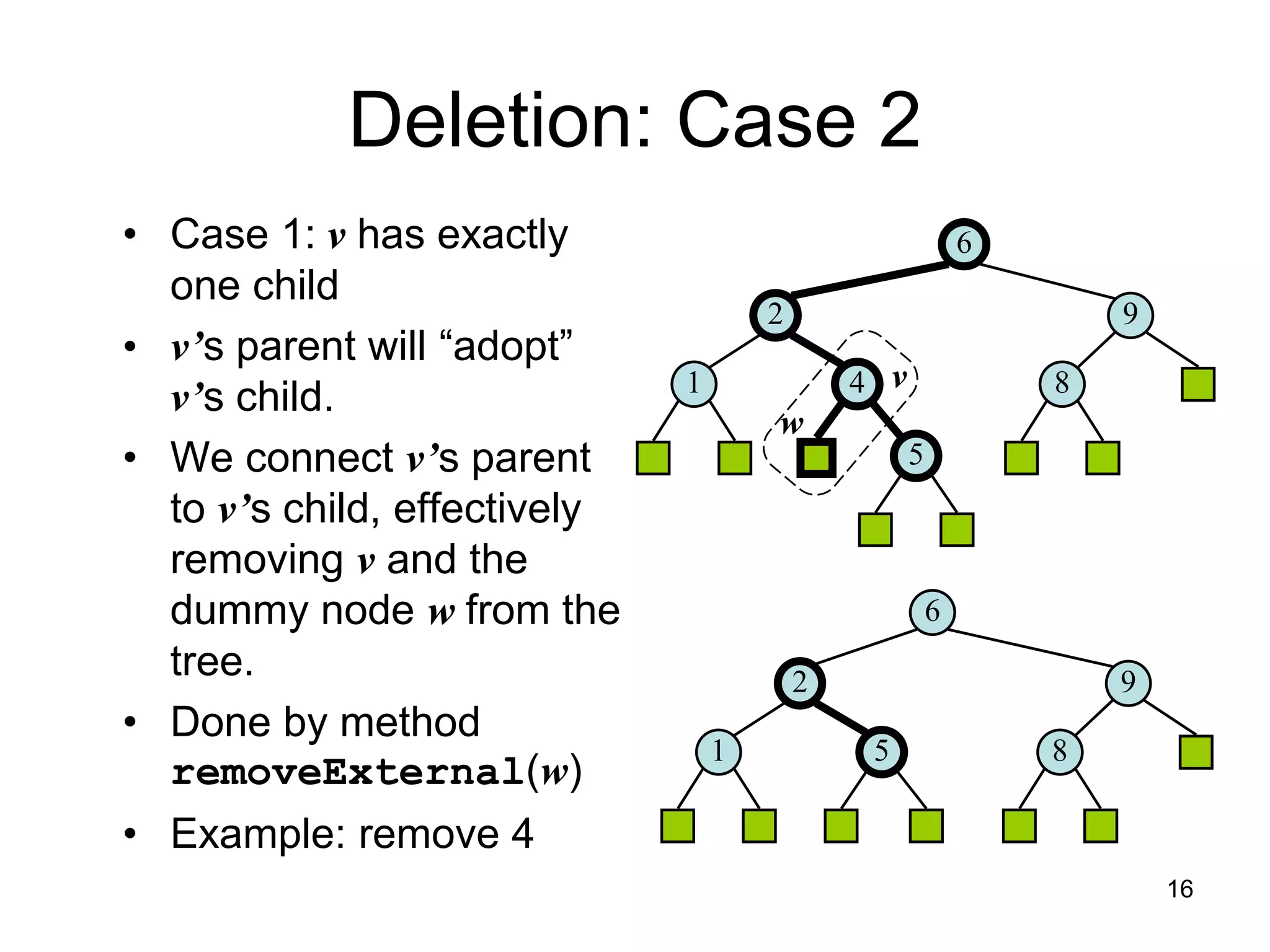
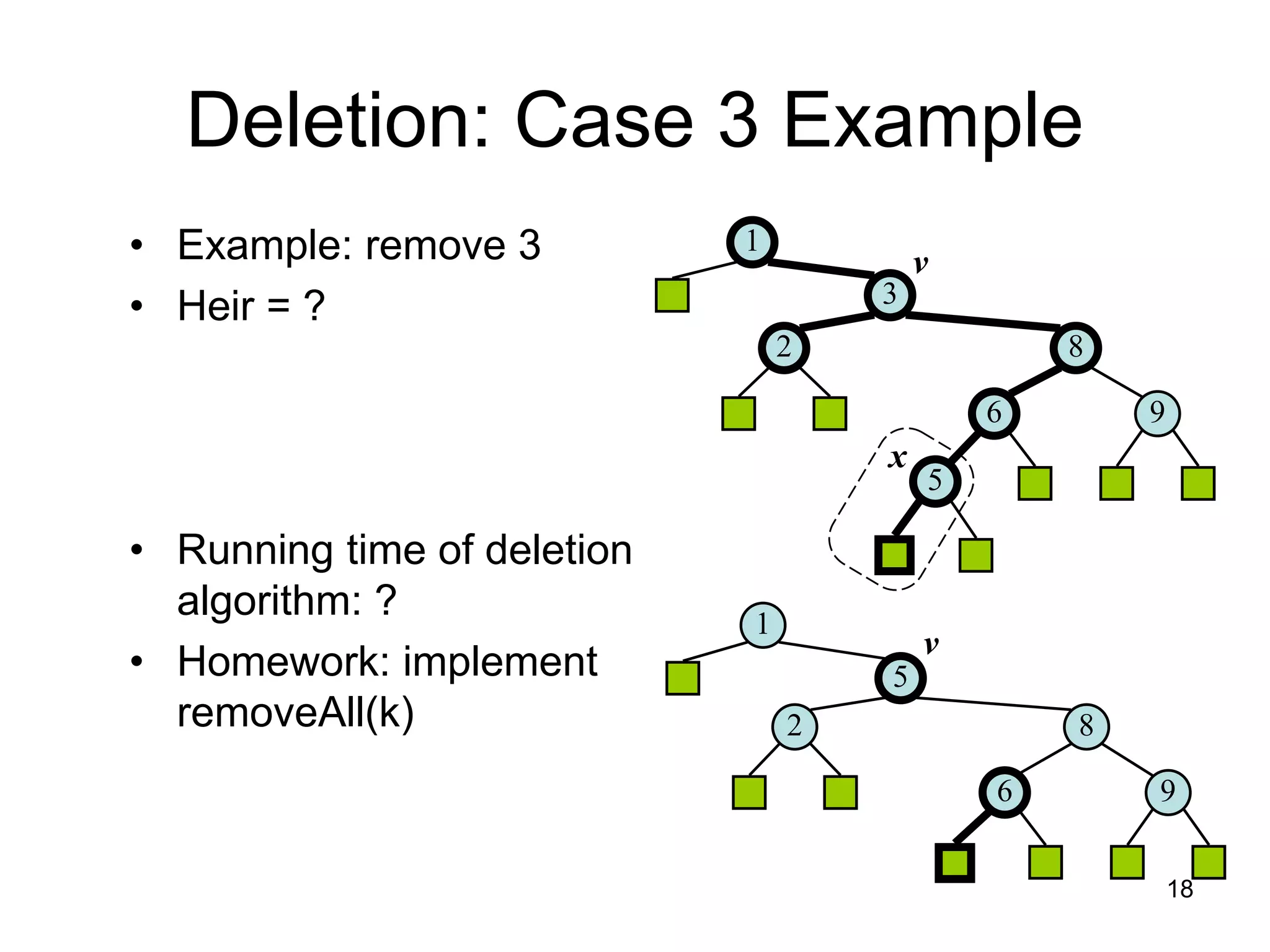
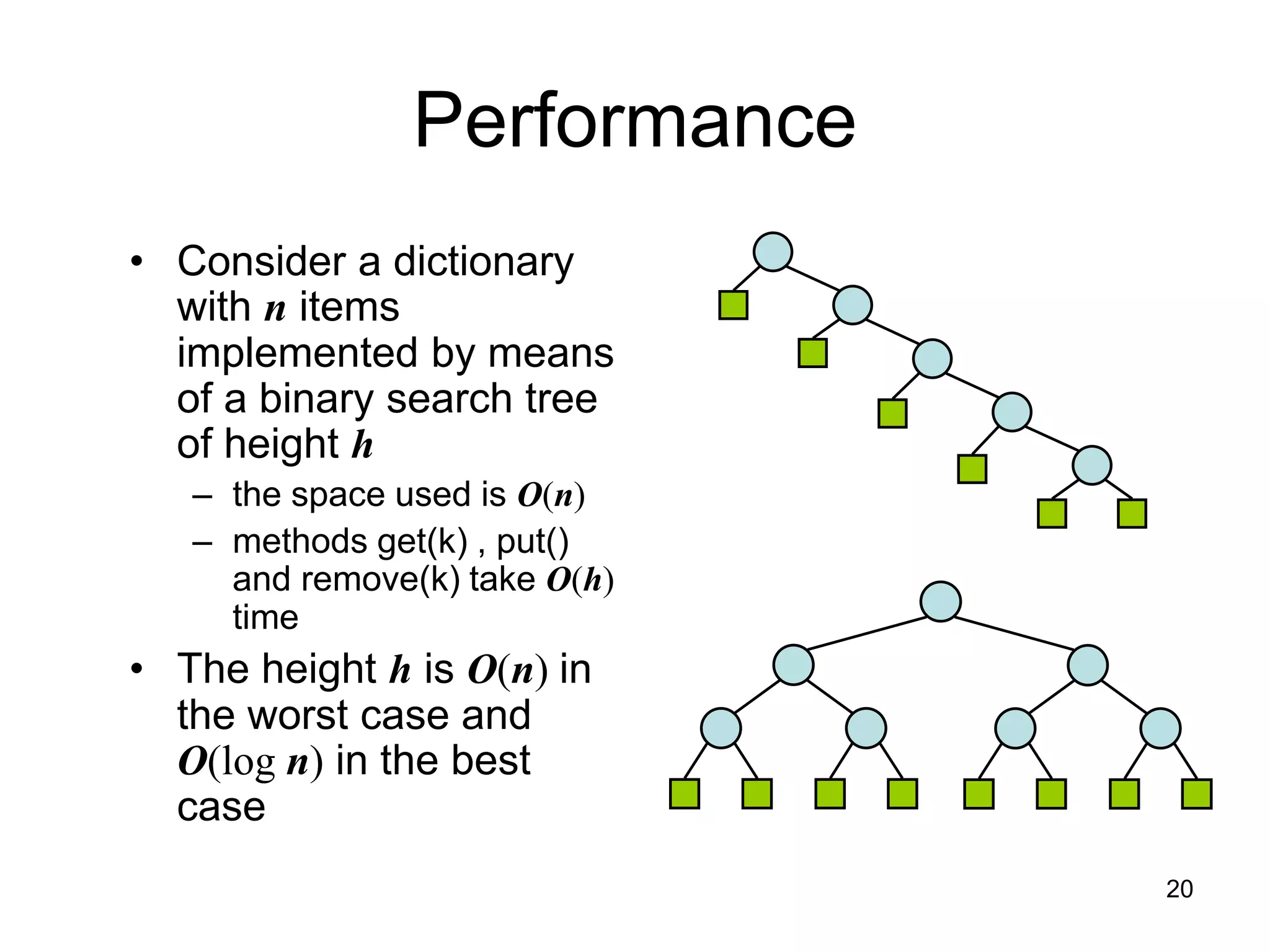
The document discusses binary search trees (BSTs), which are binary trees used to implement dictionaries. BSTs store keys or key-element pairs at internal nodes and satisfy the property that all descendants of a node have keys greater than or less than the node's key. This allows efficient search, insertion, and deletion of keys. Searching a BST takes O(h) time where h is the height, which is O(log n) on average but O(n) worst-case. Deletion handles three cases - nodes with 0, 1, or 2 children - using techniques like removing nodes, adopting children, and replacing nodes with their in-order successors.