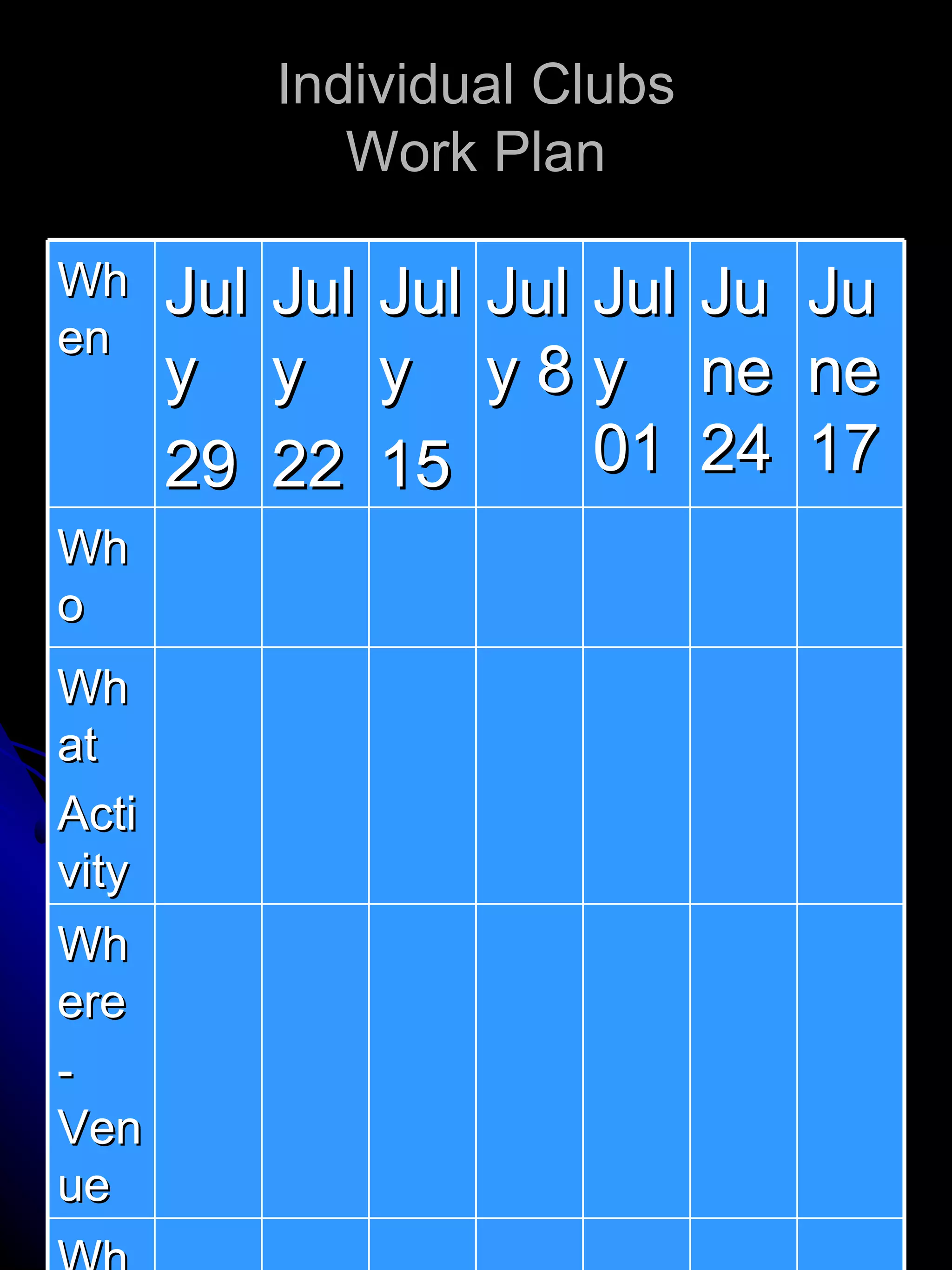
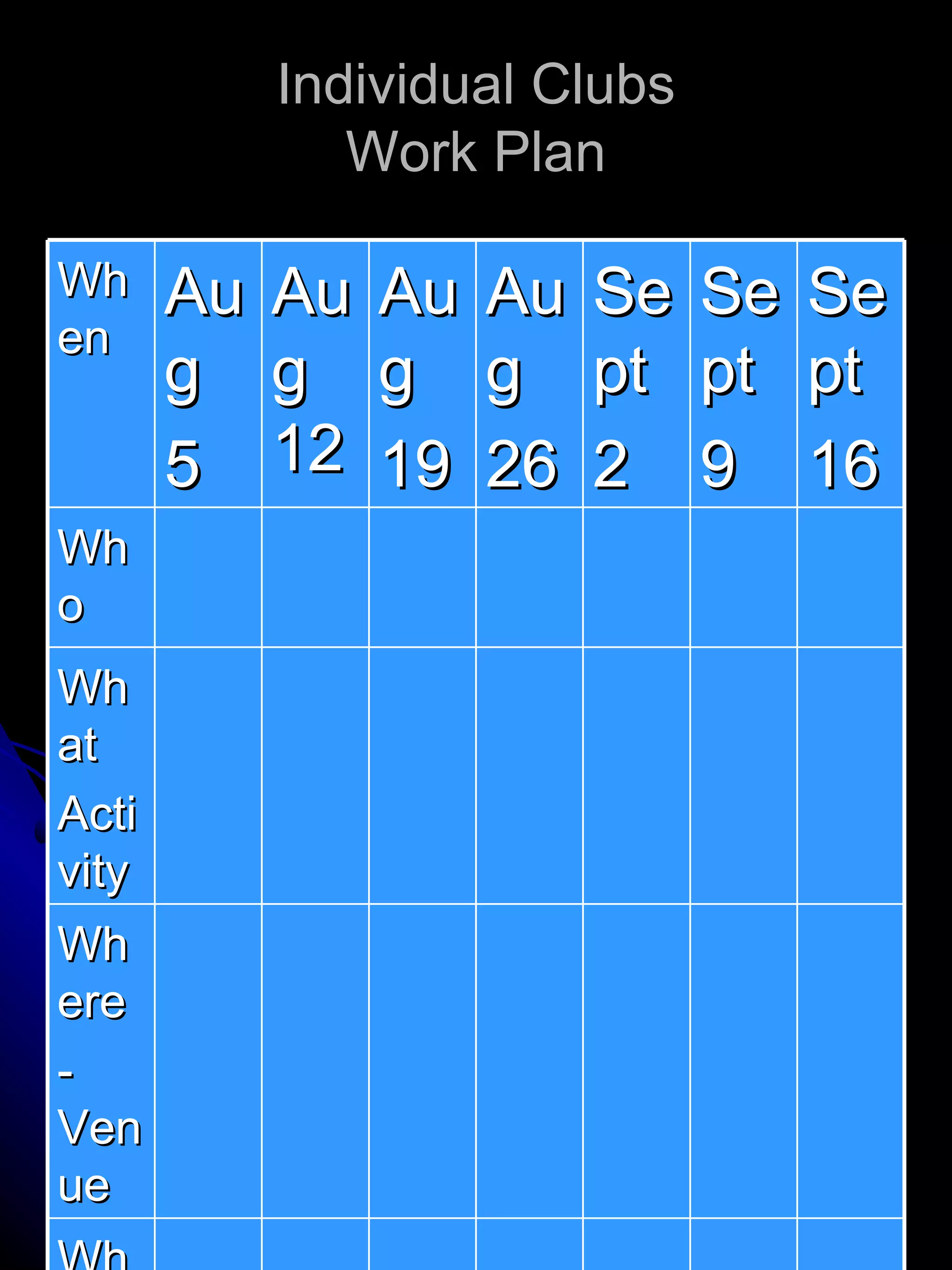
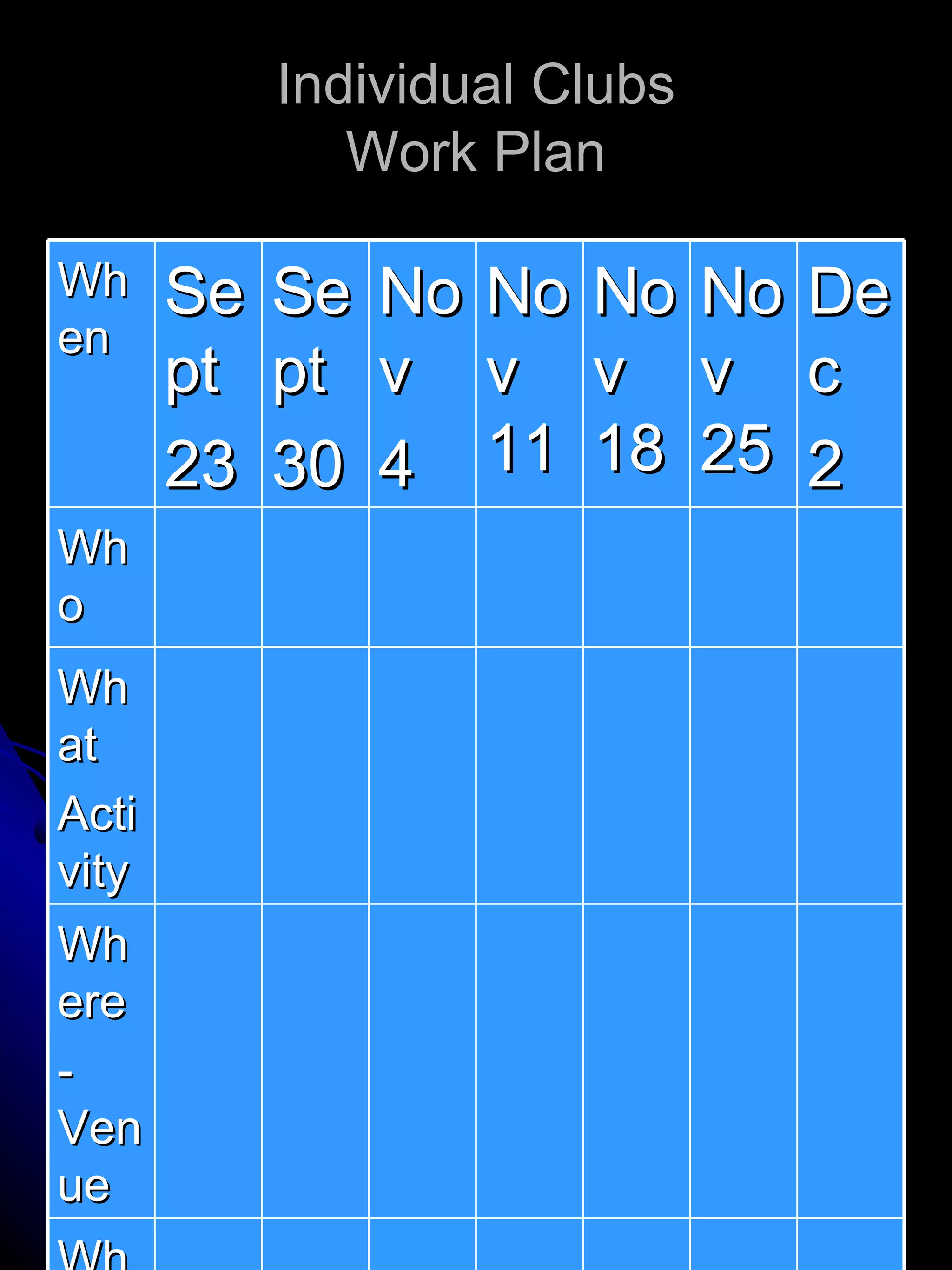
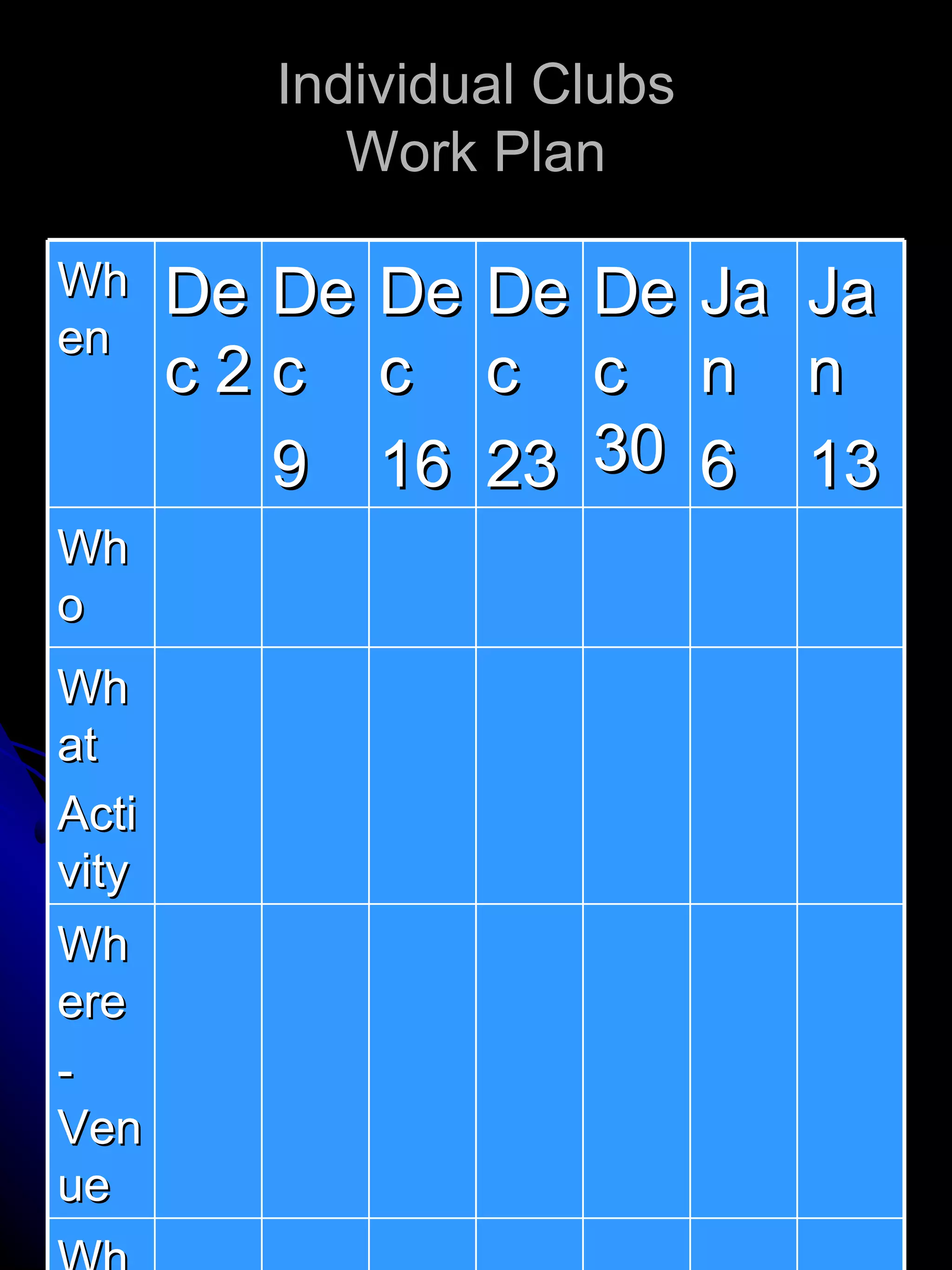
The document provides insights into the developmental stages of adolescents, focusing on their physical, psychological, and leadership characteristics from ages 0 to 20. It highlights important concerns for different age groups, addressing issues such as body image, peer identity, and vocational aspirations, alongside behavior and cognitive development. Additionally, it discusses leadership attributes, the distinction between task-oriented and relationship-oriented leaders, and methods for identifying potential leaders among adolescents.

























































![John Paul II stated “[Opus Dei] has as its aim the sanctification of one’s life, while remaining within the world at one’s place of work and profession: to live the Gospel in the world, while living immersed in the world, but in order to transform it, and to redeem it with one’s personal love for Christ.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thementorsguide-120110224315-phpapp01/75/The-Mentor-s-Guide-in-Handling-Teenage-Leaders-and-Ways-to-Handle-Bullying-by-Amb-Juan-65-2048.jpg)




![Announcement: pls. be my TV guest as the pride of your province” in : fCAT @ GNN G-Sat Asia cable tv show shown Asia pls. e-mail your Bio Data to [email_address] or add me via facebook](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thementorsguide-120110224315-phpapp01/75/The-Mentor-s-Guide-in-Handling-Teenage-Leaders-and-Ways-to-Handle-Bullying-by-Amb-Juan-70-2048.jpg)
