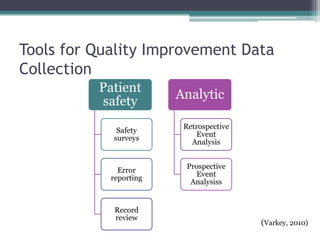
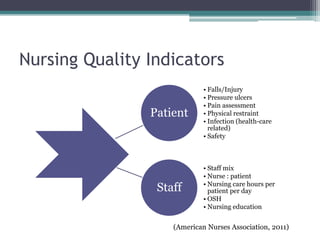
\nNurses play an important role in quality improvement by monitoring for adverse events and complications, and providing timely care to patients experiencing issues. Quality improvement in nursing involves reviewing data to identify areas for improvement, formulating goals, and evaluating nursing performance to improve patient care and work environment. Nurses can collect quality improvement data through various tools like patient safety surveys, error reporting, and record reviews. Common nursing quality indicators include falls, pressure ulcers, pain assessment, and staffing levels.