Low level somatic variant detection in FFPE samples by Sanger sequencing and MVF software
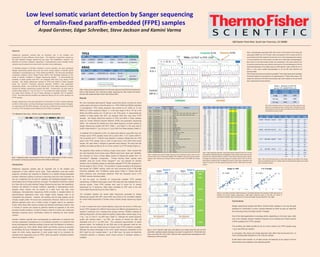
- 1. Low level somatic variant detection by Sanger sequencing of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples Arpad Gerstner, Edgar Schreiber, Steve Jackson and Kamini Varma Abstract Deleterious sequence variants play an important role in the initiation and progression of many different cancer types. The detection of germline variants by the gold standard Sanger sequencing has been well established, however, the detection of somatic mutations, especially in heterogeneous tumor samples where variants may be present at a lower level, has been more challenging. To facilitate analysis of somatic mutations in tumor samples, we have developed Sanger sequencing panels that cover the entire coding regions of specific genes implicated in tumorigenesis (e.g. TP53, KRAS and NRAS). We have also developed companion software, Minor Variant Finder (MVF), that facilitates detection of low levels of somatic mutations in Sanger sequencing studies. To demonstrate the workflow of these panels with MVF, we analyzed DNA from lung cancer FFPE samples. We initially determined variants of TP53 and KRAS in these samples using Ion Torrent™ Personal Genome Machine (PGM™) next generation sequencing (NGS). We confirmed the identity and minor allele frequency of these variants by Sanger sequencing coupled with MVF. Furthermore, we were able to confirm these results in 1 ng, 0.5 ng or 0.1 ng of DNA from these samples. Finally, we made serial dilutions of one of these samples to establish limit of detection (LOD). We show that this workflow can detect as little as 3% of a minor variant in an FFPE sample. Sanger sequencing is the gold standard for confirmation of minor variants detected by NGS. In this study, we show that Sanger sequencing of limited number of targets, in conjunction with the MVF software, can also be an ideal first line screening choice for tumor FFPE samples where limited amount of DNA is available. For Research Use only – Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Table 4. Sanger Sequencing confirmation. Variant allele frequences detected by MVF are in line with allele frequences calculated by NGS. Note: cells highlighted in yellow represent variants where the allele frequencies were significantly different in forward vs reverse Sanger sequencing reactions, however, the average of the forward and reverse allele frequency of a particular variant is still in line with the allele frequency calculated by NGS. By redesigning the primers for those regions, potentionally could improve the accuracy of the allele frequency measurments by MVF in both forward and reverse reactions. Table 5. Effect of low DNA input amount on variant allele frequency across different FFPE samples. Variants are still detectable even at 0.1 ng DNA, however the allele frequencies might be more variable below 1 ng of DNA per reaction. Figure 4. Correlation between allele frequences. Correlation between the average of allele frequences of forward and reverse Sanger sequencing vs NGS allele frequences (plot on the left) are similar to correlations between that of forward (F) vs reverse (R) Sanger sequencing (plot on the right). LOD ~3% Table 2. Effect of low DNA input amount at 1 ng, 0.5 ng and 0.1 ng on KRAS c. 182A/G minor variant detection. Note: recommended input amount is 1 ng/reaction. Below 1 ng DNA/reaction, the overall sequencing quality and the allele ratios might be more variable but the minor variant of interest could still be detected even at as low as 0.1 ng DNA. Figure 3. Limit of Detection (LOD) study. Serial dilutions were created mixing FFPE 2162 and CEPH control DNA. 1 ng DNA per reaction containing a minor variant T at position Chr17: 7,579,619 with minor variant ratio at 50%, 25%, 12.5%, 6.25%, 3.125% and 1.56%, respectively were tested against the 100 % G allele found in CEPH control DNA. Figure 1. Single-gene Sanger sequencing panel of TP53. The entire coding sequence of TP53 is covered by 24 amplicons. Similar gene-specific panels were built for KRAS and NRAS genes. Introduction Deleterious sequence variants play an important role in the initiation and progression of many different cancer types. These alterations could also predict prognosis, sensitivity and response to treatment or to specific therapy-associated toxicities. Molecular profiling of cancers is becoming more and more important not only as a diagnostic tool but also for selecting and developing targeted drugs in personalized cancer therapy (precision oncology). The detection of germline variants at a fixed ratio by the gold standard Sanger Sequencing has been well established, however, the detection of somatic mutations, especially in heterogeneous tumor samples where variants may be present at a lower level, has been more challenging. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) provides a valuable method for high-throughput applications when many targets and/or samples need to be multiplexed and screened. However, the workflow and the data analysis can be complex, lengthy (often >40 hours) and cumbersome. Moreover, NGS is not a cost- effective approach when only a limited number of targets need to be screened. Finally, NGS results often require a reliable and sensitive confirmatory method. Only a minority of cancers are caused by germline variants as opposed to the more prevalent somatic mutations, so there is clearly a need for a robust, fast, simple and affordable screening and/or confirmatory method for detecting low level somatic variants. Somatic mutations typically drive carcinogenesis by deactivation of protein(s) that normally suppresses tumorigenesis or by constitutive activation of a protein(s) that drives carcinogenesis. Molecular profiling of cancer cells, the detection of variants in specific genes (e.g. TP53, KRAS, NRAS, BRAF and EGFR) could be as important as identifying the tumor histological type. Depending on the tumor type, in certain cases the entire coding sequences of some genes need to be screened (for example tumor suppressors such as TP53), while only specific nucleotide positions need to be analyzed in others. Results We have developed gene-specific Sanger sequencing panels covering the entire coding regions (all exons) of specific genes (i.e.; TP53, KRAS and NRAS) implicated in tumorigenesis. TP53 coding sequence was covered by 24, KRAS by 12 and NRAS by 9 short amplicons (Figure 1.), in the size range of 50 to 151 bp in the KRAS and NRAS panels and 115-200 bp in the TP53 panel. To demonstrate the workflow of these panels with MVF, we analyzed DNA from lung tumor FFPE samples. We initially determined variants of TP53 and KRAS in these samples using Ion Torrent Personal Genome Machine (PGM) next generation sequencing (NGS). We confirmed the identity and minor allele frequency of these variants by Sanger Sequencing coupled with MVF (Table 1. and Figure 2.) We were able to confirm these results in 1 ng, 0.5 ng or 0.1 ng of DNA from these samples (Table 2.). To establish limit of detection (LOD), we made serial dilutions using DNA from one of these cancer FFPE samples mixed with a control DNA. A G/T variant (48/51%: F/R) at position Chr17: 7,579,619 was detected in amplicon 480354 from the TP53 panel in the FFPE sample 2162 vs 100% G base found in the CEPH DNA control sample. We used these 2 samples to generate serial dilutions. We show that this workflow can detect as little as 3% of a minor variant in an FFPE sample (Figure 3.). We expanded these results by building a larger cancer panel. Allelic variants that are most frequently found across many different solid tumor types were identified. We narrowed our focus to those alleles present at frequencies greater than 1% (Oncomine™ database, Compendia). Primers flanking these variants were identified using the on-line Primer Designer™ tool, and selected for shortest amplicon size to facilitate analysis of potentially degraded FFPE DNA (amplicons in the size range of 126 to 179 bp). This resulted in a panel consisting of 26 amplicons that queries 66 COSMIC variants, which are most commonly found (>1%) in the Oncomine database, from 18 different cancer genes (Table 3.). Please note that these amplicons also encompass additional 1906 less frequently found (<1%) COSMIC variants (including indels). To test the panel, we identified 34 commercially available FFPE samples representing 12 different tissue types where NGS data were also available from our previous studies. These FFPE samples were used to screen for 14 variants represented by 10 amplicons. Allele ratios calculated by MVF were in line with variant allele frequencies found by NGS (Table 4.). The correlation between the variant allele frequencies generated by Sanger Sequencing coupled with MVF versus NGS was similar to the correlation between the variant allele frequencies of forward versus reverse Sanger sequencing (Figure 4.). In order to explore the minor variant detection using very low amount of DNA input across FFPE samples from different tissue types and different genes/amplicons, we selected 3 amplicons and 4 samples that covered common COSMIC mutations at differing frequencies. We then tested the ability to detect allelic variants using 10 ng, 3 ng, 1 ng, 0.3 and 0.1 ng DNA input (Table 5.). Although the overall sequence quality was reduced below 1 ng DNA, the variants of interest are often still detectable even at 0.1 ng DNA level. This represents approximately 15 diploid genome copies. The sensitivity for low DNA input of this approach could be very helpful when only very limited amount of biopsy and/or FFPE material is available. Although the actual percentage of the minor variant frequency interpreted by the MVF might be more variable below 1 ng of DNA input, the panel will determine mutational positivity in situations where minute amount of template material is available. Conclusions Sanger sequencing coupled with Minor Variant Finder software is not only the gold standard for confirmation of minor variants detected by NGS but also an ideal first line screening choice at limited number of targets. One of the ideal applications is oncology where, depending on the tumor type, often only a few clinically relevant mutations required to be screened and limited amount of DNA available from FFPE samples. This workflow can detect as little as 3% of a minor variant in an FFPE sample using 1 ng or less DNA per reaction. In conclusion, this robust and simple approach also offers fast turnaround time (~4 hours including data analysis) at a low cost per sample. © 2016 Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. All rights reserved. All trademarks are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific and its subsidiaries unless otherwise specified. Table 1. Minor variants originally detected in the Colon And Lung Cancer Panel (CLCP) and the Oncomine Panel by PGM Sequencer were confirmed by Sanger sequencing from both Forward and Reverse directions (F/R) coupled with Minor Variant Finder software (MVF). 180 Oyster Point Blvd. South San Francisco, CA 94080 Table 3. Extended cancer panel for Sanger sequencing. Panel containing 66 variants, which are most commonly found (>1%) in the Oncomine database, from 18 different cancer genes was built using 26 amplicons. Note: amplicons also encompass 1906 less frequently found (<1%) COSMIC IDs (including indels). Figure 2. Electrophoregrams generated by MVF. Minor variant c.517G/T detected in FFPE sample 2182 using amplicon 836916 from the TP53 panel. Variant was detected at 8.2% in forward and 8.4% in reverse direction by the MVF compared to the main base C (or G in the corresponding reverse reaction). C (or G) was detected in the control sample at the allelic ratio of 100% (bottom electrophoregrams). Minor variant A in the forward reaction (similarly, the corresponding T in the reverse reaction) of the Test specimen would have been easily missed by visual inspection of the electropherograms of the test sample (electrophoregrams in the middle), however, the MVF algorithm is able to identify the A (or T) allele as a minor variant candidate (electrophoregrams on the top after Noise Subtraction and Submission (NSS)). PCR and sequencing reactions were performed using BigDye™ Direct Sanger Sequencing Kit with BigDye XTerminator Purification Kit and separated on the Applied Biosystems™ 3500xL Genetic Analyzer. FFPE samples were referenced to CEPH DNA control processed under similar conditions on the same 96-well plate, in both forward and reverse directions.
