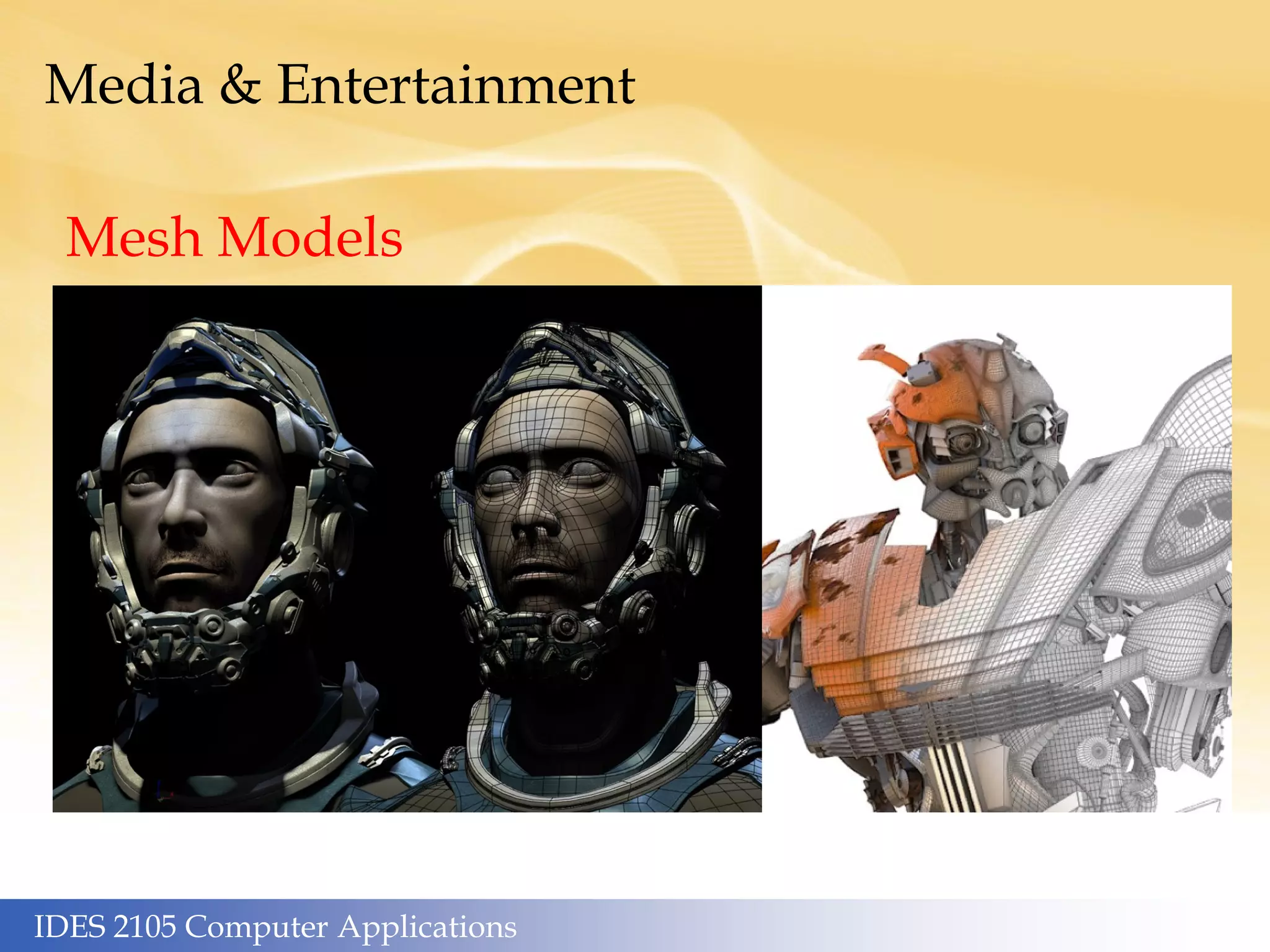
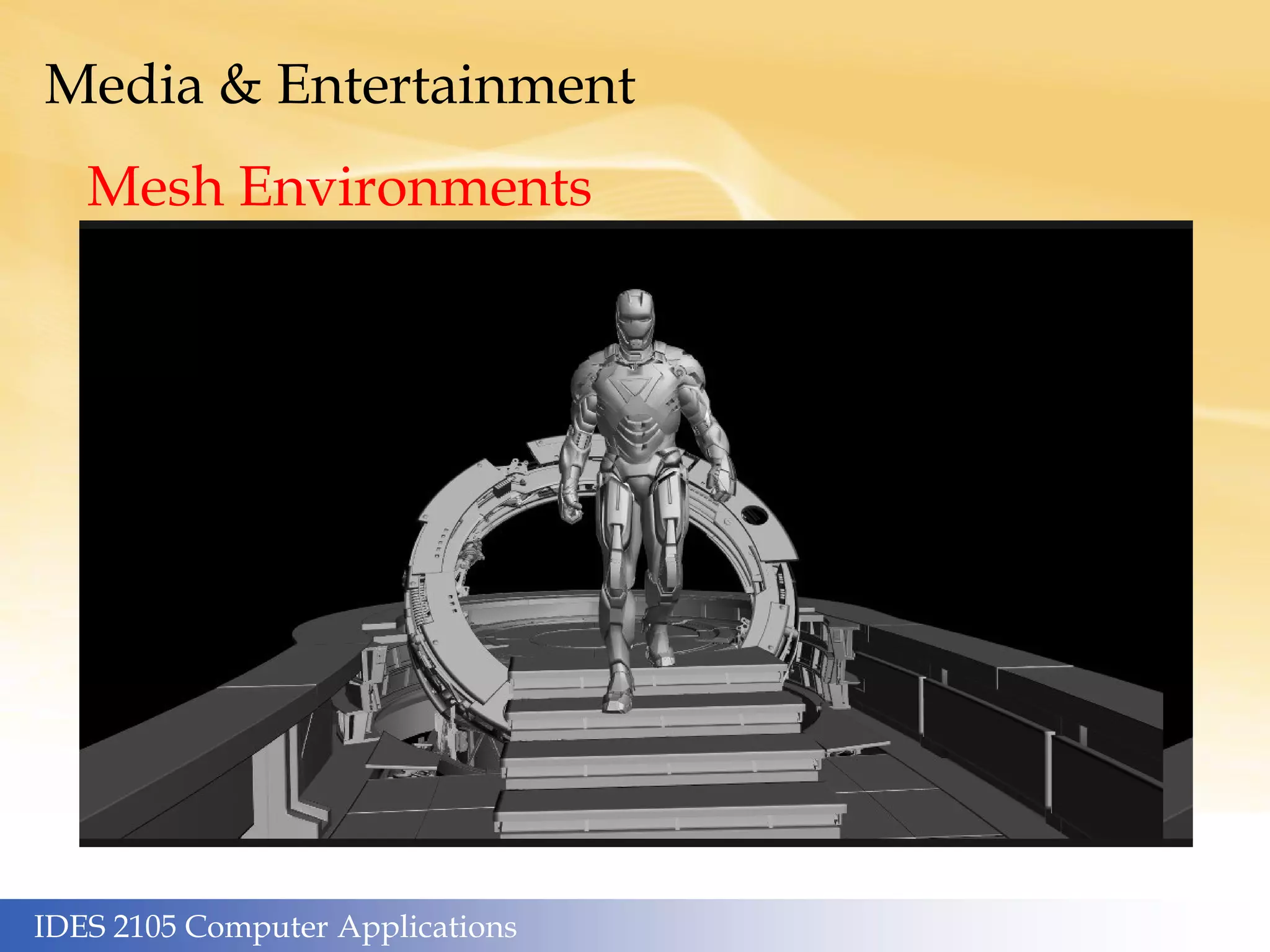
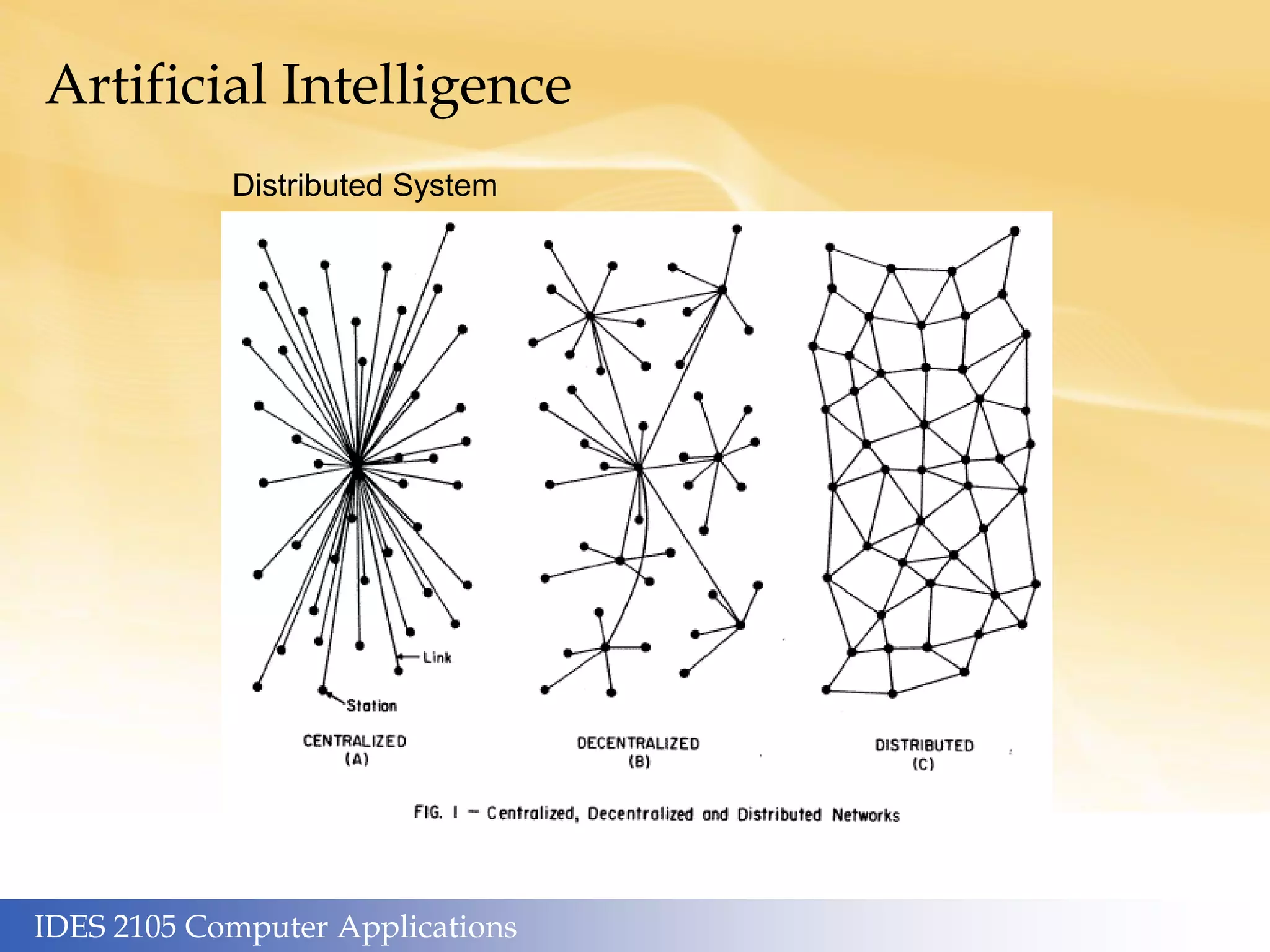
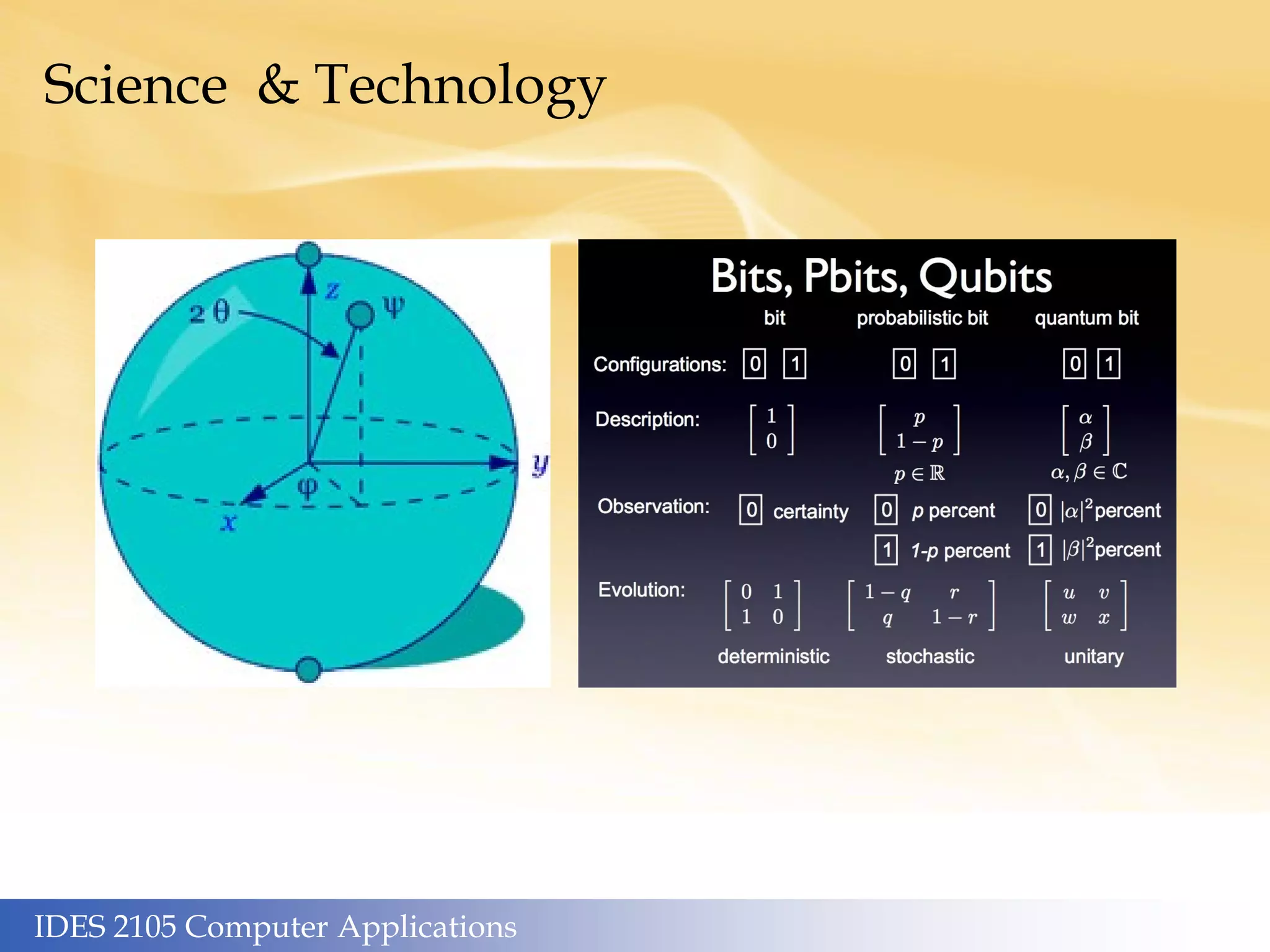
This document outlines the topics covered in different weeks for an IDES 2105 Computer Applications course. Week 1 covers human computers and genetic/social algorithms. Week 2 covers machine hardware, heuristics, and algorithms. Week 3 discusses machine software, the internet, W3 standards, and online marketing. Week 4 focuses on frameworks like the innovator's dilemma. Week 5 is about graphics, media, the Utah teapot, and robots/automation. Week 6 examines artificial intelligence, supercomputers, cognitive pathways, and machine learning. Additional sections cover media and entertainment applications, mesh models/environments, live action and CGI, and reproduction in media. The artificial intelligence section discusses key applications like supercomputers, big data, and Moore