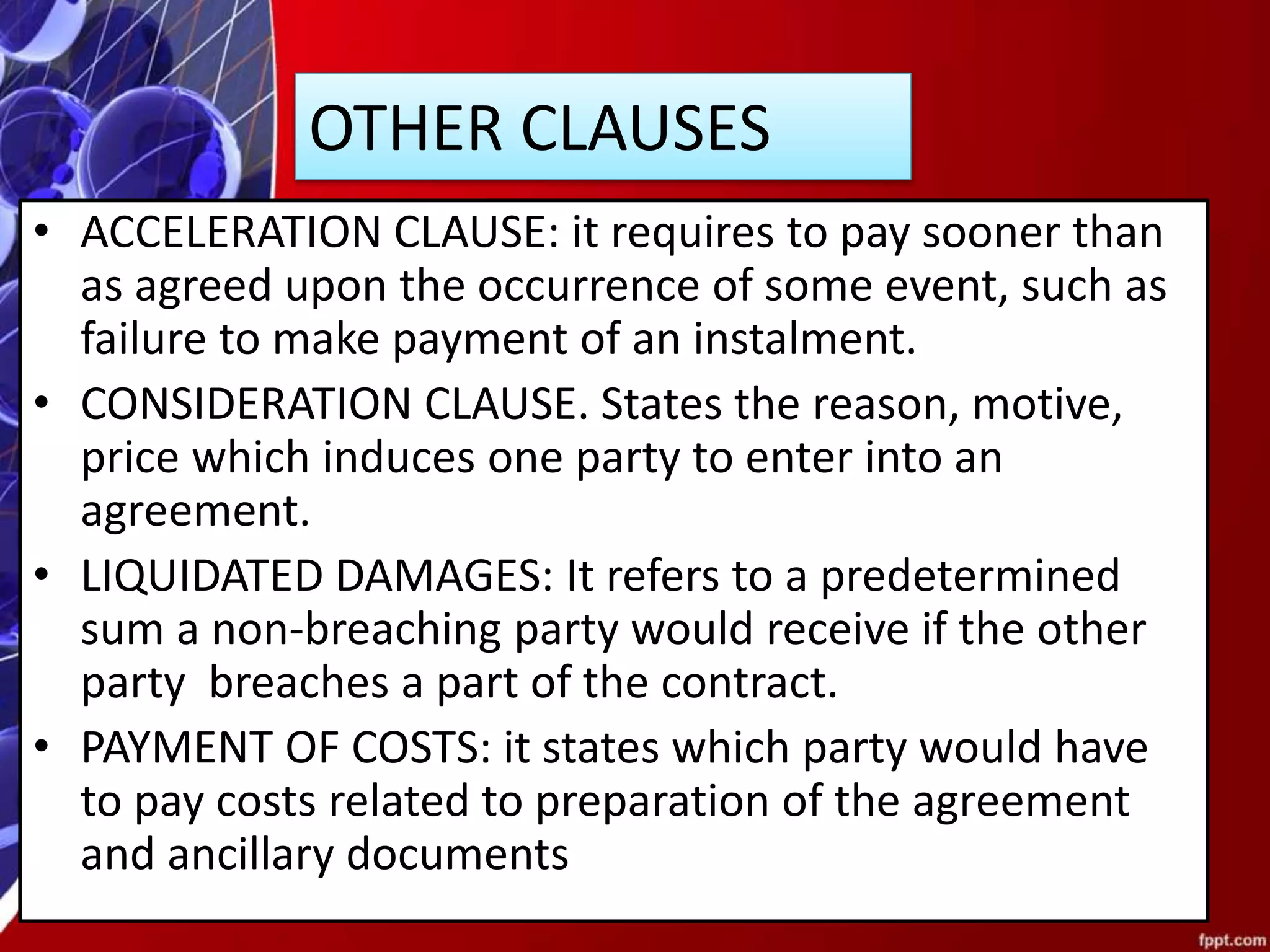
This document provides an overview of common clauses found in contracts. It defines termination, confidentiality, intellectual property rights, assignment, and force majeure clauses. It also describes acceleration, consideration, liquidated damages, payment of costs, and retention of title (R.O.T.) clauses. Additionally, it defines the differences between warranties and guarantees, noting that a warranty guarantees a product while a guarantee is a written promise ensuring performance. Examples are provided for each clause type.