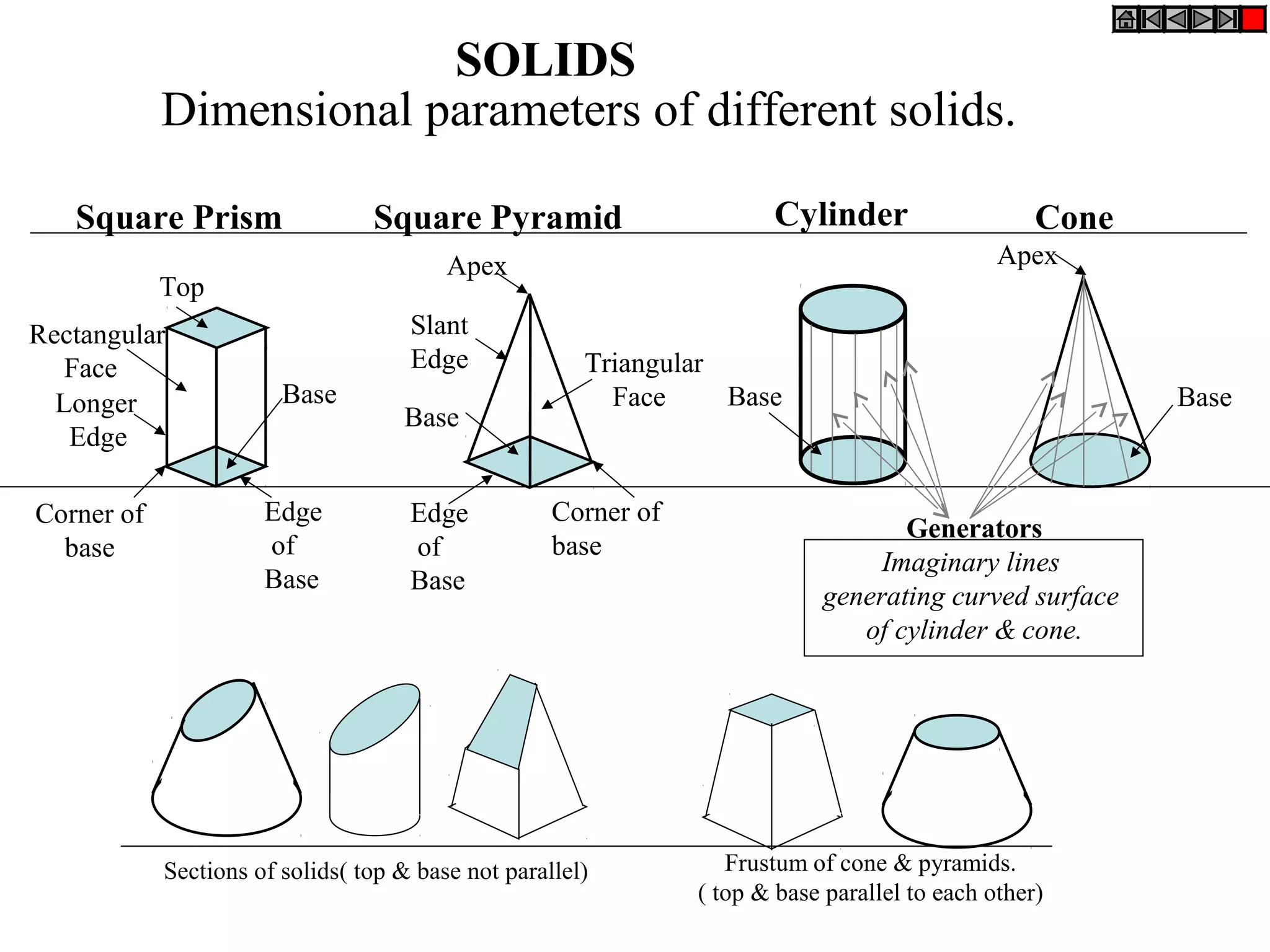
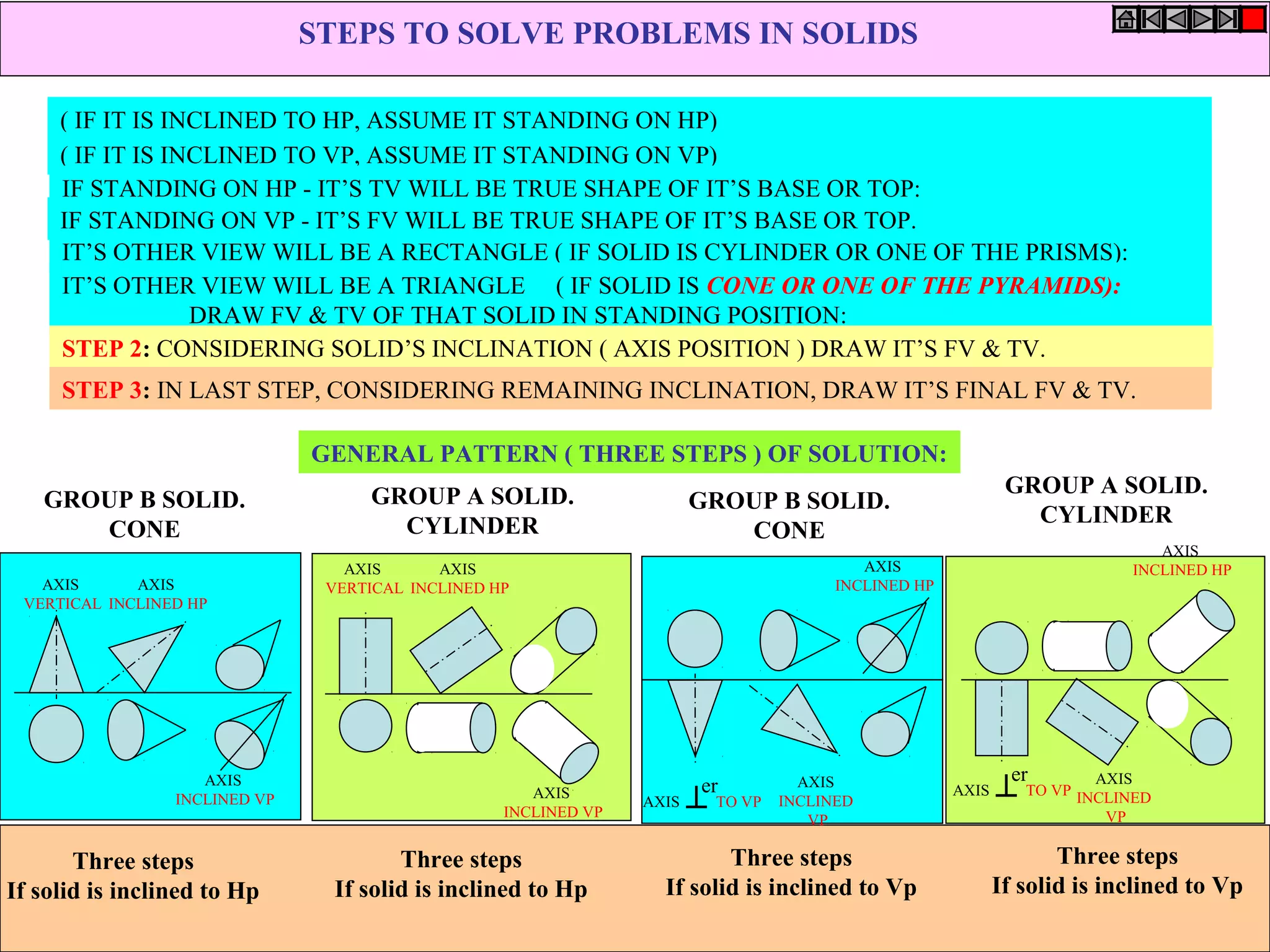
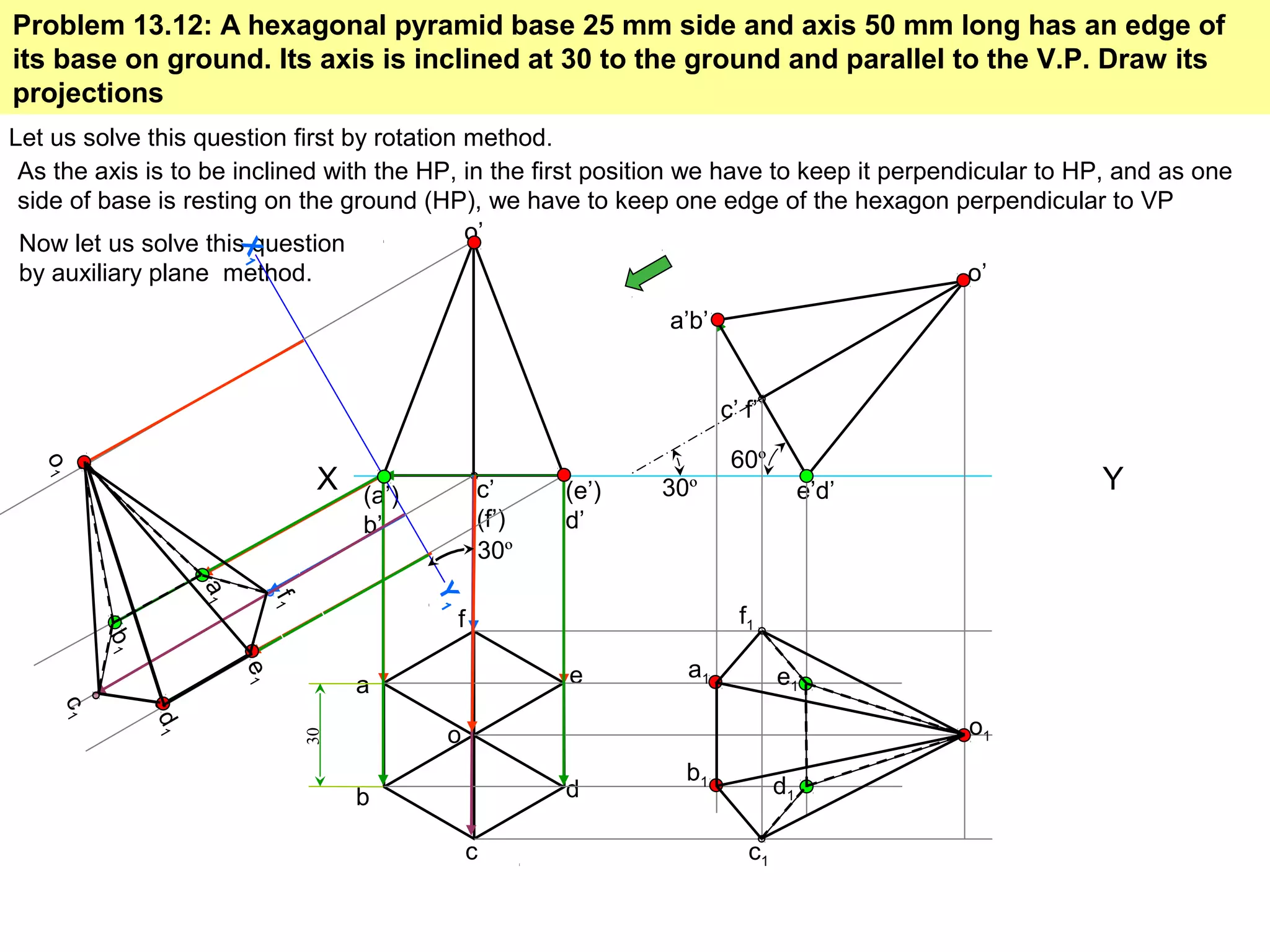
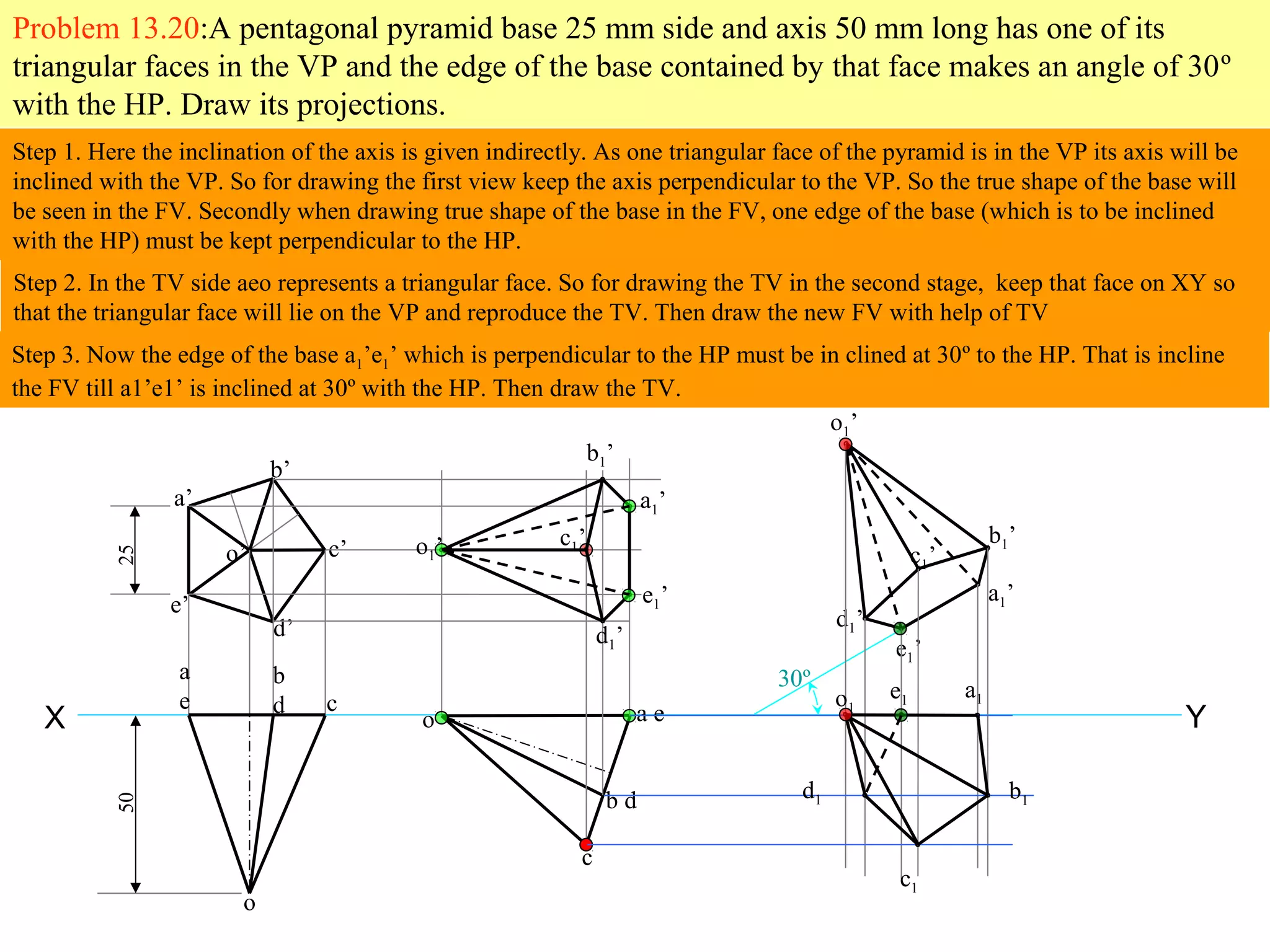
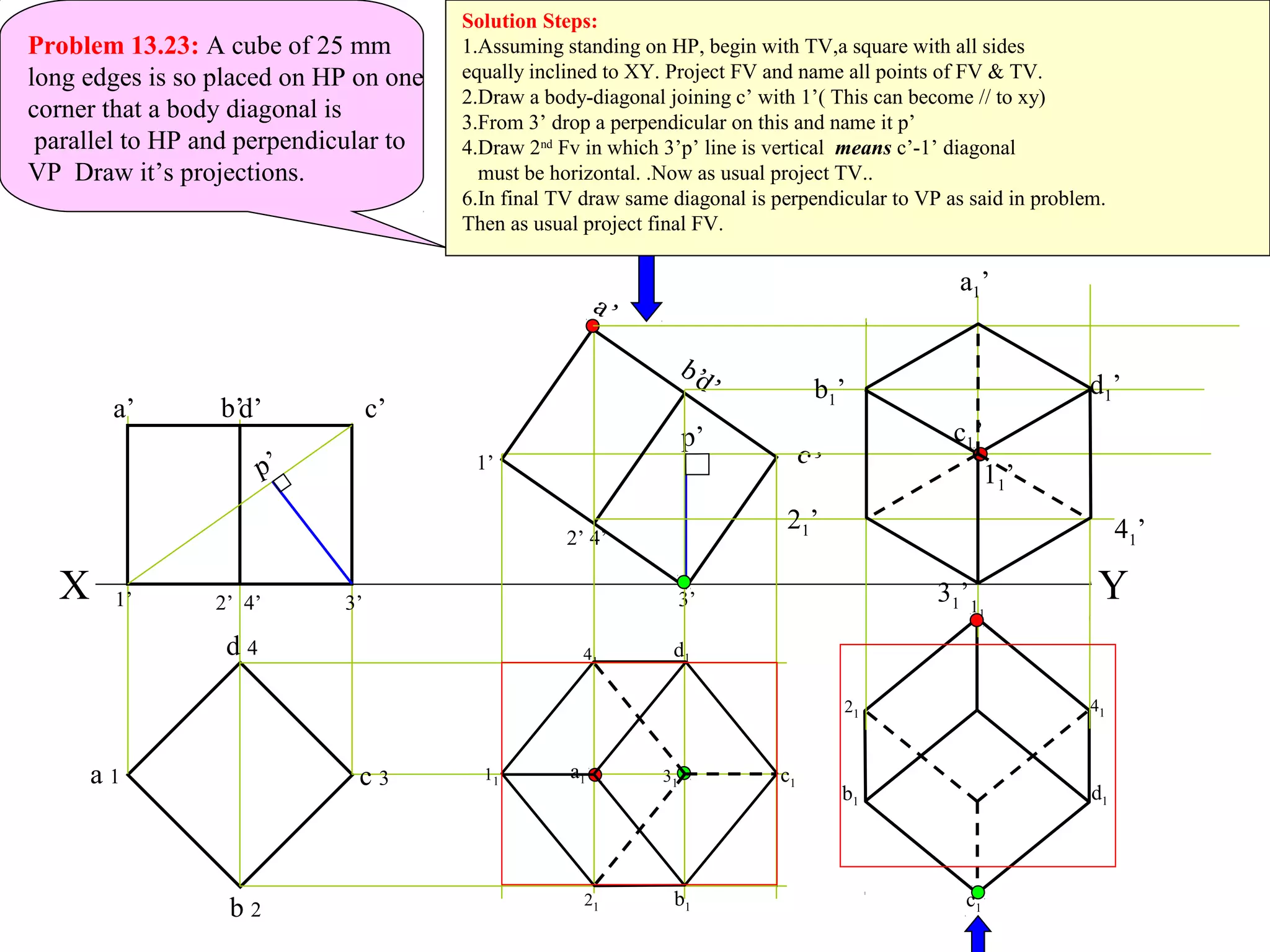
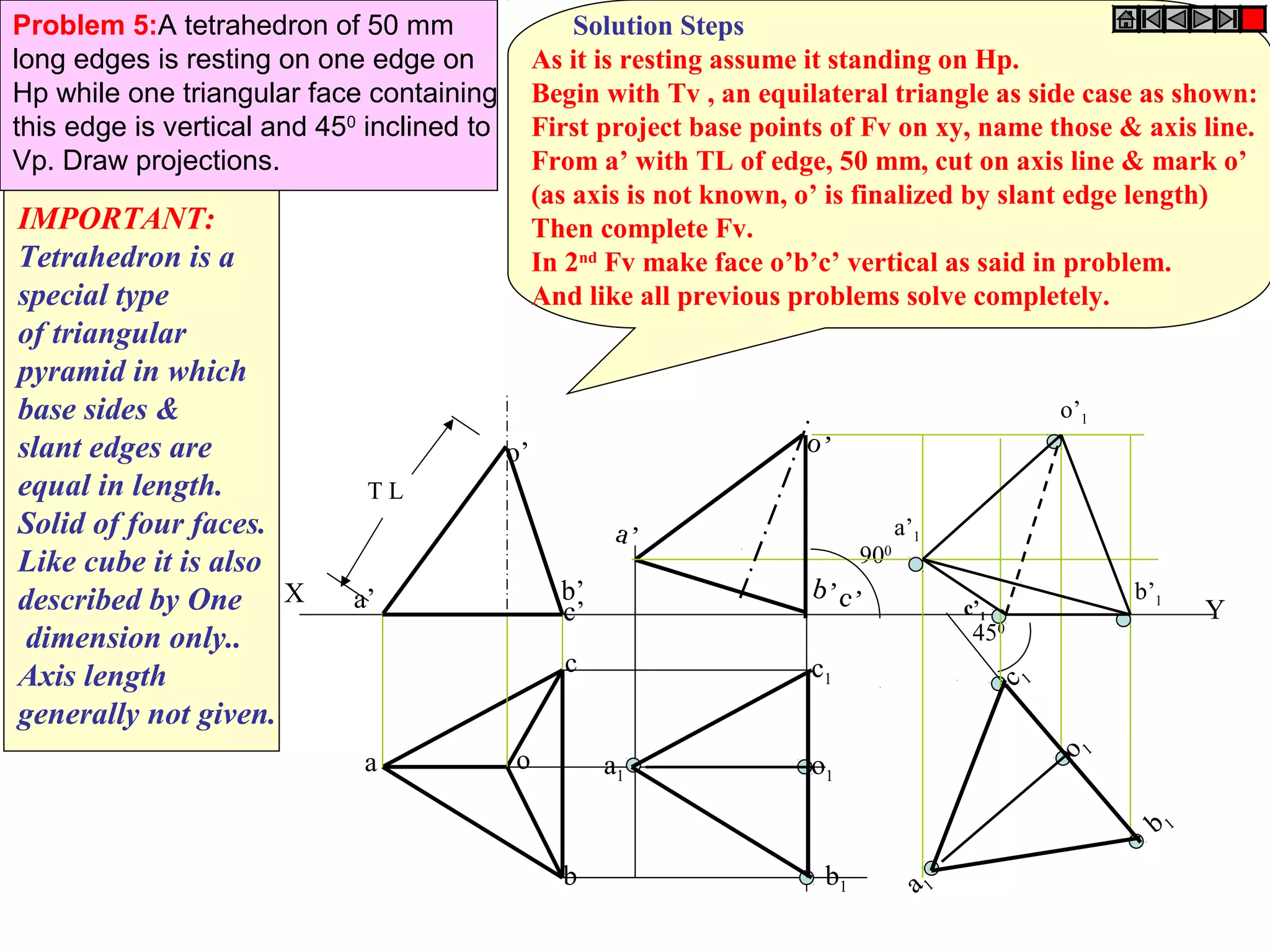
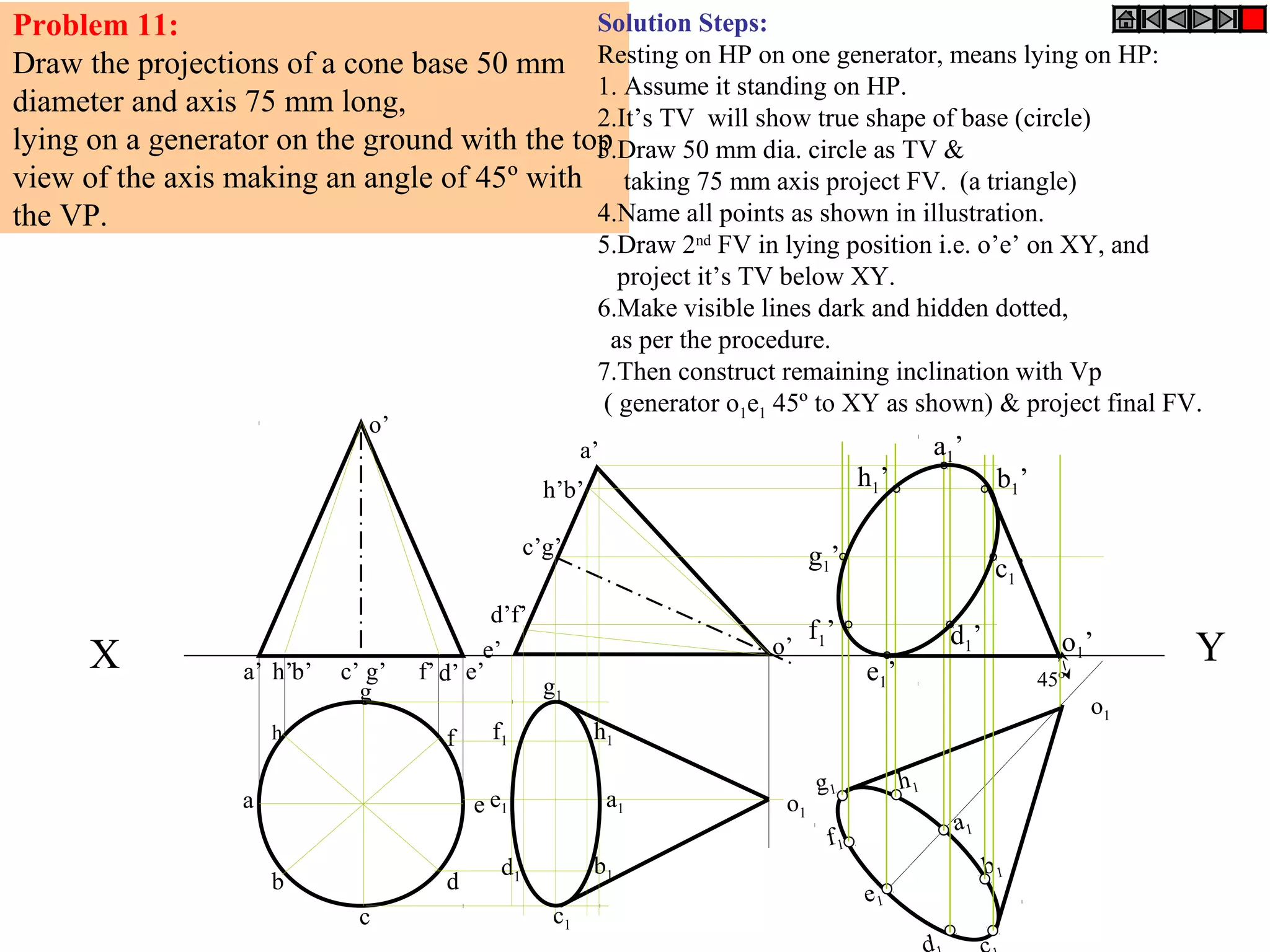
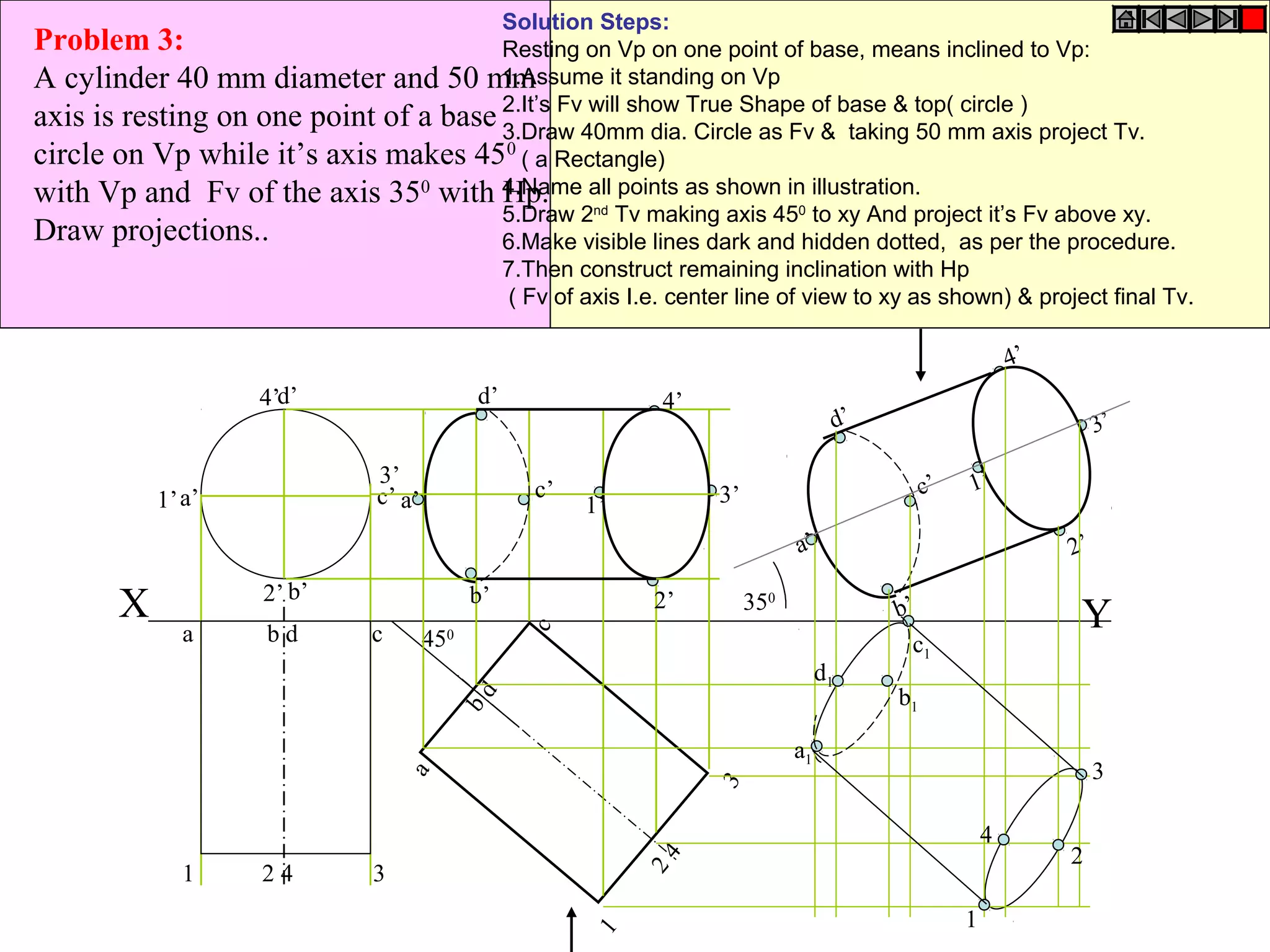
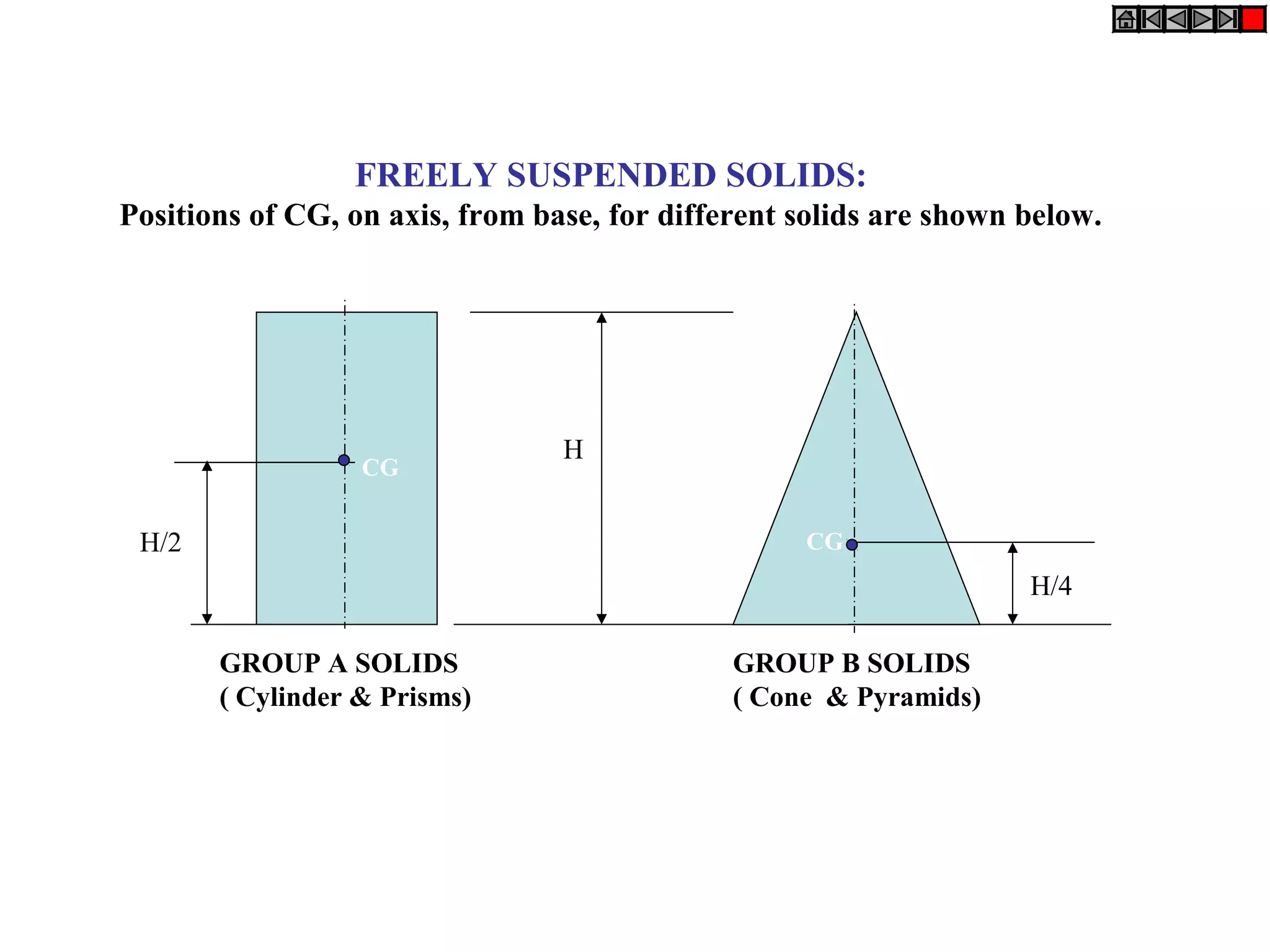
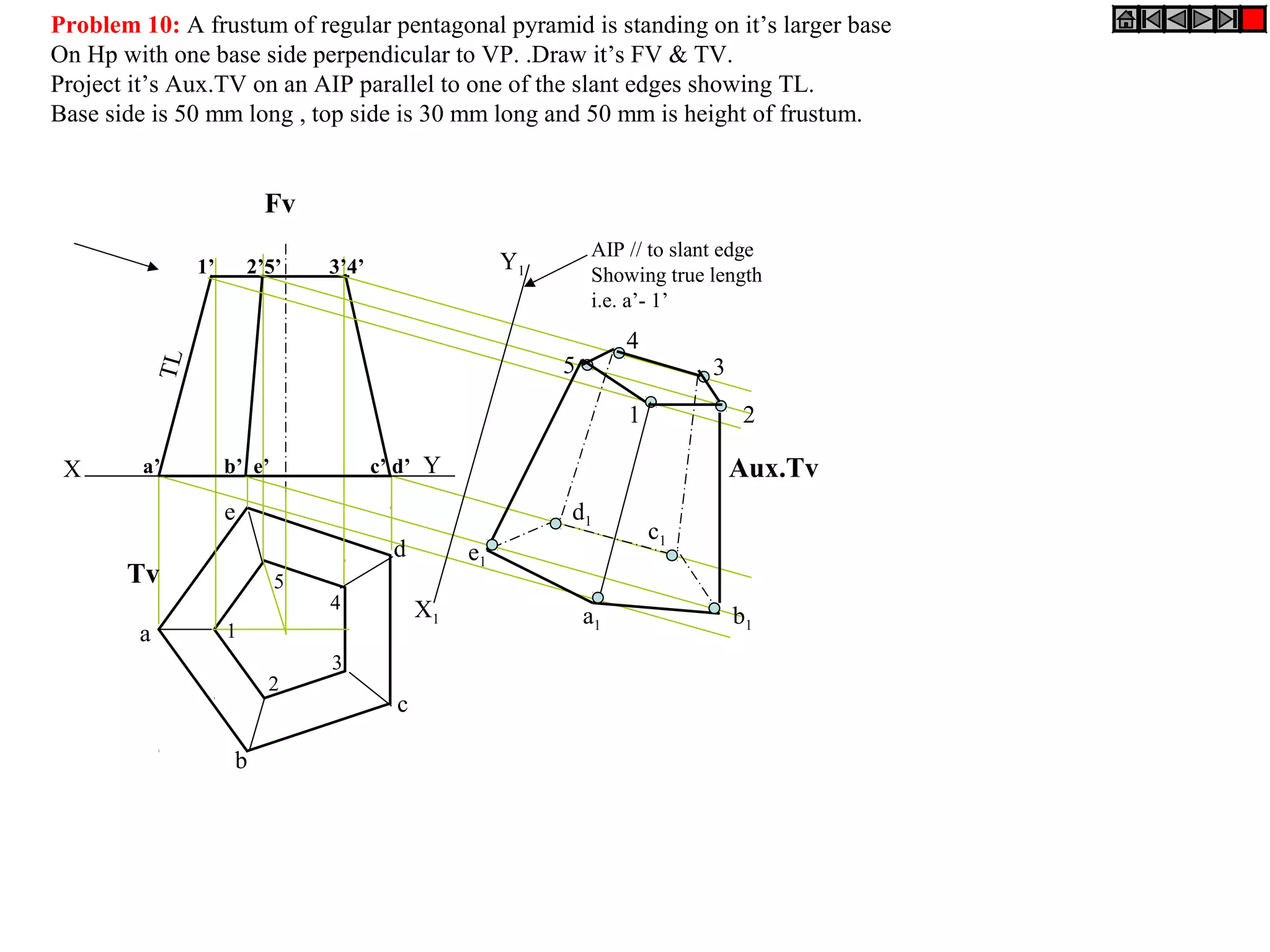
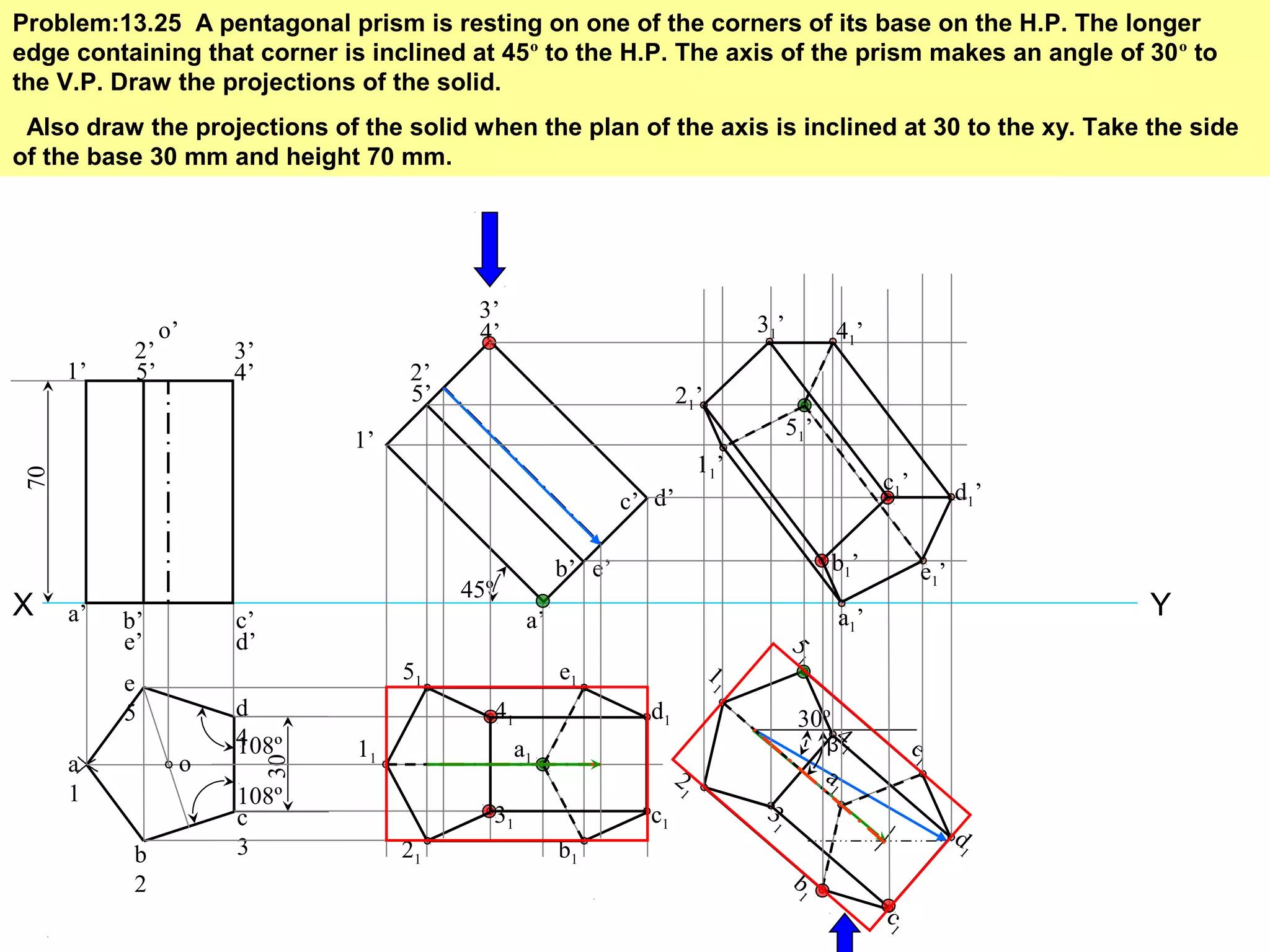
The document provides a comprehensive overview of solids, classifying them into two main groups based on their shapes and dimensions, primarily focusing on the geometric properties of various solids like prisms, pyramids, cylinders, and cones. It outlines methodologies for solving problems related to the projections of these solids when inclined to horizontal and vertical planes, detailing steps and considerations for accurate representations. Additionally, it includes example problems demonstrating the application of these principles in projecting solids in various positions and orientations.