NM Junction & Muscle Contraction
- 2. REVIEW OF THE SARCOMERE STRUCTURE Dr. Phiri S B
- 3. MOTOR UNIT •Def. A motor neuron and the muscle fibers it innervates • A muscle (whole muscle) can be innervated by several motor units • Some muscles are innervated by one motor neuron • Small motor units--Fine control • small motor units contain as few as 3-6 muscle fibers per nerve fiber • Example– eye muscle • Large motor units--Strength control • gastrocnemius muscle has 1000 fibers per nerve fiber Dr. Phiri S B
- 5. • The neuromuscular junction is by definition a synapse • Presynaptic motor axons are demyelinated and stop 30 nanometers from the sarcolemma. • This 30-nanometer space forms the synaptic cleft through which signalling molecules are released. • The sarcolemma has invaginations called postjunctional folds, which increase the surface area of the membrane exposed to the synaptic cleft. • These postjunctional folds form what is referred to as the motor endplate, which possess acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) at a density of 10,000 receptors/micrometer in skeletal muscle. • The presynaptic axons form bulges called terminal boutons that project into the postjunctional folds of the sarcolemma. Dr. Phiri S B
- 6. • The presynaptic boutons have active zones that contain vesicles, quanta, full of acetylcholine molecules. • These vesicles can fuse with the presynaptic membrane and release ACh molecules into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis after depolarization. • AChRs are localized opposite the presynaptic terminals by protein scaffolds at the postjunctional folds of the sarcolemma. • Dystrophin, a structural protein, connects the sarcomere, sarcolemma, and extracellular matrix components. • Rapsyn is another protein that docks AChRs and structural proteins to the cytoskeleton. • Also present is the receptor tyrosine kinase protein MuSK, a signaling protein involved in the development of the neuromuscular junction, which is also held in place by rapsyn Dr. Phiri S B
- 7. ACTIVITY OF NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION MUSCLE FIBER MUSCLE IMPULSE Dr. Phiri S B
- 8. Dr. Phiri S B
- 9. NEUROMUSCULAR DESEASES 1.AUTOIMMUNE a.Myasthenia gravis b.Neonatal myasthenia gravis c. Lambart-Eaton myasthenic syndrome d.Neuromyotonia (Isaac’s syndrome) 2. GENETIC a.Congenital myasthenic syndrome b.Duchene muscular dystrophy c. Bulbospinal muscular atrophy (Kennedy’s syndrome) Dr. Phiri S B
- 10. ACTIVITY OF NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION • When an action potential in a motor neuron arrives at the axon terminal, • it depolarizes the nerve plasma membrane, • opening voltage-sensitive calcium channels and allowing calcium ions to diffuse into the axon terminal from the extracellular fluid. • This calcium binds to proteins that enable the membranes of acetylcholine containing vesicles to fuse with the nerve plasma membrane • thereby releasing acetylcholine into the extracellular cleft separating the axon terminal and the motor end plate. Dr. Phiri S B
- 11. • ACh diffuses from the axon terminal to the motor end plate • where it binds to receptors [of the nicotinic type]. • The binding of ACh opens an ion channel in each receptor protein. • Both sodium and potassium ions can pass through these channels. • Because of the differences in electrochemical gradients across the plasma membrane, • more sodium moves in than potassium out, • producing a local depolarization of the motor end plate known as an end-plate potential (EPP) Dr. Phiri S B
- 12. GENERATION AND PROPAGATION OF ACTION POTENTIAL IN THE SARCOLEMMA Dr. Phiri S B
- 13. Dr. Phiri S B
- 14. Dr. Phiri S B
- 15. • There is sudden influx of sodium ions into the muscle fiber when the acetylcholine channels open • This causes the electrical potential inside the fiber at the local area of the end plate to increase in the positive direction as much as 50 to 75 millivolts, • Creating a local potential called the end plate potential. • An increase in end plate membrane potential(EPP) initiate more and more opening of sodium voltage sensitive channels, thus initiating an action potential at the muscle fiber membrane (sarcolemma). • Then the action potential sweep all around the sarcolemma and via the T-tubular system Dr. Phiri S B
- 16. • The conversion of this excitation into a contraction is called electromechanical coupling • In the skeletal muscle, this process begins with the action potential exciting voltage sensitive dihydropyridine receptors (DHPR) of the sarcolemma in the region of the triads. • The DHPR are arranged in rows, and directly opposite them in the adjacent membrane of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) are rows of Ca2+ channels called ryanodine receptors (type 1 in skeletal muscle: RYR1). • Every other RYR1 is associated with a DHPR • RYR1 open when they directly “sense” by mechanical means an AP-related conformational change in the DHPR • Then calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in the sarcoplasm Dr. Phiri S B
- 17. Dr. Phiri S B
- 18. MECHANISM OF CONTRACTION 1. Cross bridge formation 2. The power stroke 3. Cross bridge detachment 4. Reactivation of myosin head Dr. Phiri S B
- 19. MECHANISM OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION & RELAXATION Dr. Phiri S B
- 20. Dr. Phiri S B
- 21. • In resting muscle, troponin I is bound to actin and tropomyosin and covers the sites where myosin heads interact with actin. • Also at rest, the myosin head contains tightly bound ADP. • Following an action potential cytosolic Ca2+ is increased and free Ca2+ binds to troponin C. • This binding results in a weakening of the troponin I interaction with actin and exposes the actin binding site for myosin to allow for formation of myosin/actin cross-bridges. • Upon formation of the cross-bridge, ADP is released, causing a conformational change in the myosin head that moves the thin filament relative to the thick filament, comprising the cross- bridge “power stroke.” Dr. Phiri S B
- 22. • ATP quickly binds to the free site on the myosin, which leads to a detachment of the myosin head from the thin filament. • ATP is hydrolyzed and inorganic phosphate (Pi) released, causing a “re- cocking” of the myosin head and completing the cycle. • As long as Ca2+ remains elevated and sufficient ATP is available, this cycle repeats. • Many myosin heads cycle at or near the same time, and they cycle repeatedly, producing gross muscle contraction. • Each power stroke shortens the sarcomere about 10 nm. • Each thick filament has about 500 myosin heads, and each head cycles about five times per second during a rapid contraction. Dr. Phiri S B
- 23. SUMMARY OF CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION MECHANISMS Dr. Phiri S B DR BIG GIRB F
- 24. Dr. Phiri S B
- 25. 1. Action potential is initiated and propagates in motor neuron axon. 2. Action potential triggers release of ACh from axon terminals at neuromuscular junction. 3. ACh diffuses from axon terminals to motor end plate in muscle fiber. 4. ACh binds to receptors on motor end plate, opening Na, K ion channels. 5. More Na moves into the fiber at the motor end plate than K moves out, depolarizing the membrane, producing the EPP. Dr. Phiri S B
- 26. 6. Local currents depolarize the adjacent plasma membrane to its threshold potential, generating an action potential that propagates over the muscle fiber surface and into the fiber along the transverse tubules. 7. Action potential in transverse tubules triggers release of Ca2 from lateral sacs of sarcoplasmic reticulum. 8. Ca2 binds to troponin on the thin filaments, causing tropomyosin to move away from its blocking position, thereby uncovering cross-bridge binding sites on actin. 9. Energized myosin cross bridges on the thick filaments bind to actin 10. Cross-bridge binding triggers release of the strained conformational state of myosin, producing an angular movement of each cross bridge Dr. Phiri S B
- 27. 11. ATP binds to myosin, breaking linkage between actin and myosin and thereby allowing cross bridges to dissociate from actin 12. ATP bound to myosin is split, energizing the myosin cross bridge 13. Cross bridges repeat steps 9 to 12, producing movement of thin filaments past thick filaments. Cycles of cross-bridge movement continue as long as Ca2 remains bound to troponin. 14. Cytosolic Ca2 concentration decreases as Ca2 is actively transported into sarcoplasmic reticulum by Ca-ATPase. 15. Removal of Ca2 from troponin restores blocking action of tropomyosin, the cross-bridge cycle ceases, and the muscle fiber relaxes Dr. Phiri S B
- 28. Contraction - when tension develop in a muscle as a result of a stimulus Muscle “contraction” term may be confusing, because in some contractions the muscle does not shorten in length As a result, it has become increasingly common to refer to the various types of muscle contractions as muscle actions instead
- 29. Isometric contraction ◦tension is developed within muscle but joint angles remain constant ◦static contractions ◦significant amount of tension may be developed in muscle to maintain joint angle in relatively static or stable position
- 30. In isotonic contraction, the tension in the muscle remains constant despite a change in muscle length. This can occur only when a muscle's maximal force of contraction exceeds the total load on the muscle. Divided into concentric and eccentric contraction
- 31. Concentric contraction ◦ muscle develops tension as it shortens ◦ occurs when muscle develops enough force to overcome applied resistance ◦ causes movement against gravity or resistance ◦ described as being a positive contraction
- 32. In eccentric contraction, the force generated is insufficient to overcome the external load on the muscle and the muscle fibers lengthen as they contract. An eccentric contraction is used as a means of decelerating a body part or object, or lowering a load gently rather than letting it drop.
- 33. Eccentric contraction (muscle action) ◦ Some refer to this as a muscle action instead of a contraction since the muscle is lengthening as opposed to shortening Various exercises may use any one or all of these contraction types for muscle development
- 34. Dr. Phiri S B
- 35. Dr. Phiri S B
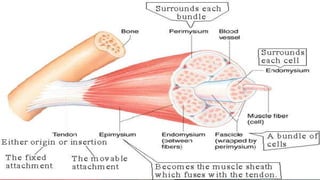
- 36. A resting muscle containing ATP can be stretched like a rubber band A muscle’s resistance to stretch (Noncontractile component) series elastic components Tendons Parallel elastic components Fascia (fibrous tissue) epimysium, perimysium, Endomysium giant filamentous elastic molecule called titin (connectin) Dr. Phiri S B
- 37. The length of the muscle can be varied by changing the distance between its two attachments. At each length, the passive tension is measured, the muscle is then stimulated electrically, and the total tension is measured. The difference between the two values at any length is the amount of tension actually generated by the contractile process, the active tension. Plot passive tension and total tension against muscle length. The length of the muscle at which the active tension is maximal is called its resting length Dr. Phiri S B
- 38. Strength of muscle contraction is a function of the number of cross-links made between the actin and myosin chains within the sarcomeres alterations in the proximity (length) of the actin and myosin myofilaments affects the contraction force (tension) of a muscle after stimulation maximum contractile force in the sarcomere occurs when the full length of the actin strands at each end of the sarcomere are in contact with the myosin molecule. Dr. Phiri S B
- 39. The total force of a muscle is the sum of its active force and its extension force at rest. The active force is determined by the magnitude of all potential actin-myosin interactions, which varies in accordance with the initial sarcomere length. Resting length is the length to which a sarcomere is stretched in a resting state. The effect of resting fiber length on muscular contraction is referred to as the length-tension relationship. Frank–Starling law stated that the “energy of contraction is proportional to the initial length of the cardiac muscle fiber” Dr. Phiri S B
- 40. 1. Skeletal muscle can develop maximum active (isometric) force (F0) from its resting length (Lmax; sarcomere length = 2 to 2.2 μm). 2. When the sarcomeres shorten (L ‹ Lmax), part of the thin filaments overlap, allowing only forces smaller than F0 to develop. 3. When L is 70% of Lmax (sarcomere length: 1.65 μm), the thick filaments make contact with the Z disks, and F becomes even smaller. 4. a greatly pre-extended muscle (L›Lmax) can develop only restricted force, because the number of potentially available actin–myosin bridges is reduced. 5. When extended to 130% or more of the Lmax, the actin-myosin interaction is completely lost and tension comes to zero. Dr. Phiri S B
- 41. Dr. Phiri S B
- 42. Dr. Phiri S B
- 43. THANK YOU Dr. Phiri S B