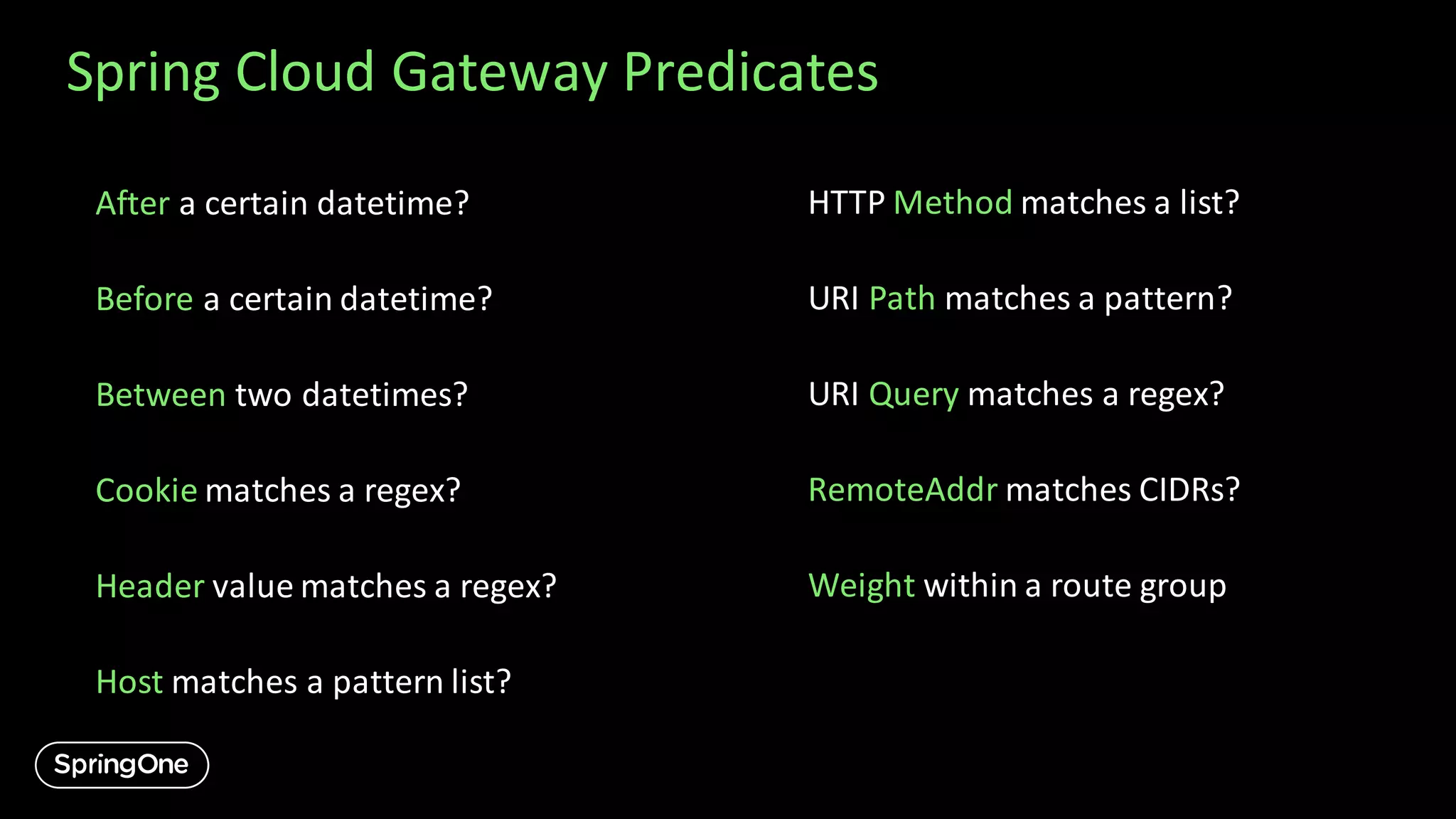
The document introduces VMware's Spring Cloud Gateway and API Hub for VMware Tanzu, outlining its features and functions such as routing, security, rate limiting, and single sign-on. It emphasizes that the information is for illustrative purposes only and is subject to changes, and should not influence purchasing decisions. Additionally, it details how to configure various settings and the integration process within the Tanzu platform.


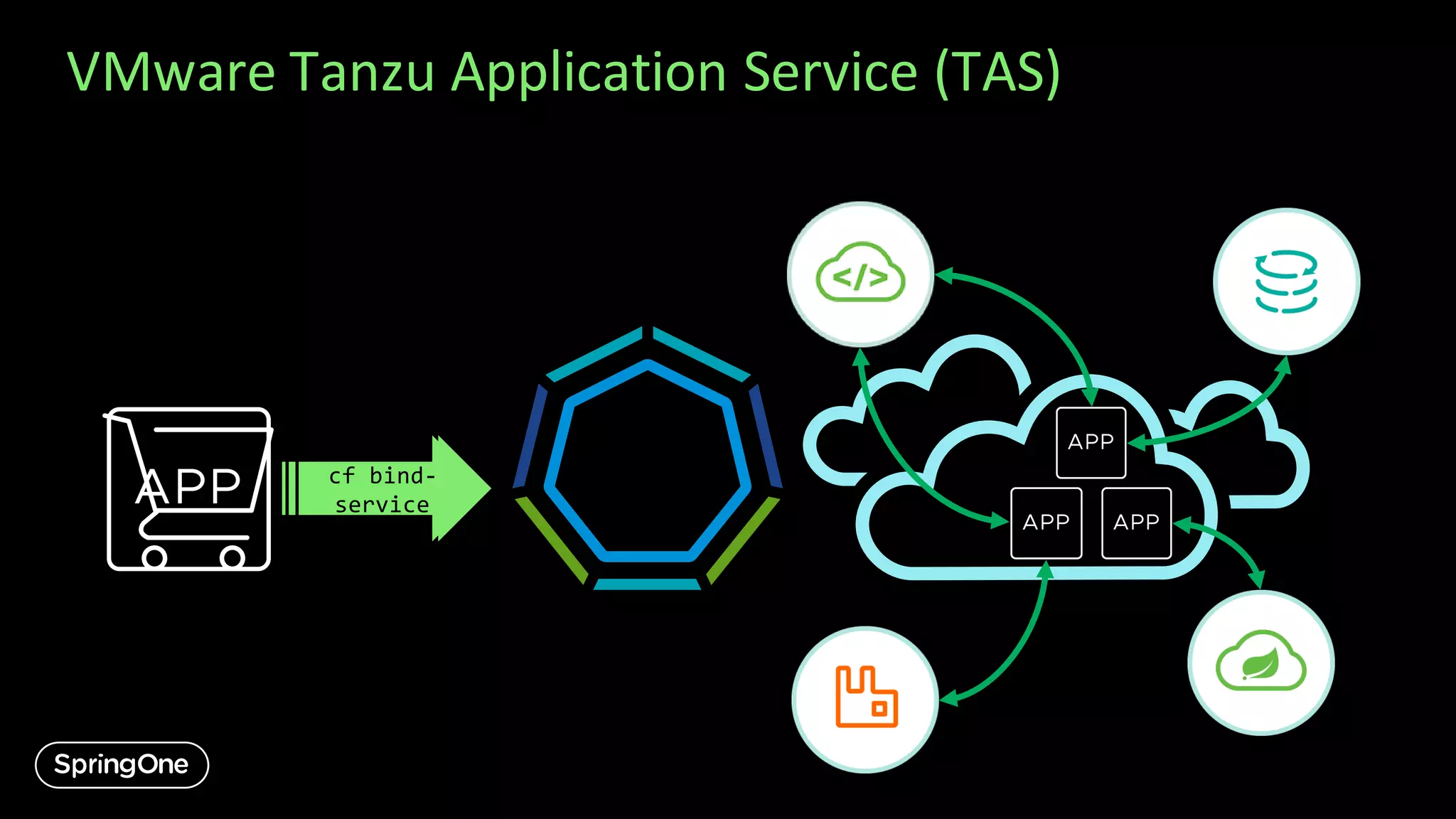

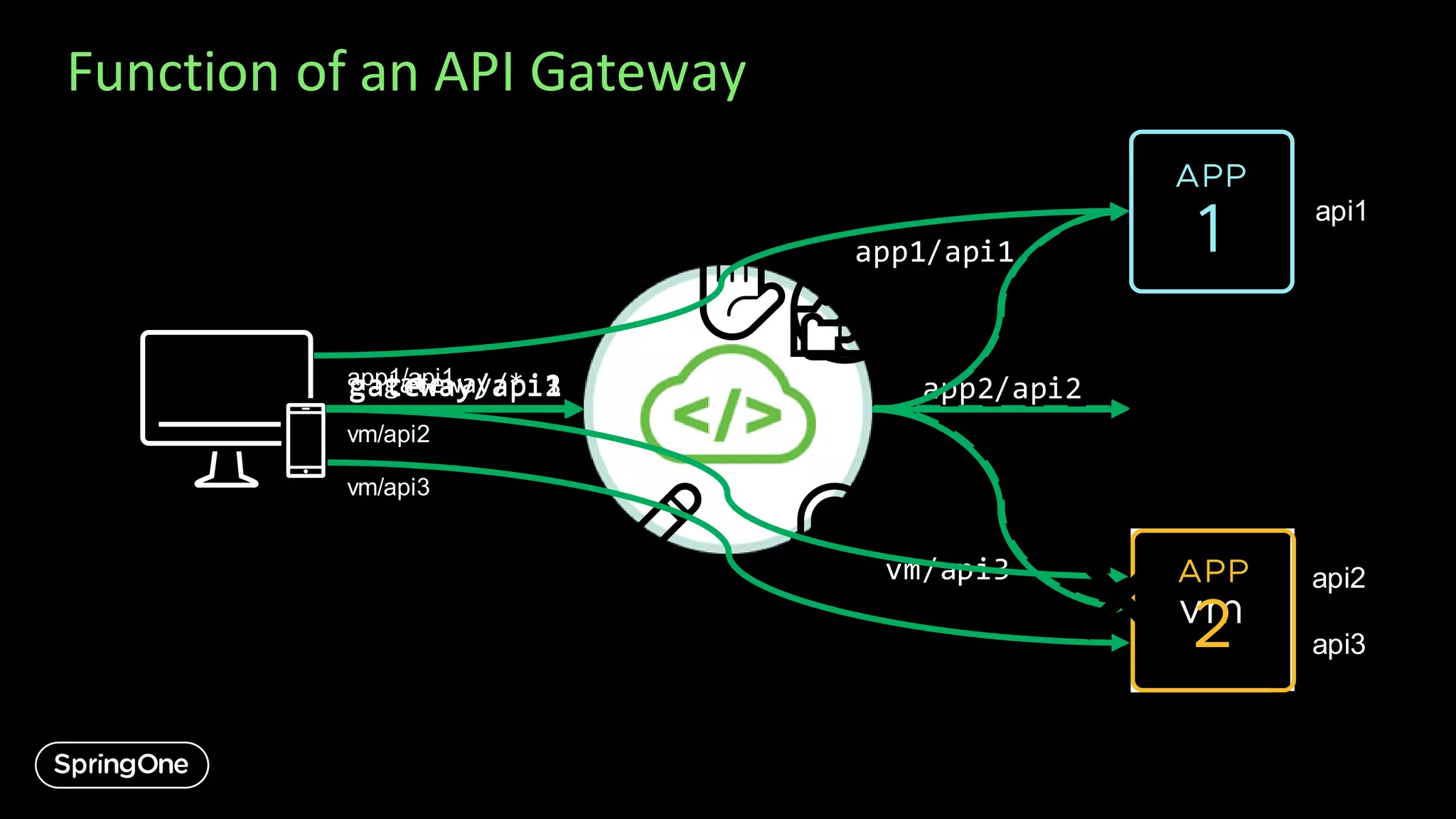

![Let’s Create a Gateway
-c '{
"routes": [{
"predicates": [
"Path=/a/**",
"Method=GET,POST"
],
"filters": [
"StripPrefix=1"
],
"uri": "http://example.com"
}]
}'
"path": "/a/**",
"method": "GET,POST",
"uri": "http://example.com"
}]
}'
cf create-service p.gateway standard my-gateway](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introducingspringcloudgatewayandapihubforvmwaretanzu-export-200911004235/75/Introducing-Spring-Cloud-Gateway-and-API-Hub-for-VMware-Tanzu-8-2048.jpg)
![Service Bindings
Exposing a route to an app running on Tanzu applicationplatform is simpler:
cf bind-service my-app my-gateway -c '{
"routes": [{
"path": "/a/**",
"method": “GET,POST"
}]
}'
To remove routes:
cf unbind-service my-app my-gateway](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introducingspringcloudgatewayandapihubforvmwaretanzu-export-200911004235/75/Introducing-Spring-Cloud-Gateway-and-API-Hub-for-VMware-Tanzu-9-2048.jpg)
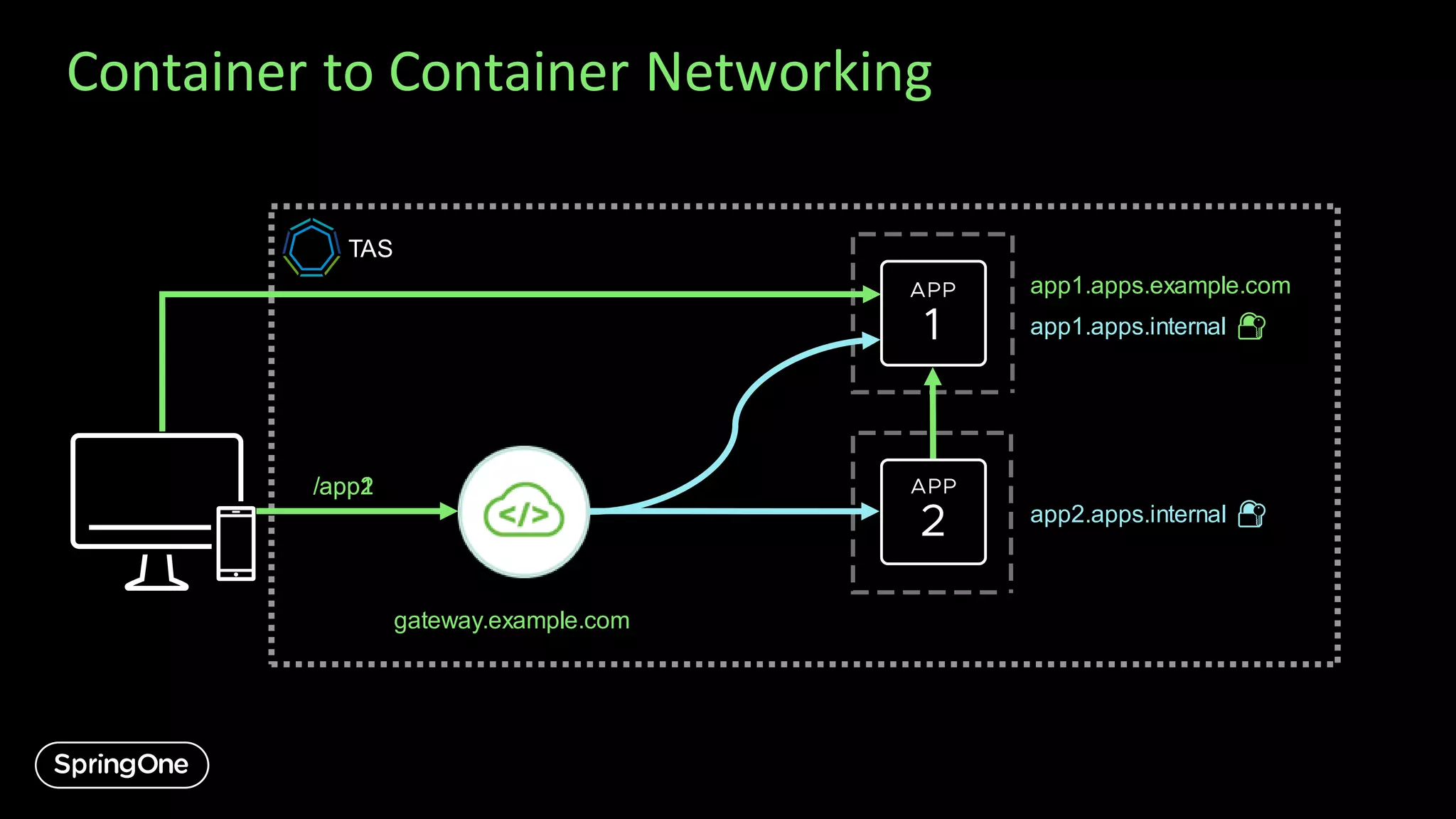
![Updating Routes
To update routes that were created at Gateway creation time, use:
cf update-service my-gateway -c '{"routes": [...]}'
Binding and unbindingis one way to modify routes to on-platform apps after the
Gateway has been created.
Another way is to use Gateway’s bound-appsactuatorAPI
curl -X PUT https://<gateway uri>/actuator/bound-apps/<app id>/routes
-d "@./updated-route-config.json"
-H "Authorization: $(cf oauth-token)"
-H "Content-Type: application/json"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introducingspringcloudgatewayandapihubforvmwaretanzu-export-200911004235/75/Introducing-Spring-Cloud-Gateway-and-API-Hub-for-VMware-Tanzu-11-2048.jpg)

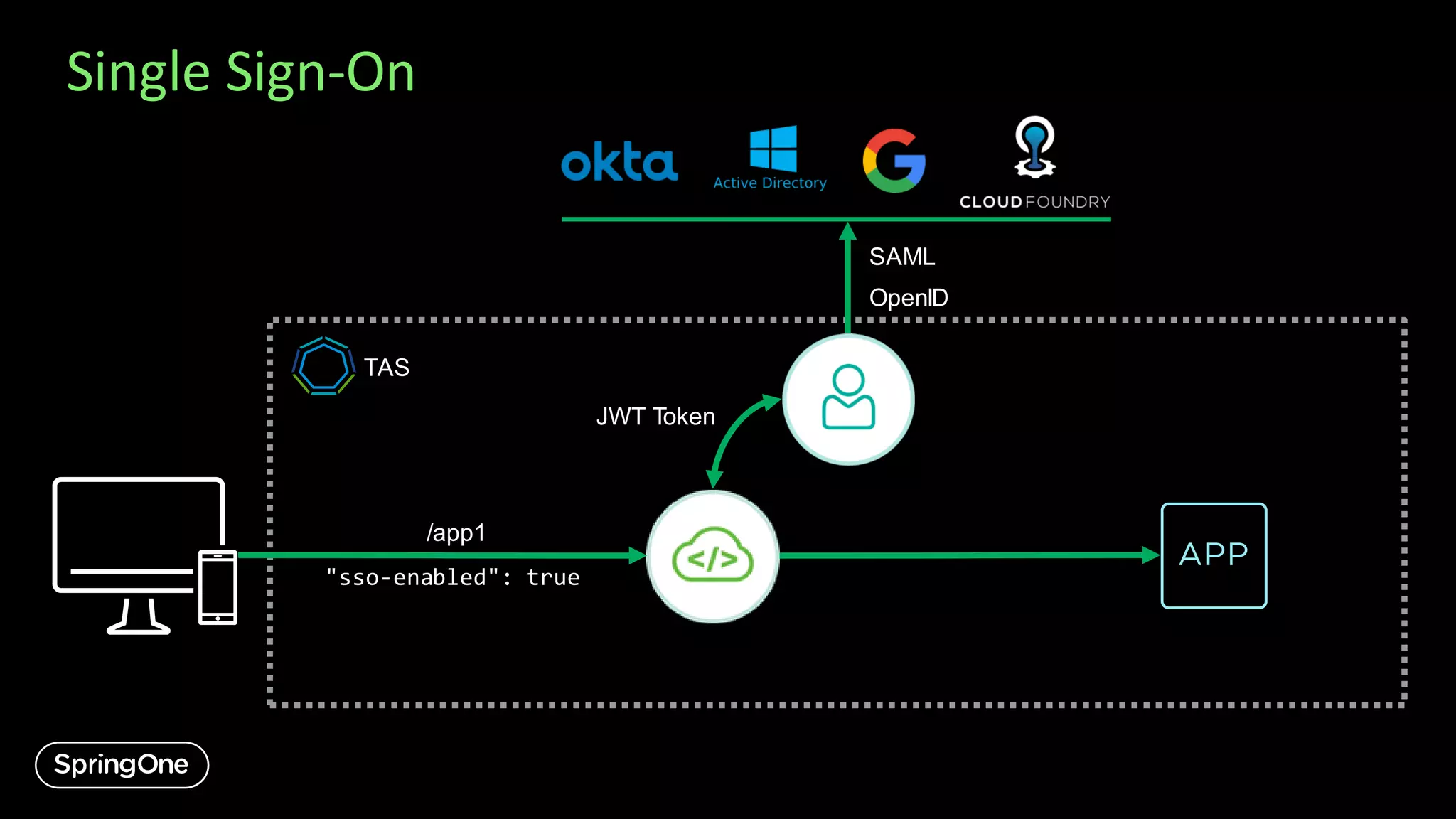
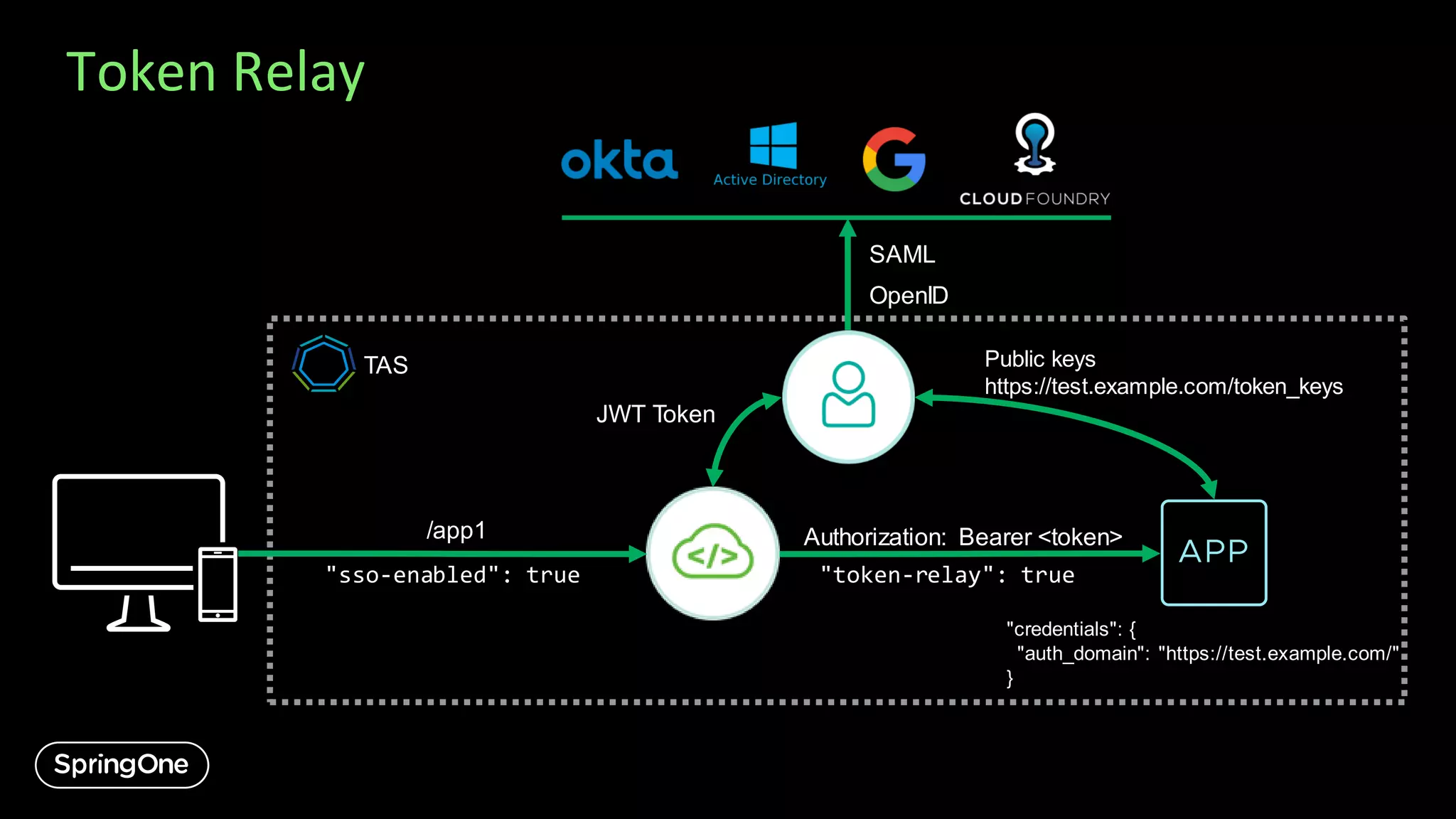
![Single Sign-On
/app1
"sso-enabled": true,
"scopes": [ "accounts.view" ],
"roles": [ "Auditor" ]
SAML
OpenID
JWT Token
"scope": [ "openid" ],
"roles": [ "Support" ]
TAS
❌](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introducingspringcloudgatewayandapihubforvmwaretanzu-export-200911004235/75/Introducing-Spring-Cloud-Gateway-and-API-Hub-for-VMware-Tanzu-16-2048.jpg)
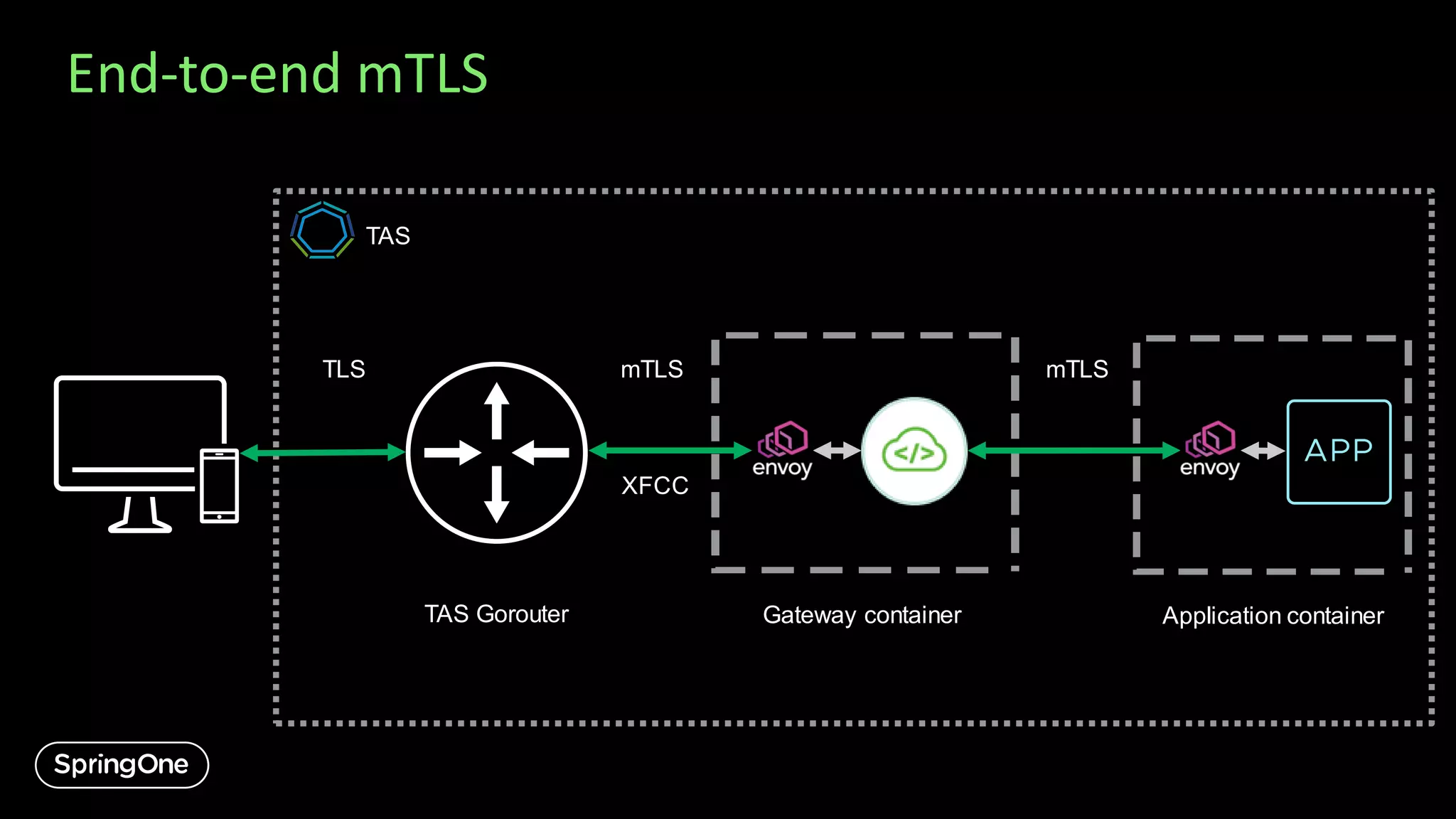
![Client Certificate validation
cf bind-service my-app my-gateway -c '{ "routes": [{
...,
"filters":["ClientCertificateHeader=*.example.com,sha-1:aa:bb:00:99"]
}] }'
This filter checks:
• the client certificate presented in inbound requests for chain of trust (always)
• (optionally) certificate Common Name value
• (optionally) SHA-1 or SHA-256 fingerprint](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introducingspringcloudgatewayandapihubforvmwaretanzu-export-200911004235/75/Introducing-Spring-Cloud-Gateway-and-API-Hub-for-VMware-Tanzu-19-2048.jpg)
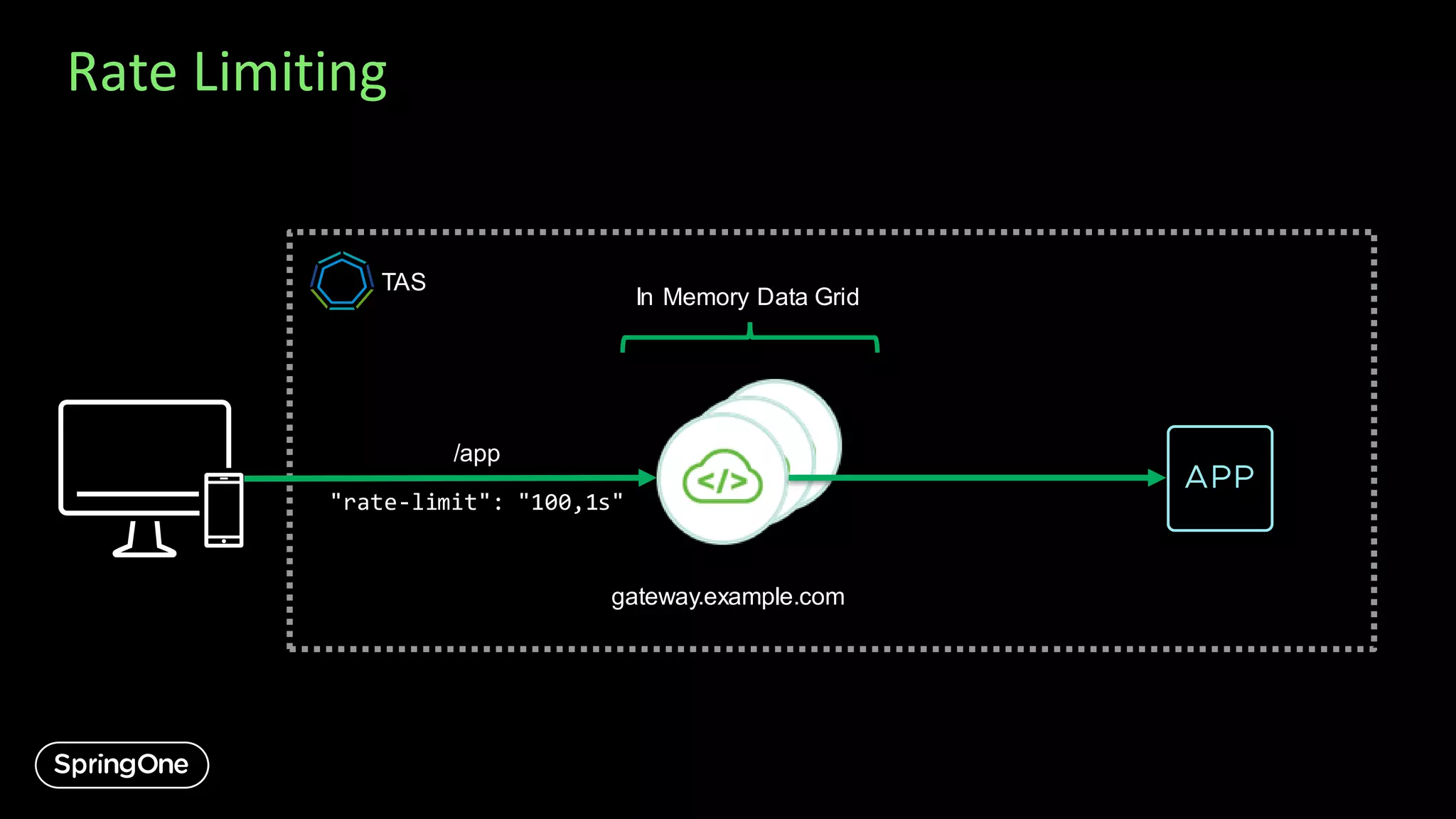
![Rate Limiting
cf bind-service my-app my-gateway -c '{
"routes": [ {
...,
"rate-limit": “100,1s"
} ]
}'
Prevents APIs from becoming overloadedby requests
Easily specify the maximum number of requests per time interval per route](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introducingspringcloudgatewayandapihubforvmwaretanzu-export-200911004235/75/Introducing-Spring-Cloud-Gateway-and-API-Hub-for-VMware-Tanzu-21-2048.jpg)



![Cross Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) Configuration
Gateway can be configured to handleCORS requests:
cf create-service p.gateway standard my-gateway -c '{
"cors": {
"allowed-origins": [ "https://example.com" ],
"allowed-methods": [ "GET", "POST" ],
"allowed-headers": [ "X-Custom-Header" ],
"allow-credentials": true,
"max-age": 300,
"exposed-headers": [ "X-Custom-Header" ]
}
}'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introducingspringcloudgatewayandapihubforvmwaretanzu-export-200911004235/75/Introducing-Spring-Cloud-Gateway-and-API-Hub-for-VMware-Tanzu-25-2048.jpg)