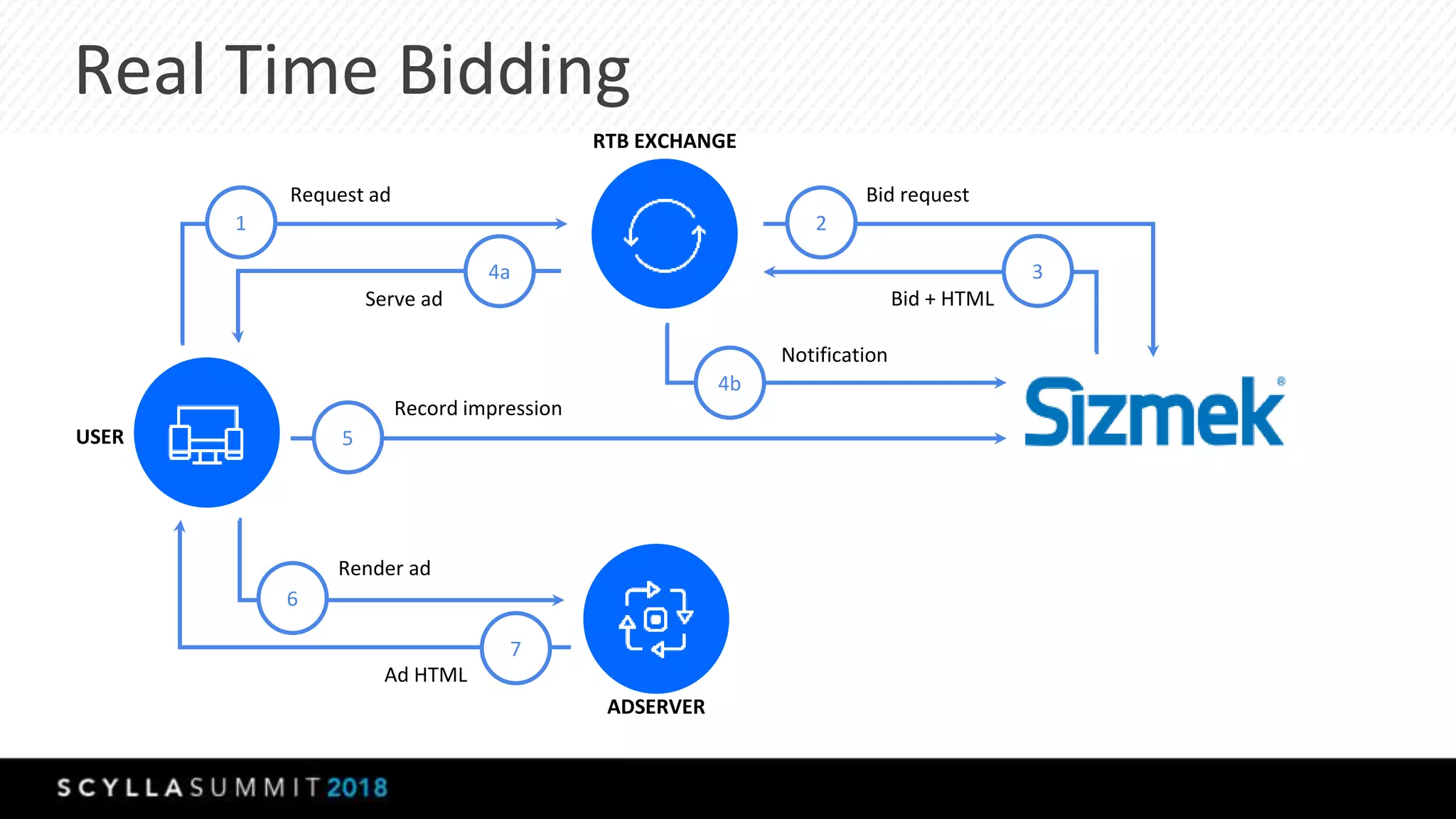
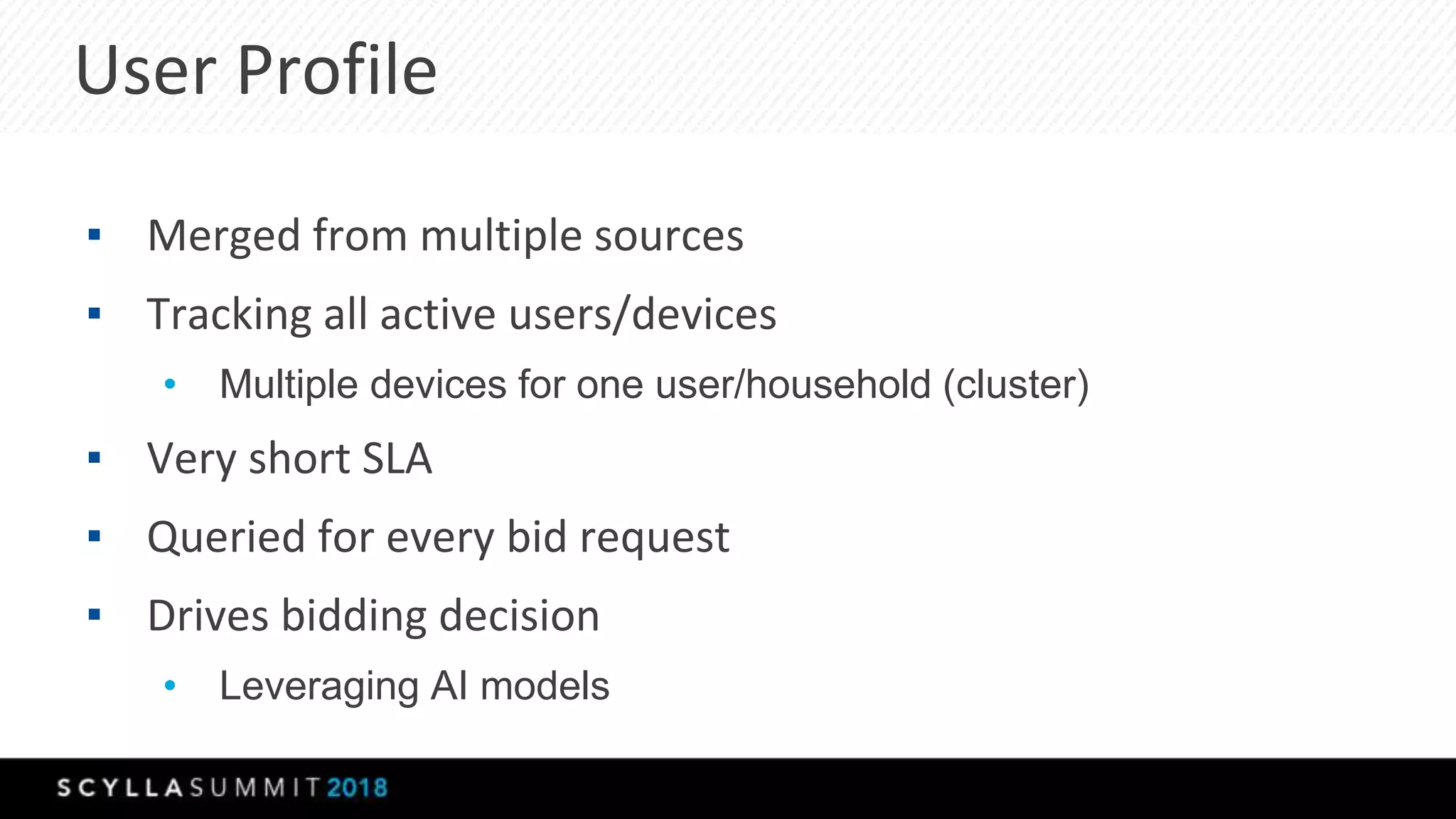
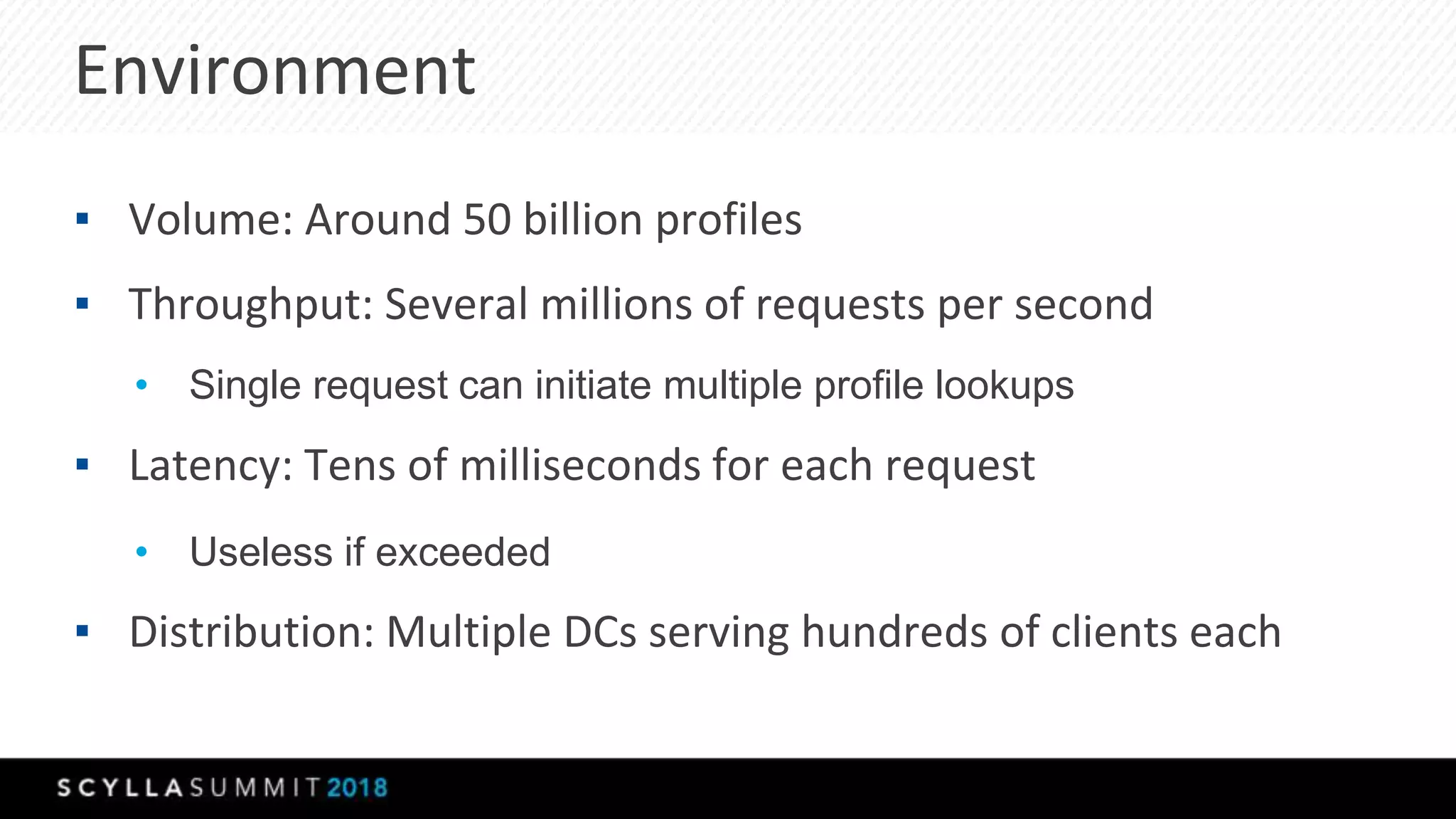
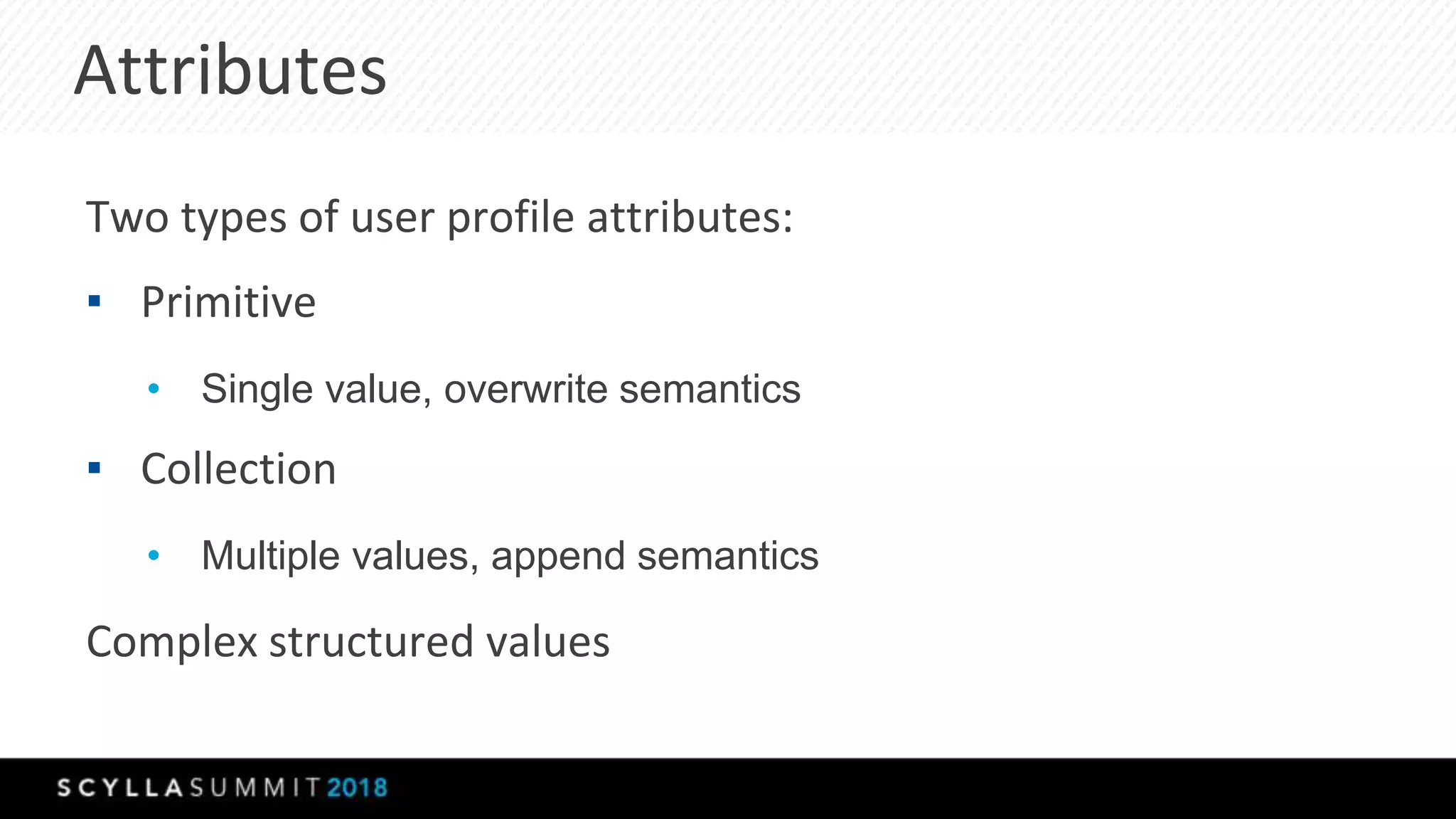
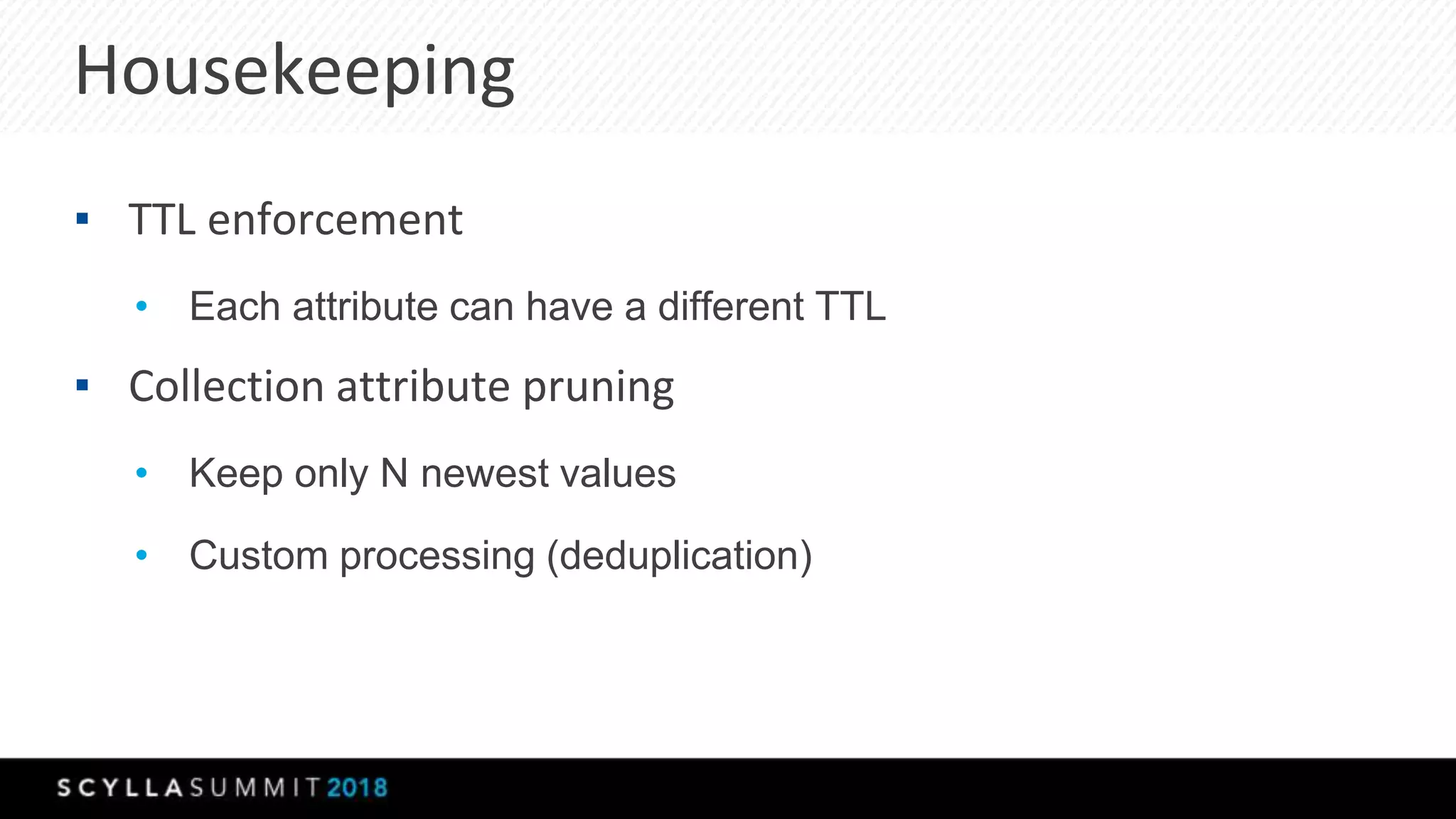
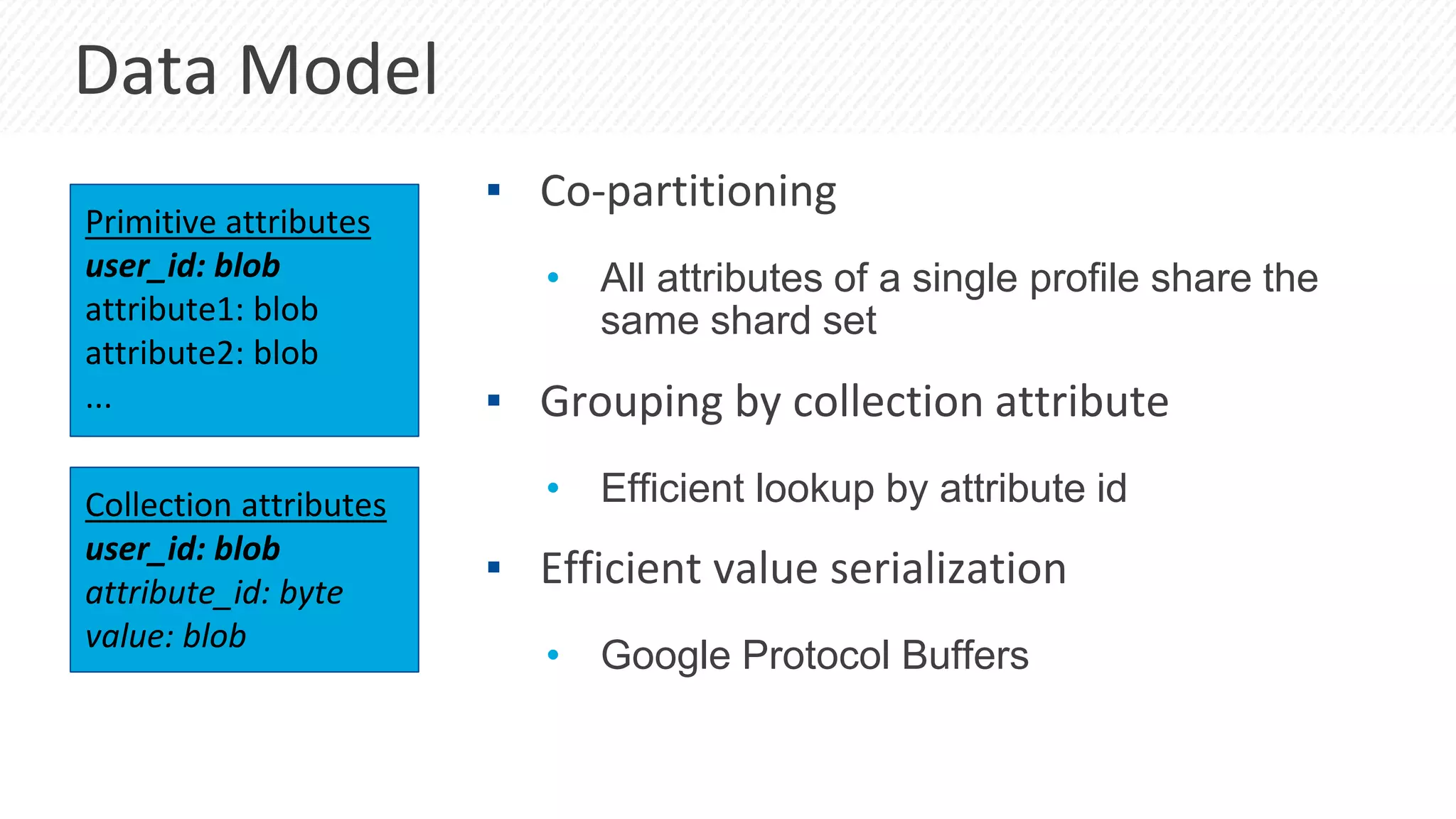
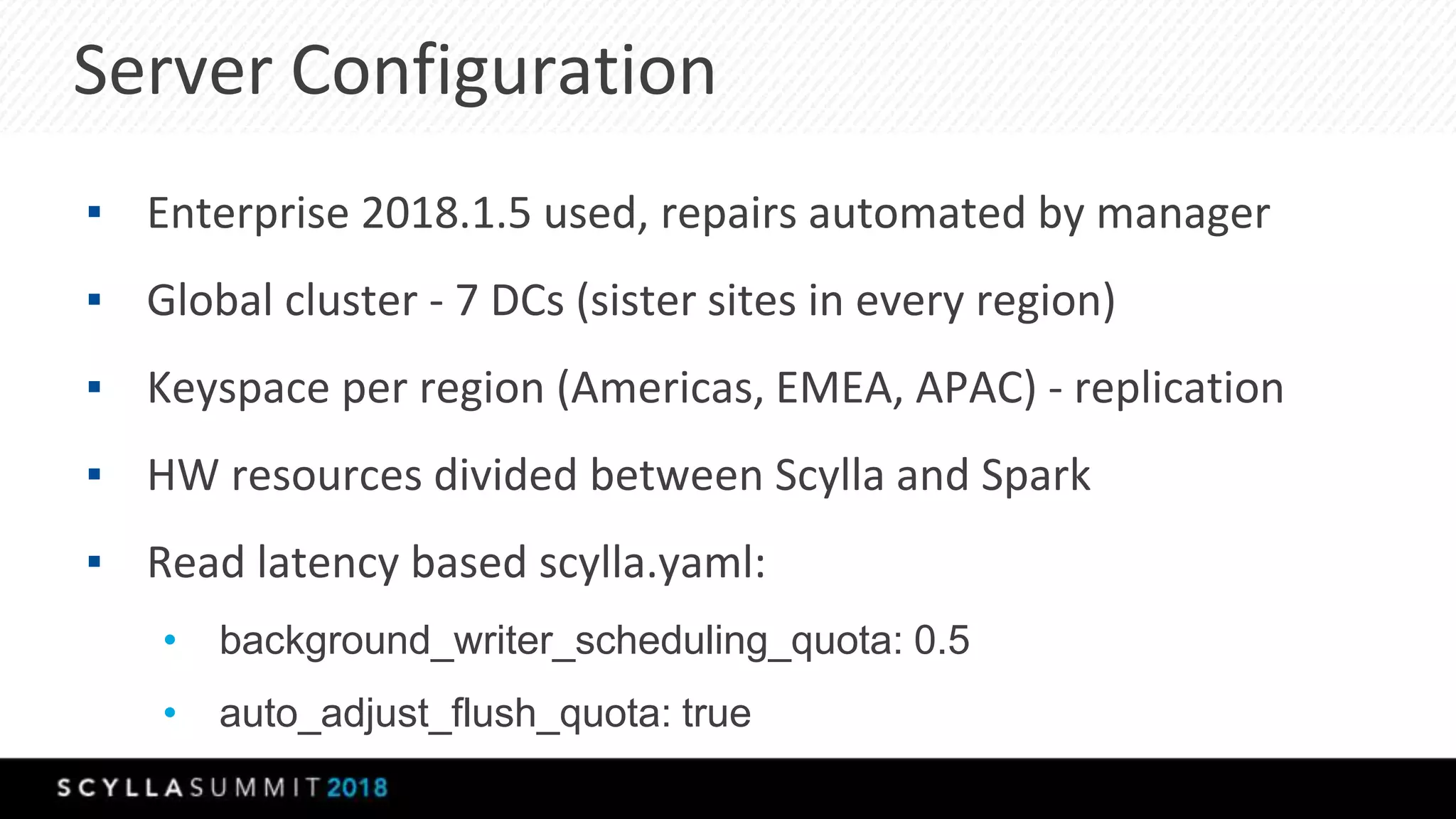
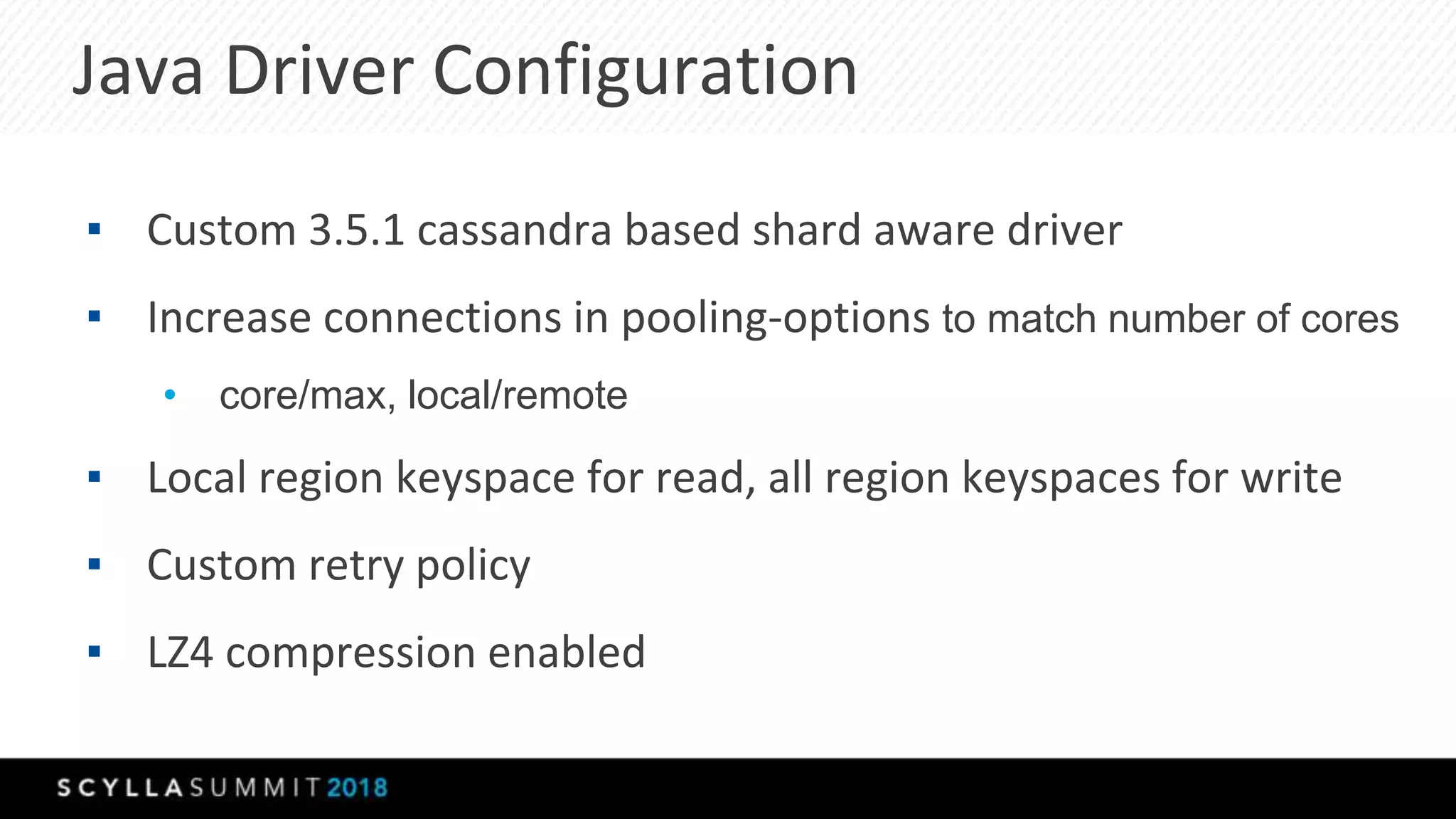
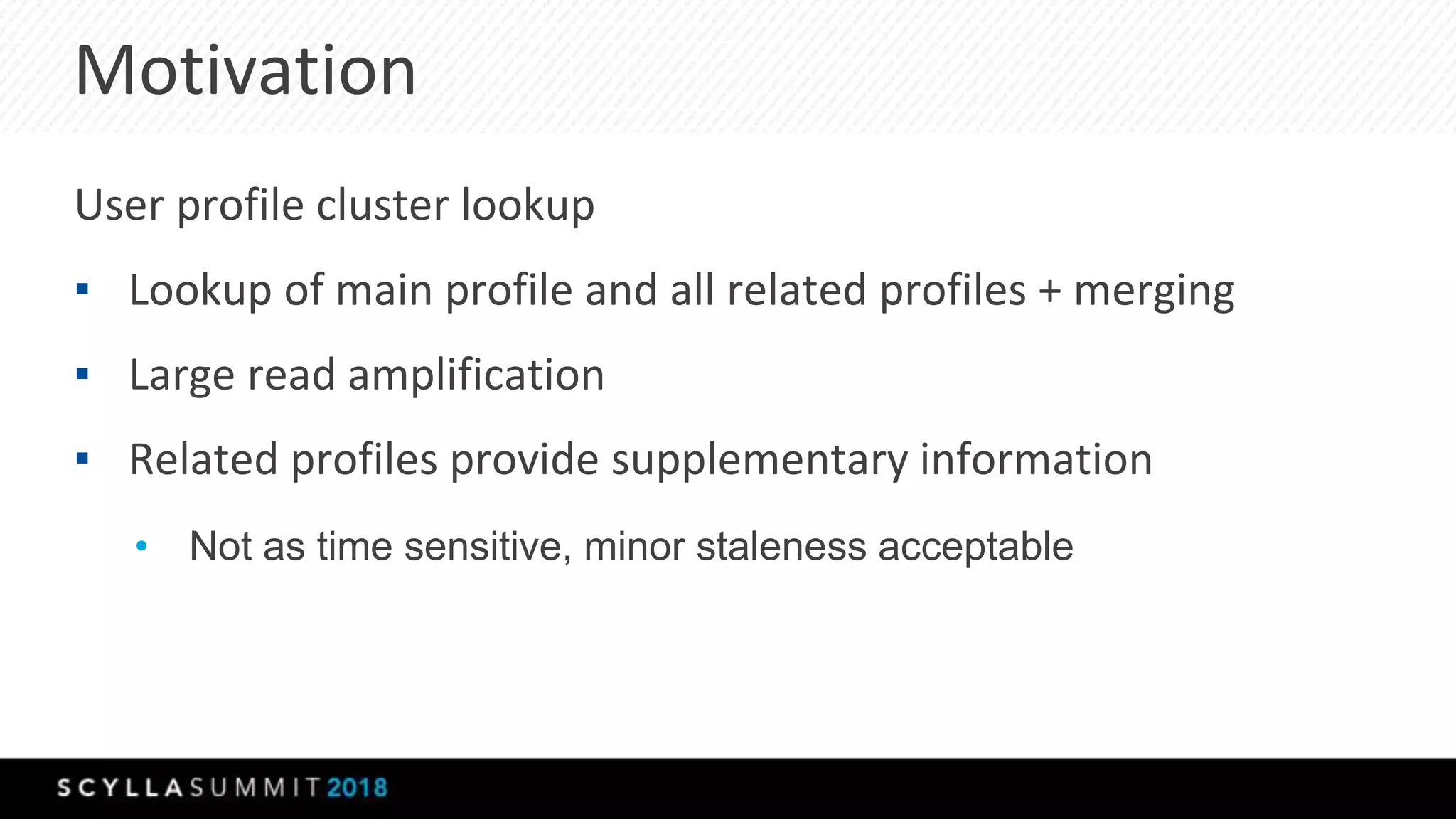
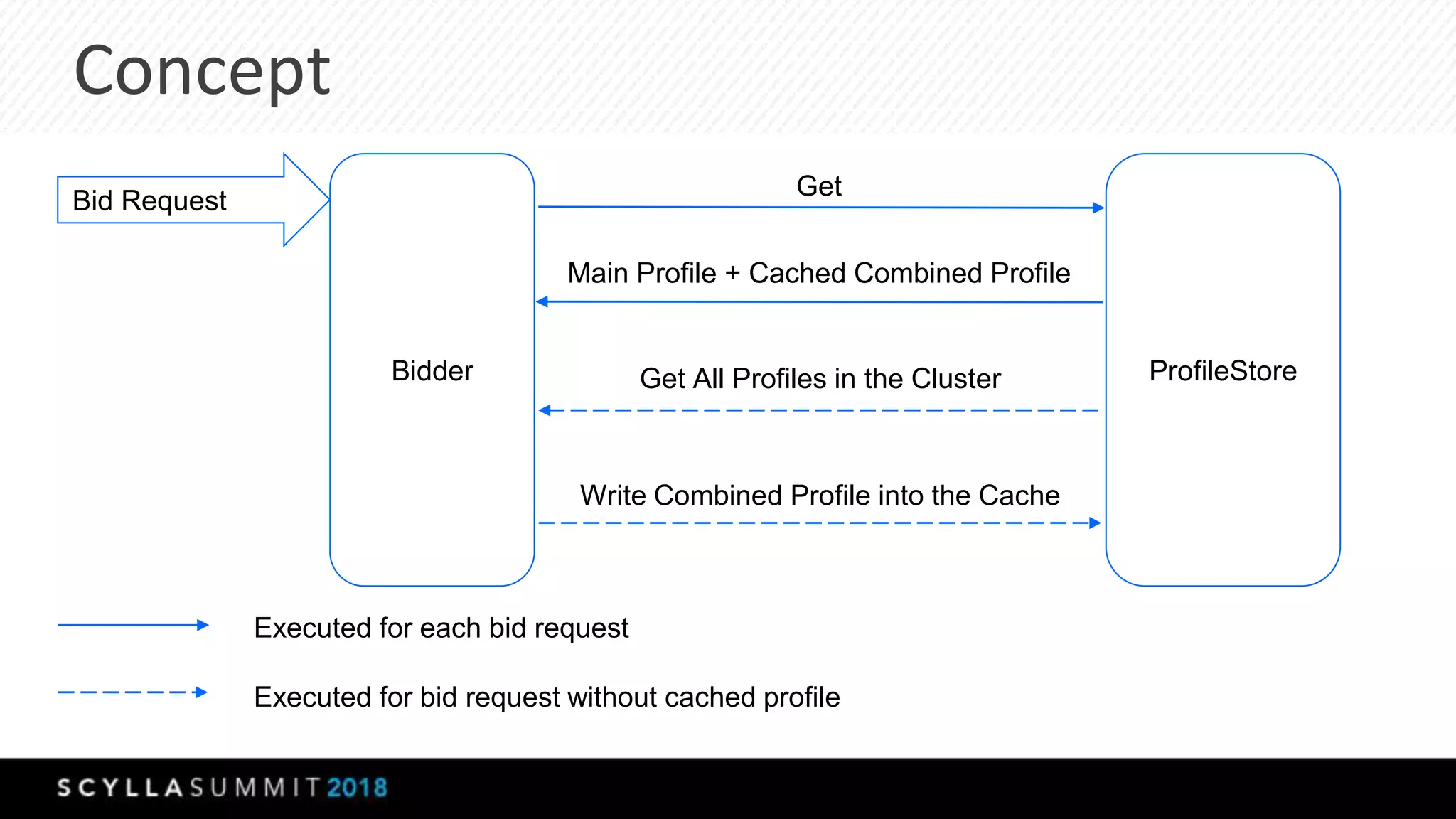
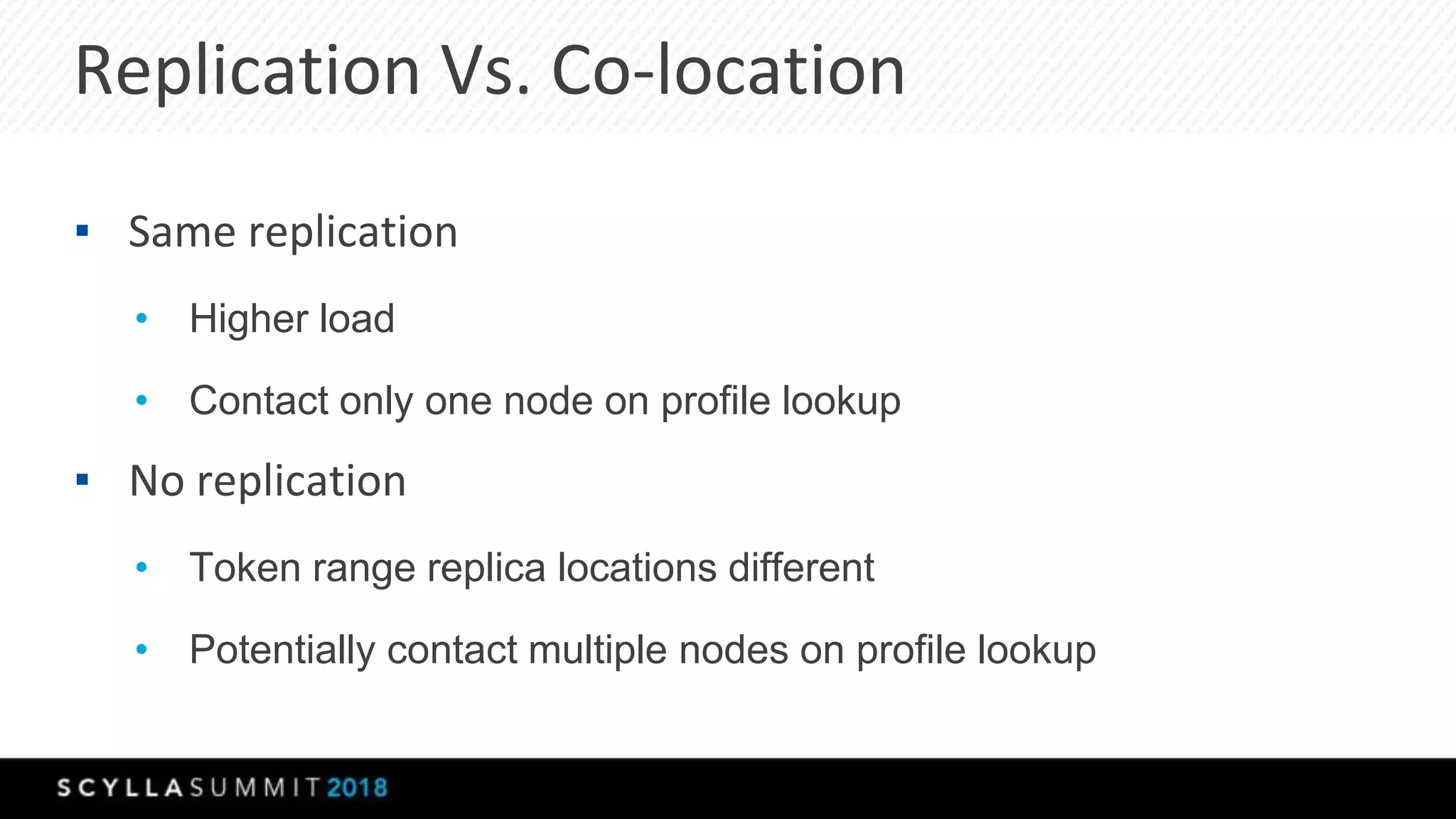
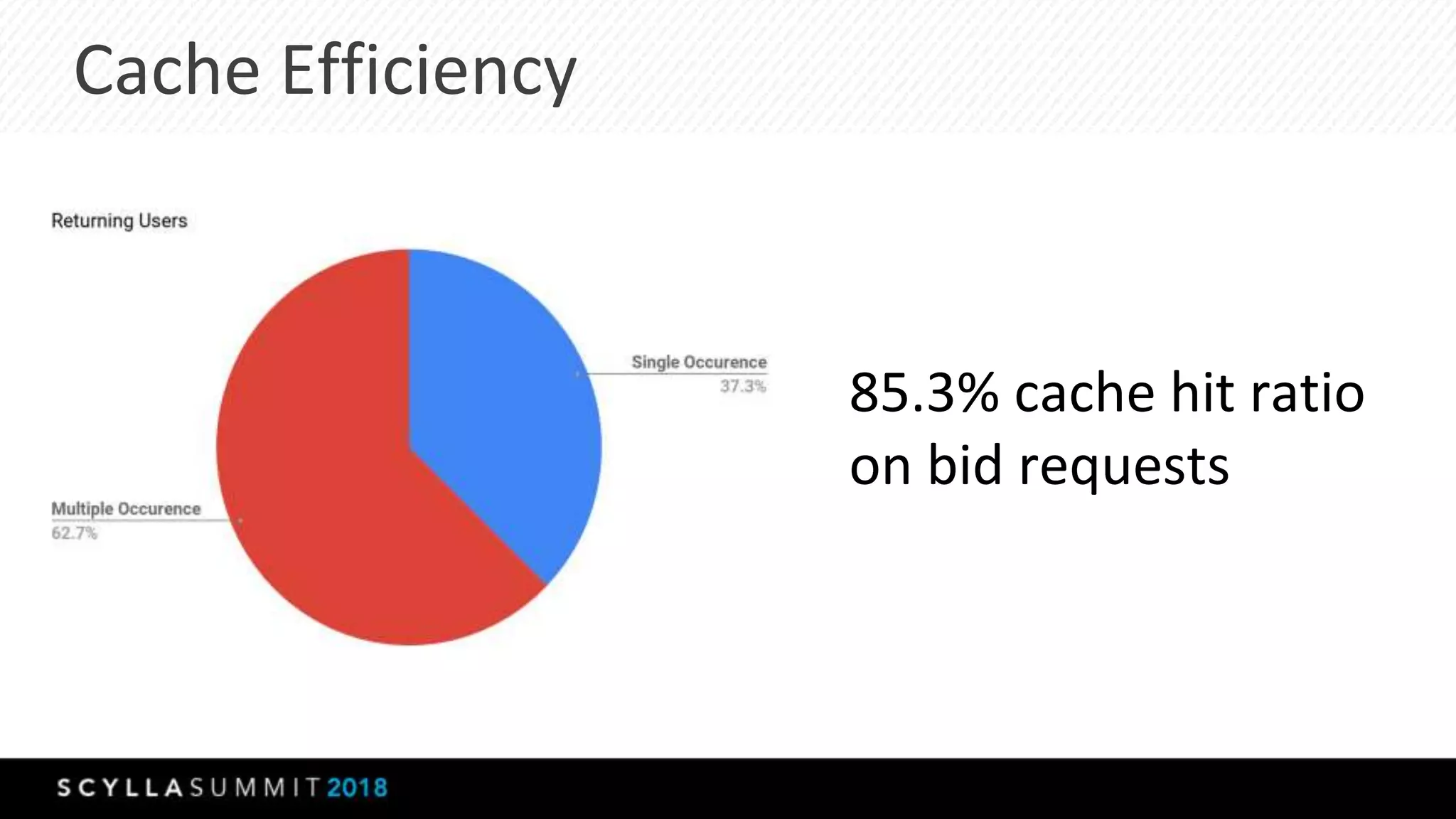
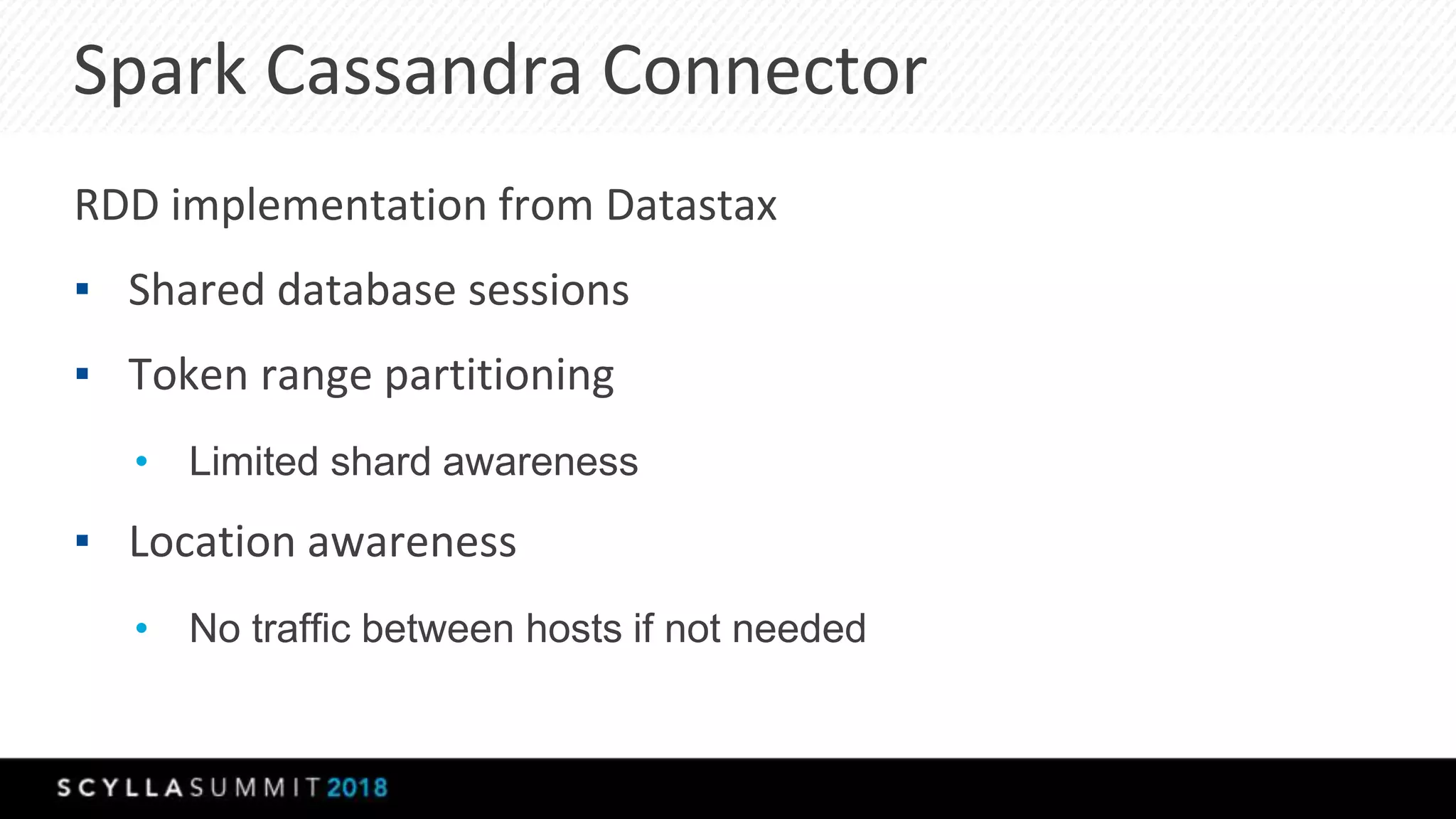
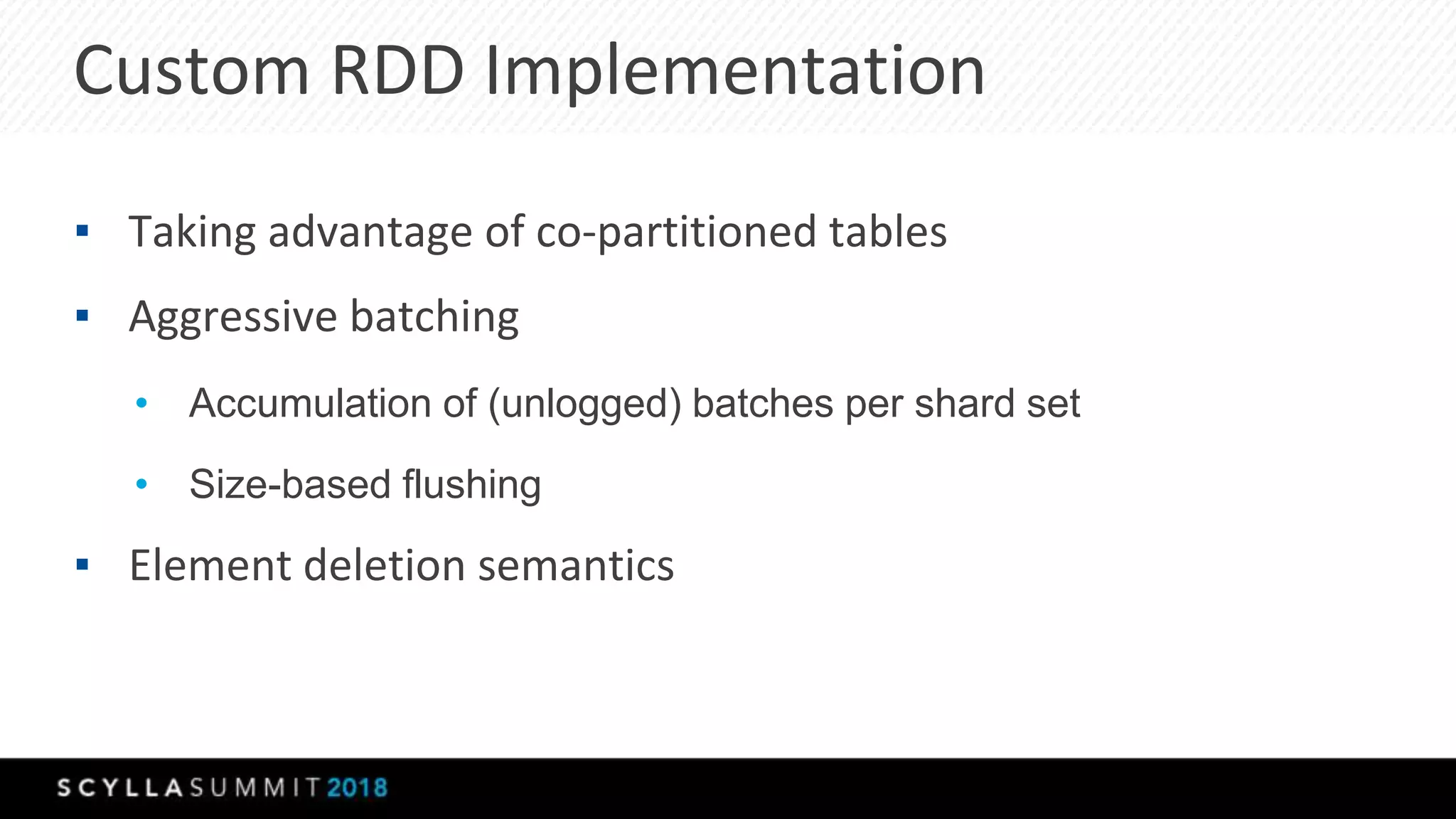
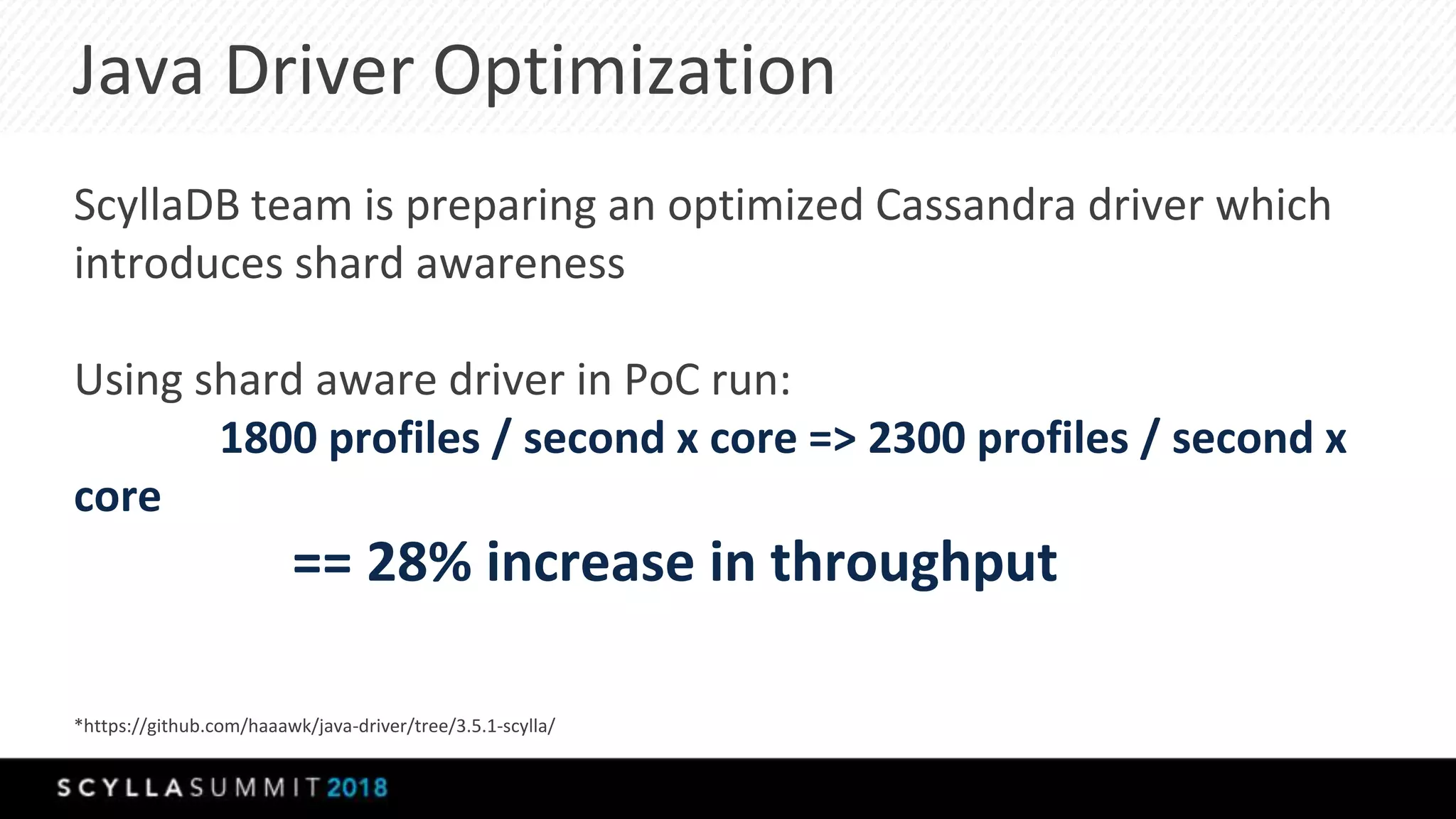
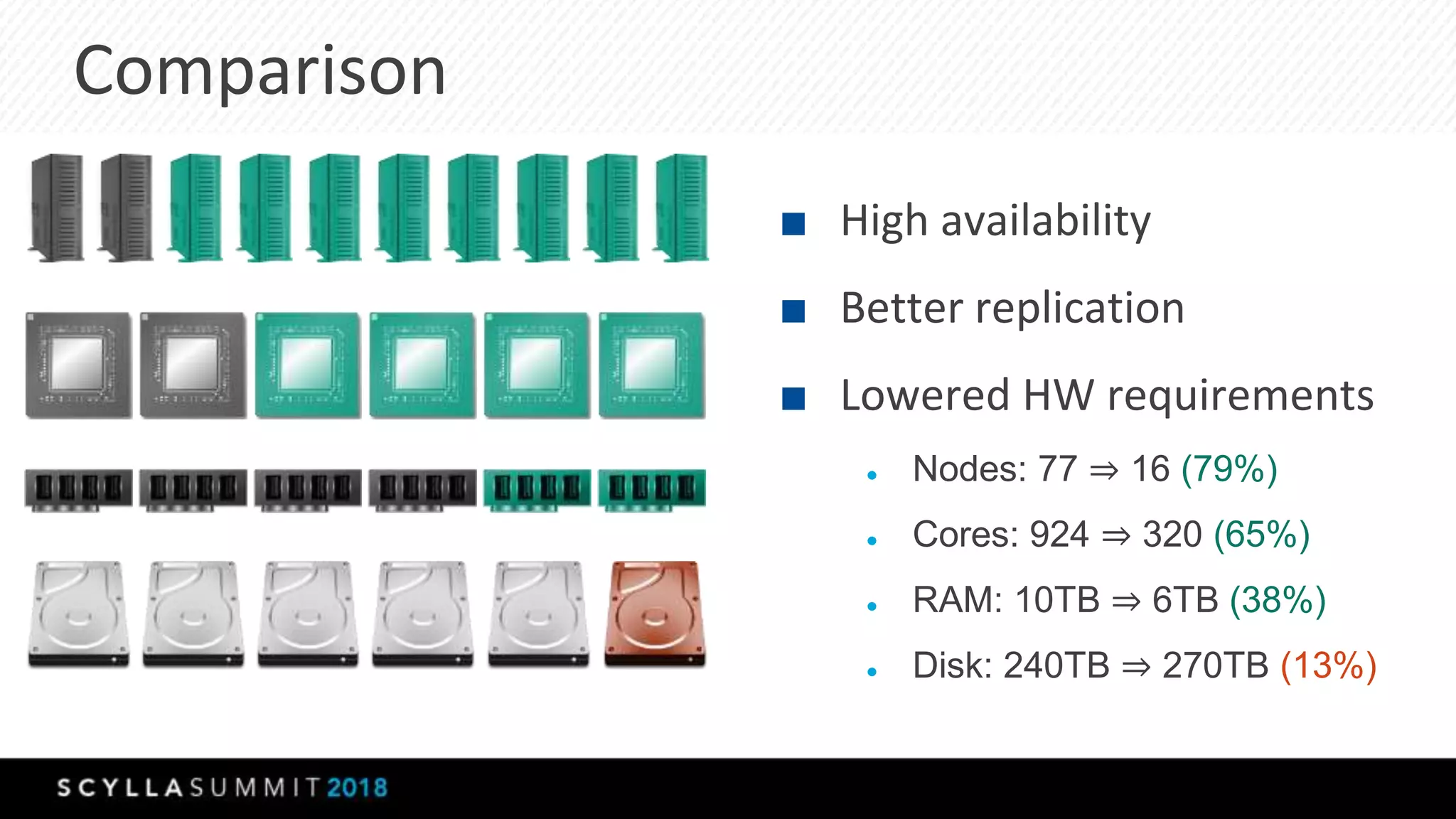
The document discusses a presentation by Lubos Kosco and Michal Senkyr on processing 50 billion user profiles in real-time for Sizmek's advertising platform. Key topics include a data model for user profiles, server configurations, caching strategies, and optimizations that enhance throughput and reduce hardware requirements. The presentation concludes with comparisons showing significant gains in efficiency and performance due to these improvements.