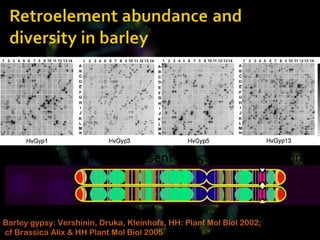
The document discusses genome evolution in plants, with a focus on wheat and its wild relatives. It describes how:
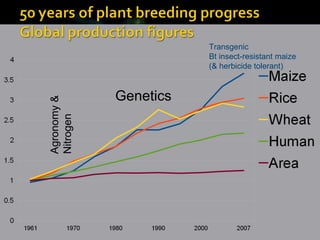
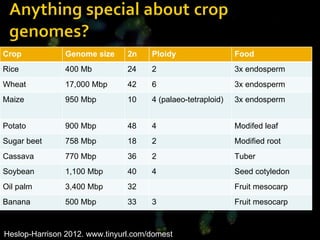
- Wheat has a very large and repetitive genome compared to other plants like Arabidopsis.
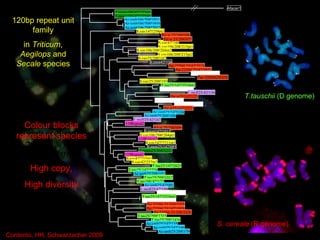
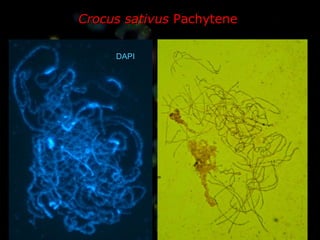
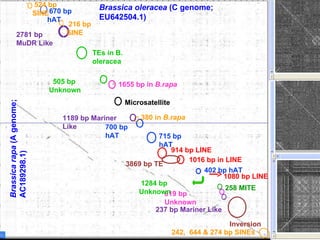
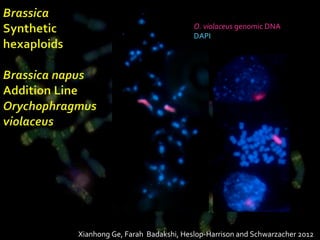
- Repetitive DNA sequences play an important role in genome and chromosome evolution, and can be used to track chromosomes.
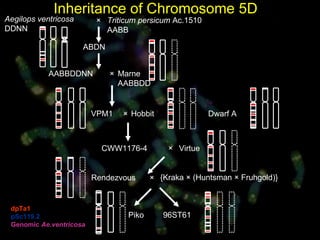
- Wild relatives like Aegilops ventricosa have been used in chromosome engineering to introduce useful traits like disease resistance to wheat.
- Molecular cytogenetics techniques allow studying the inheritance and distribution of repetitive sequences during speciation and hybridization.
![Pat Heslop-Harrison [email_address] www.molcyt.com pw/user: ‘visitor’ Pathh1 on Twitter and AoBBlog.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heslopharrisonassisiweb-111001164648-phpapp02/85/Heslopharrisonassisiweb-1-320.jpg)



























































![Pat Heslop-Harrison [email_address] www.molcyt.com pw/user: ‘visitor’ and AoBBlog.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heslopharrisonassisiweb-111001164648-phpapp02/85/Heslopharrisonassisiweb-70-320.jpg)