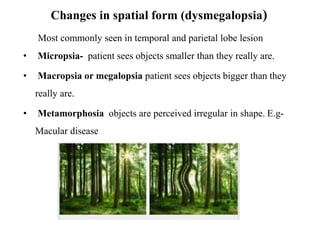
Disorder of perception can involve sensory distortions or deceptions. Sensory distortions include changes in intensity, quality, spatial form, or the experience of time of sensory information. Sensory deceptions include illusions which are misinterpretations of stimuli, hallucinations which are false perceptions without an adequate external stimulus, and pseudohallucinations which are vivid mental images known to be not real. Disorders of perception can result from psychiatric conditions, sensory organ disorders, sensory deprivation, or central nervous system issues.