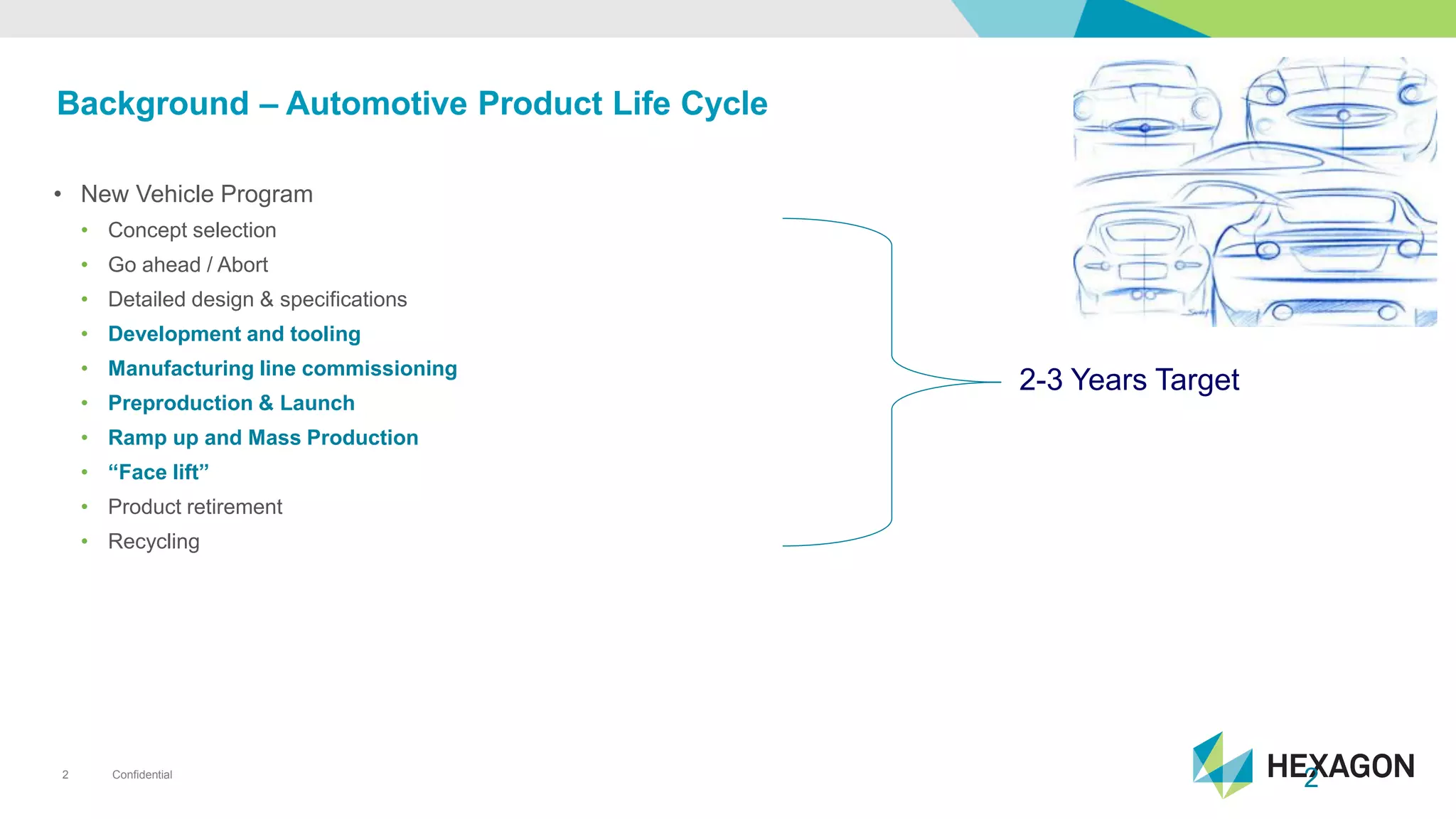
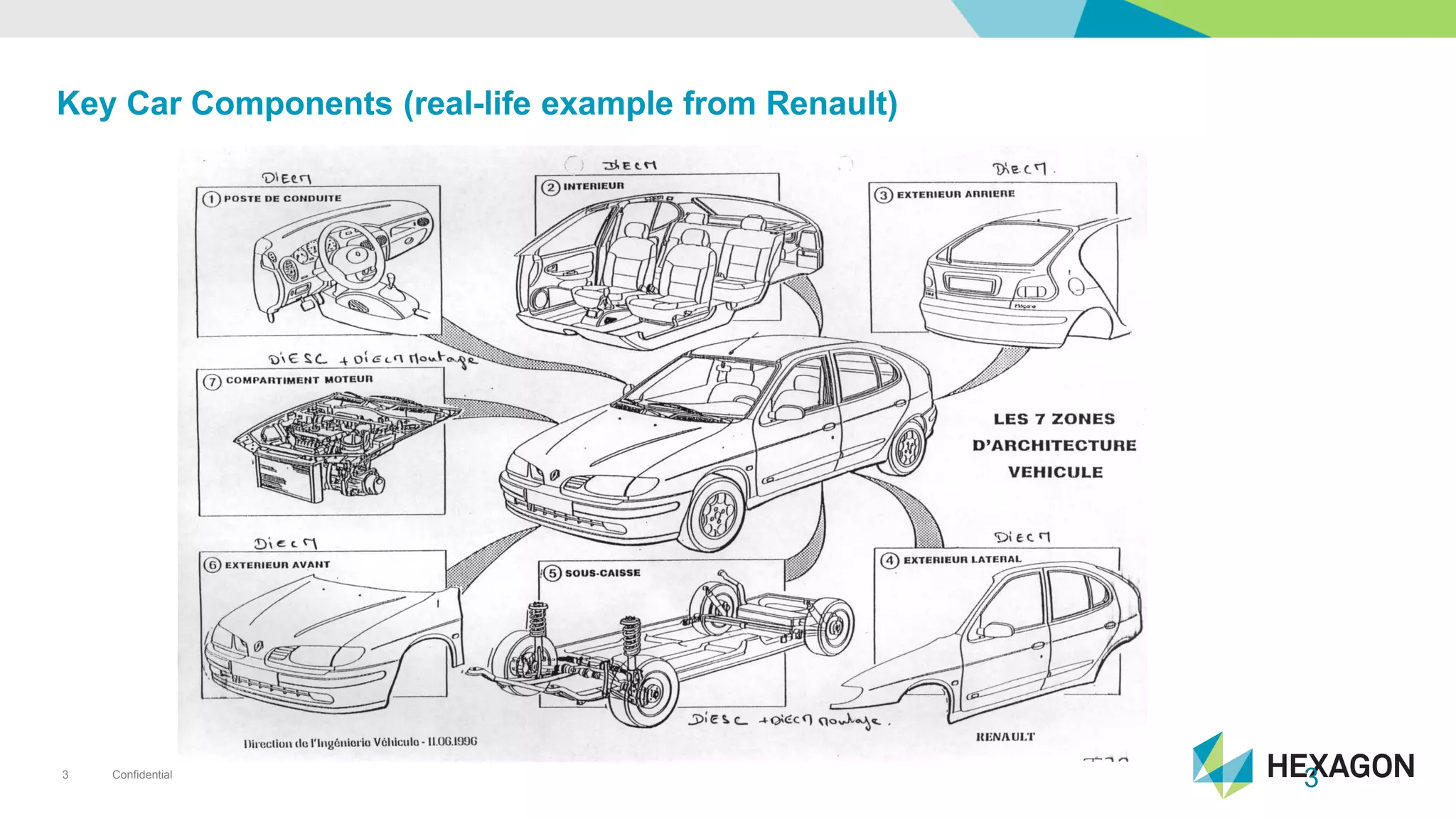
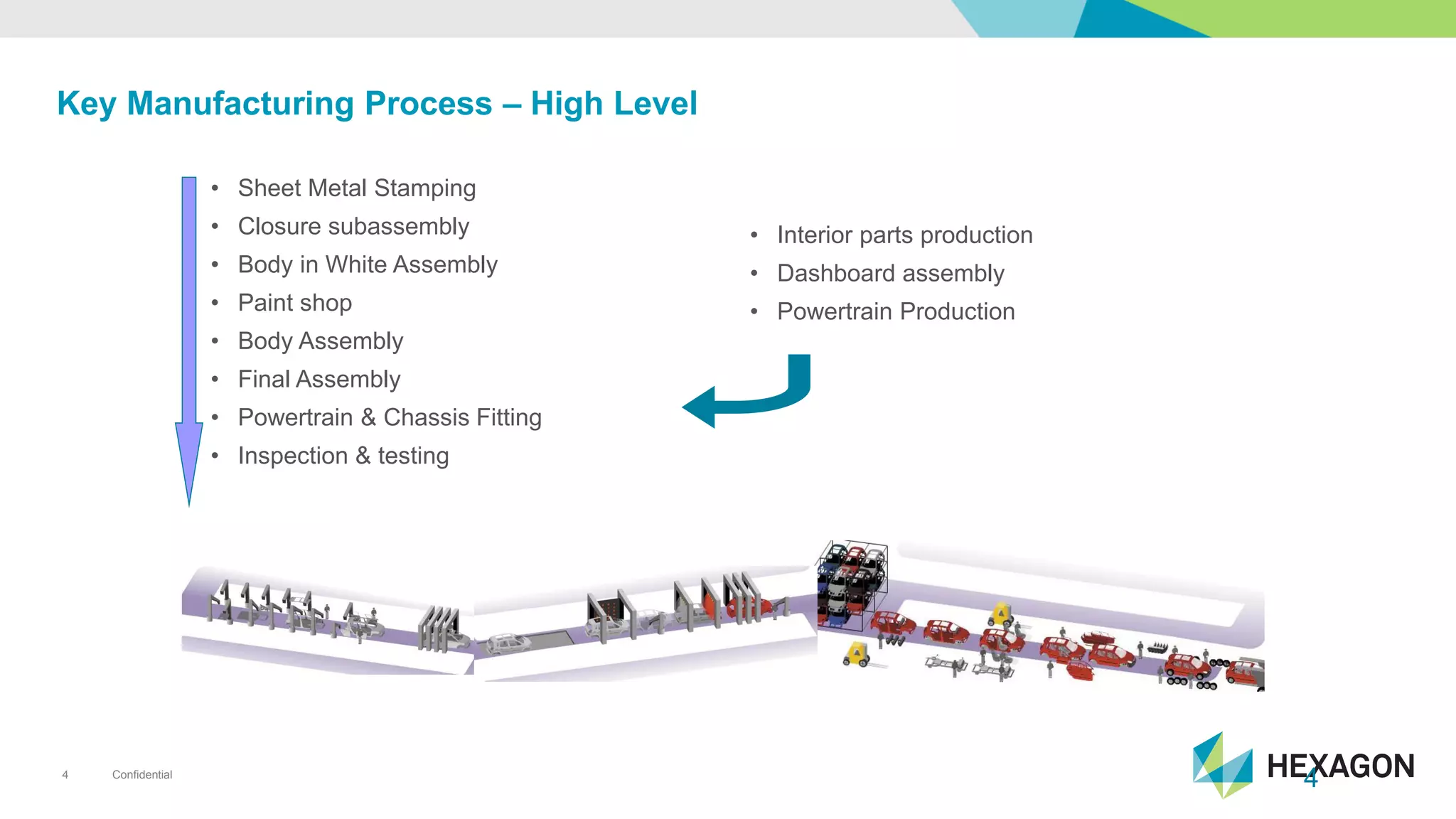
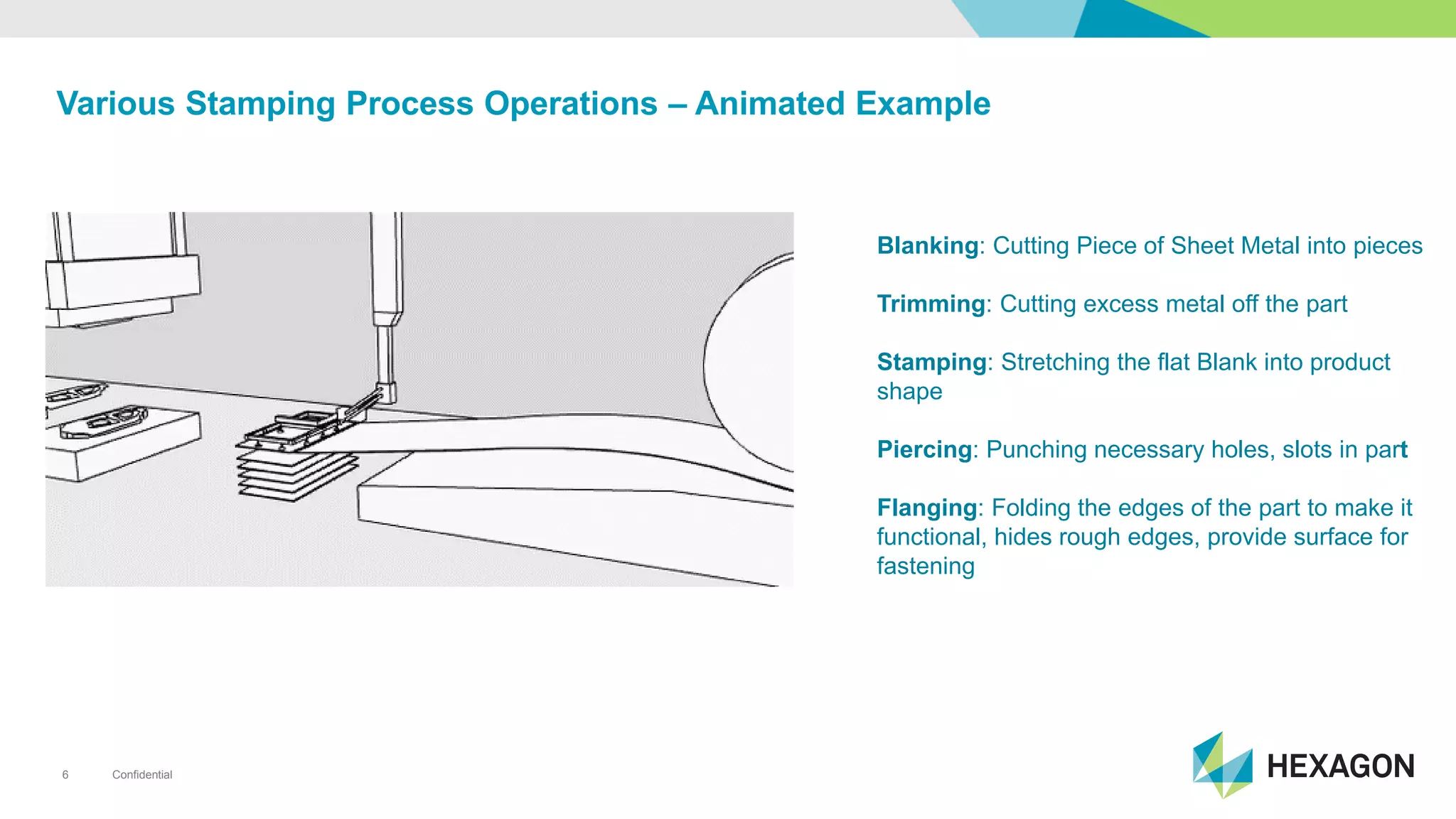
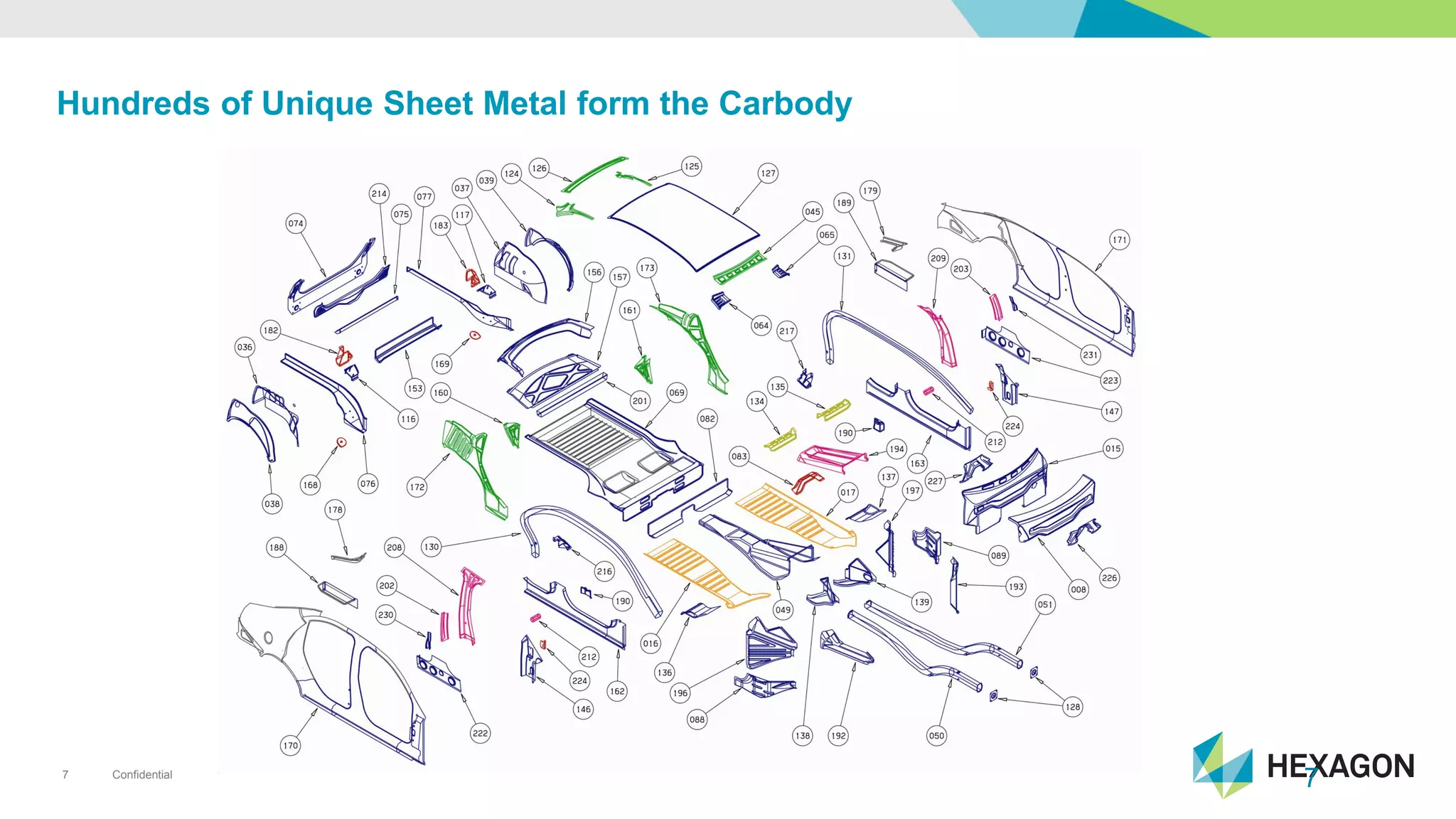
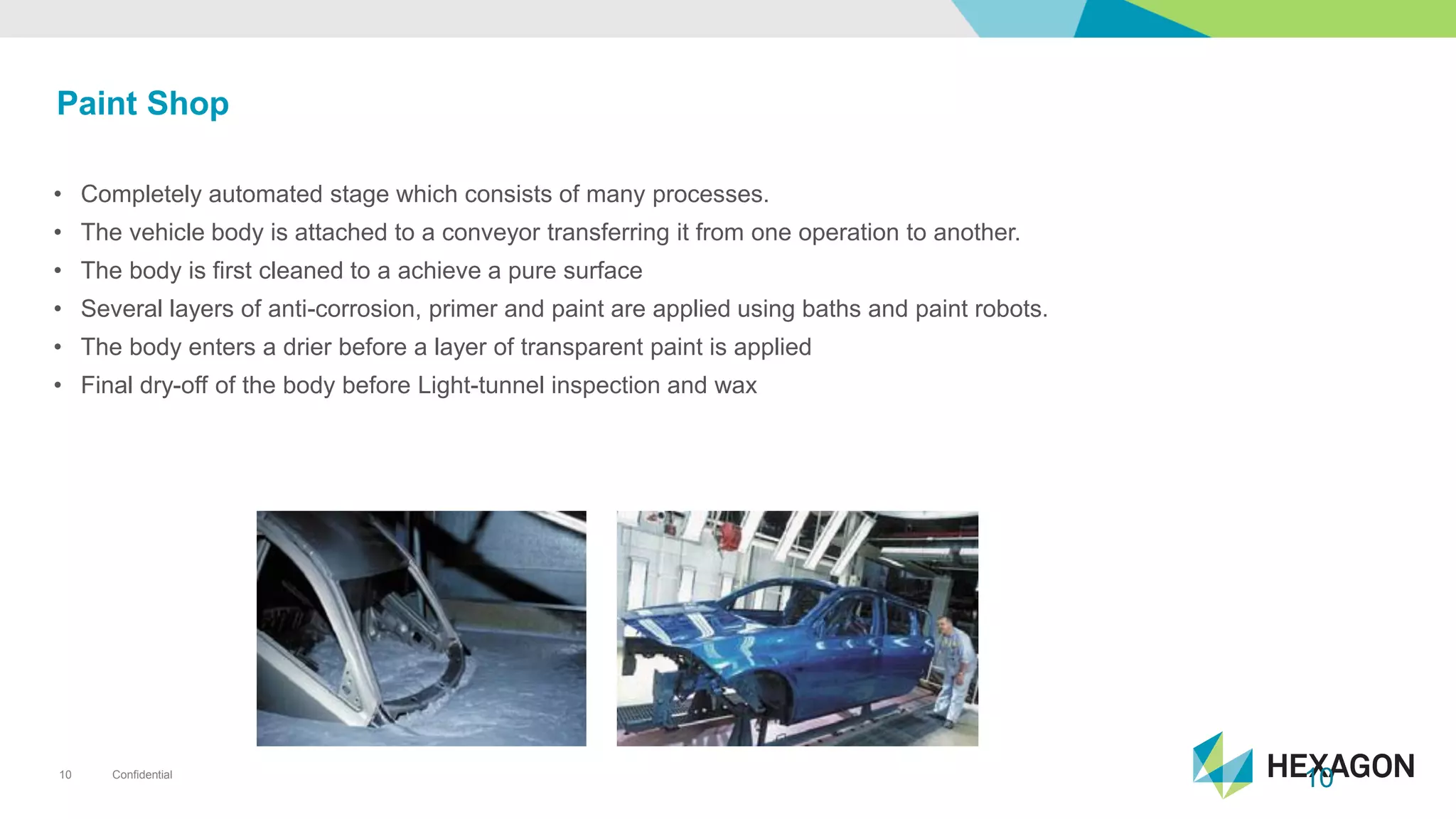
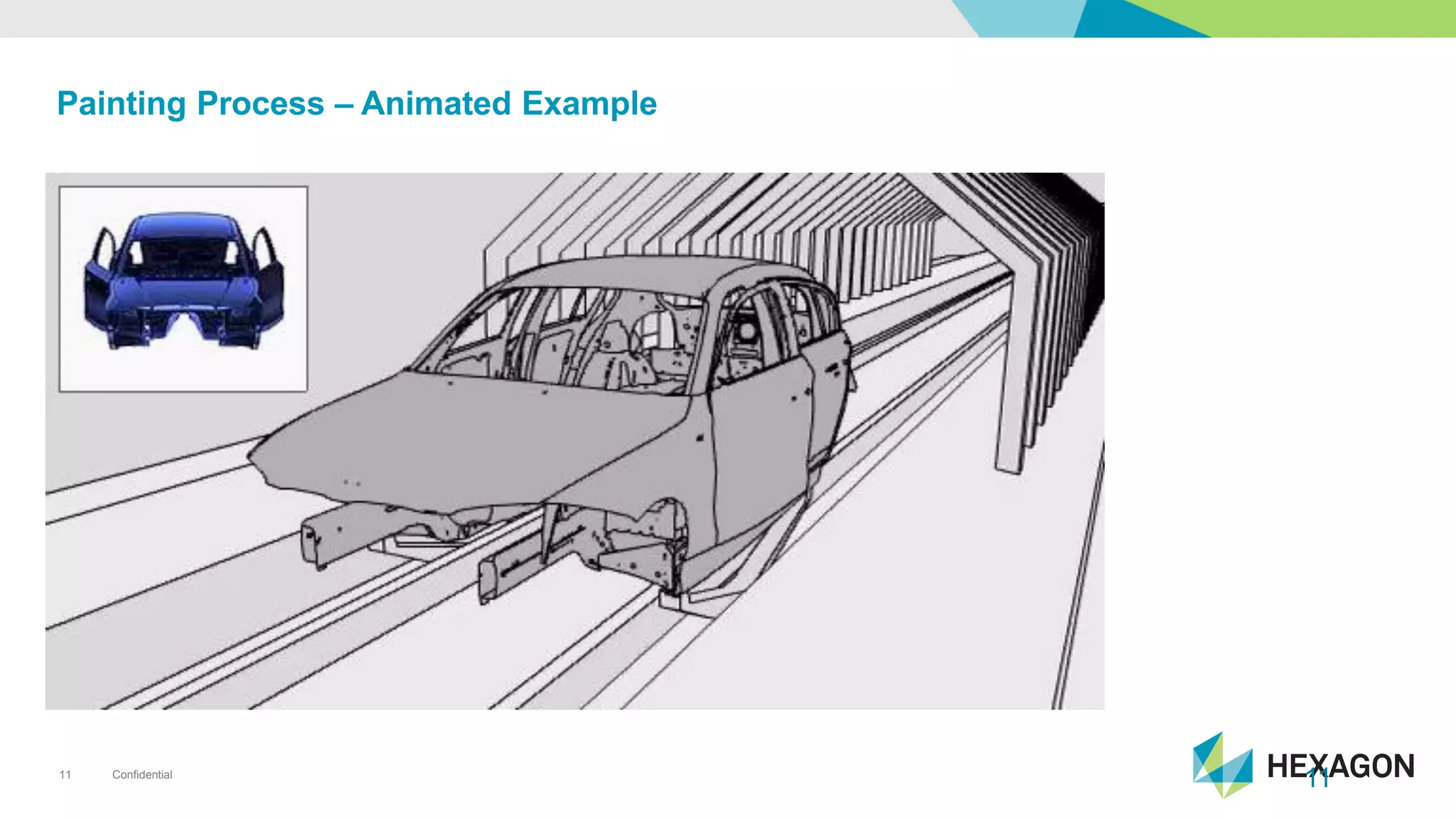
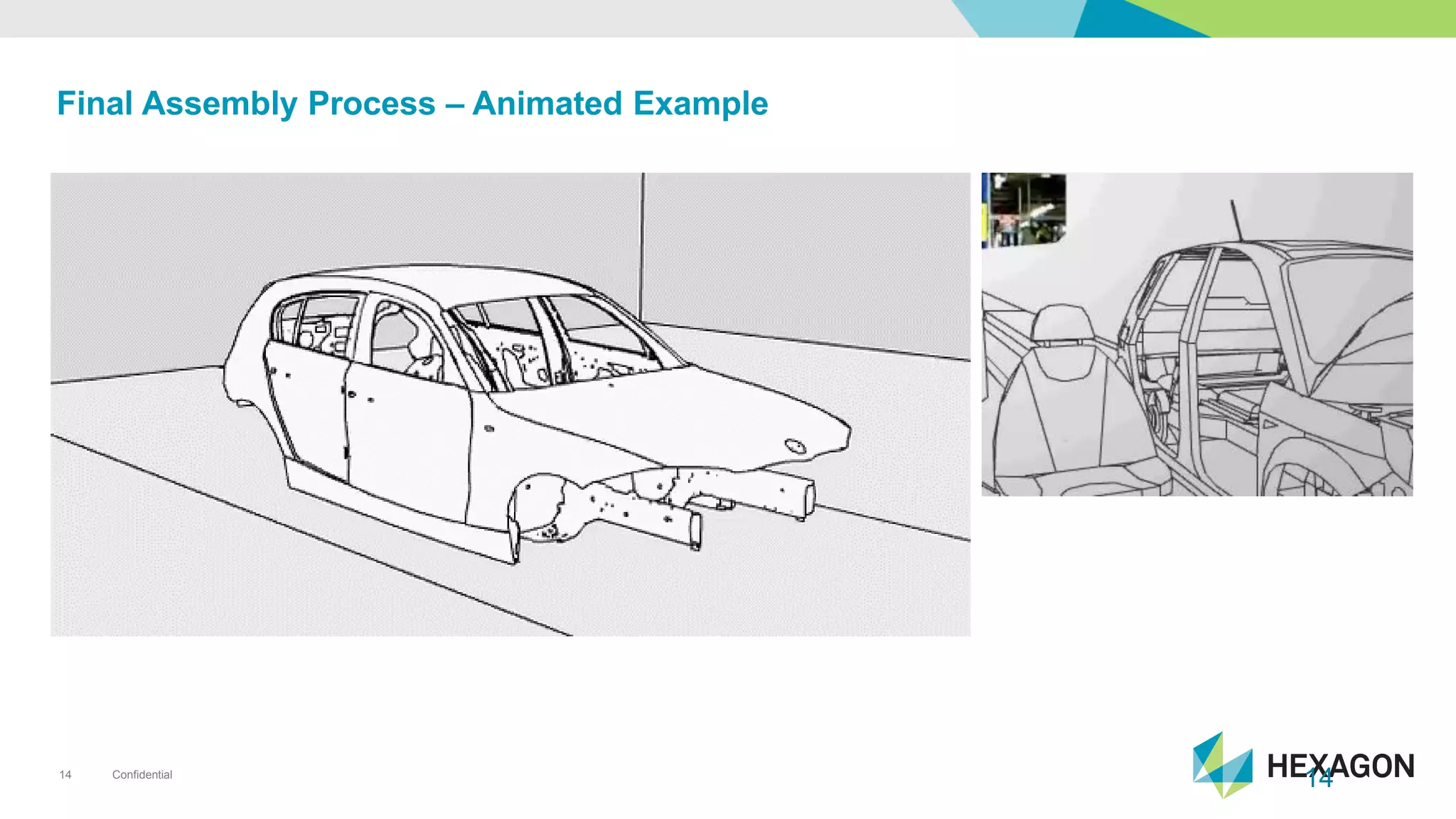
The document provides an overview of automotive manufacturing processes, detailing the automotive product life cycle from concept selection to recycling. It outlines key components of car manufacturing, including stamping, assembly, painting, and powertrain fitting, along with the challenges of maintaining quality and dimensional stability during production. The importance of inline dimensional control and automated quality solutions is emphasized for successful model launches.