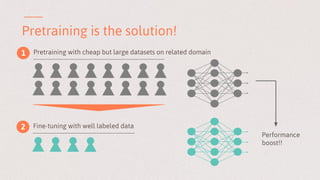
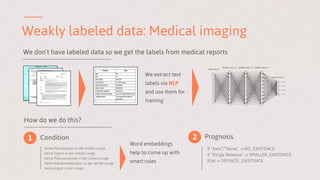
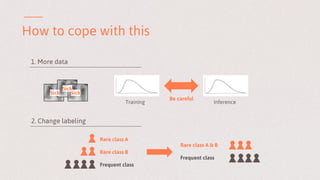
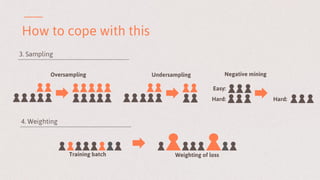
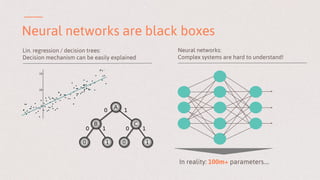
The document discusses key learnings from applying deep learning to real-world problems, highlighting three main takeaways. These include the importance of pretraining with large datasets, the challenges posed by imbalanced real-world datasets, and the complexities of understanding neural network models. The insights are relevant for advancing deep learning applications in various sectors, including medical diagnostics and credit scoring.