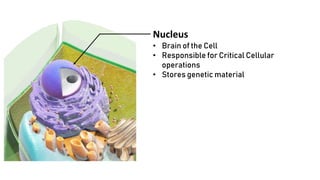
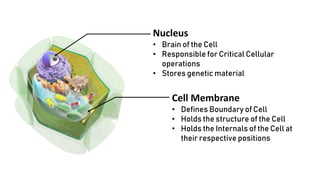
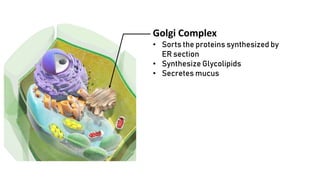
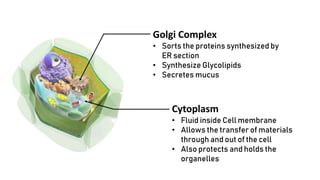
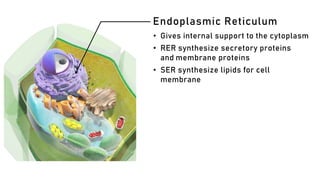
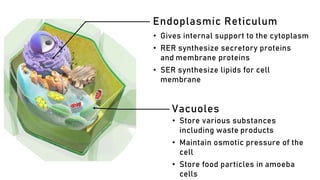
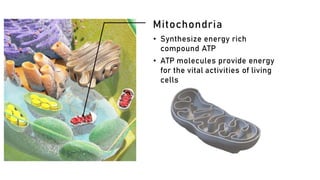
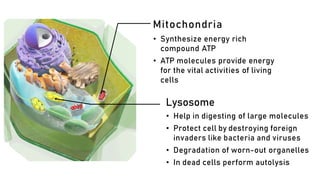
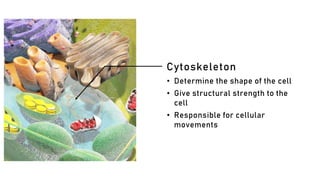
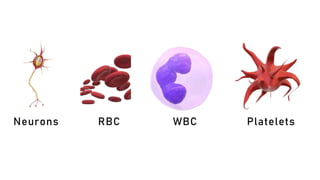
The document discusses the basic structure and functions of cells, highlighting the cell theory and historical discoveries related to cells. It outlines various cellular components, such as the nucleus, cell membrane, Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, lysosomes, and cytoskeleton, explaining their roles in cellular operations. Additionally, it presents interesting facts about cells, including their division, composition, and the total number of cells in the human body.