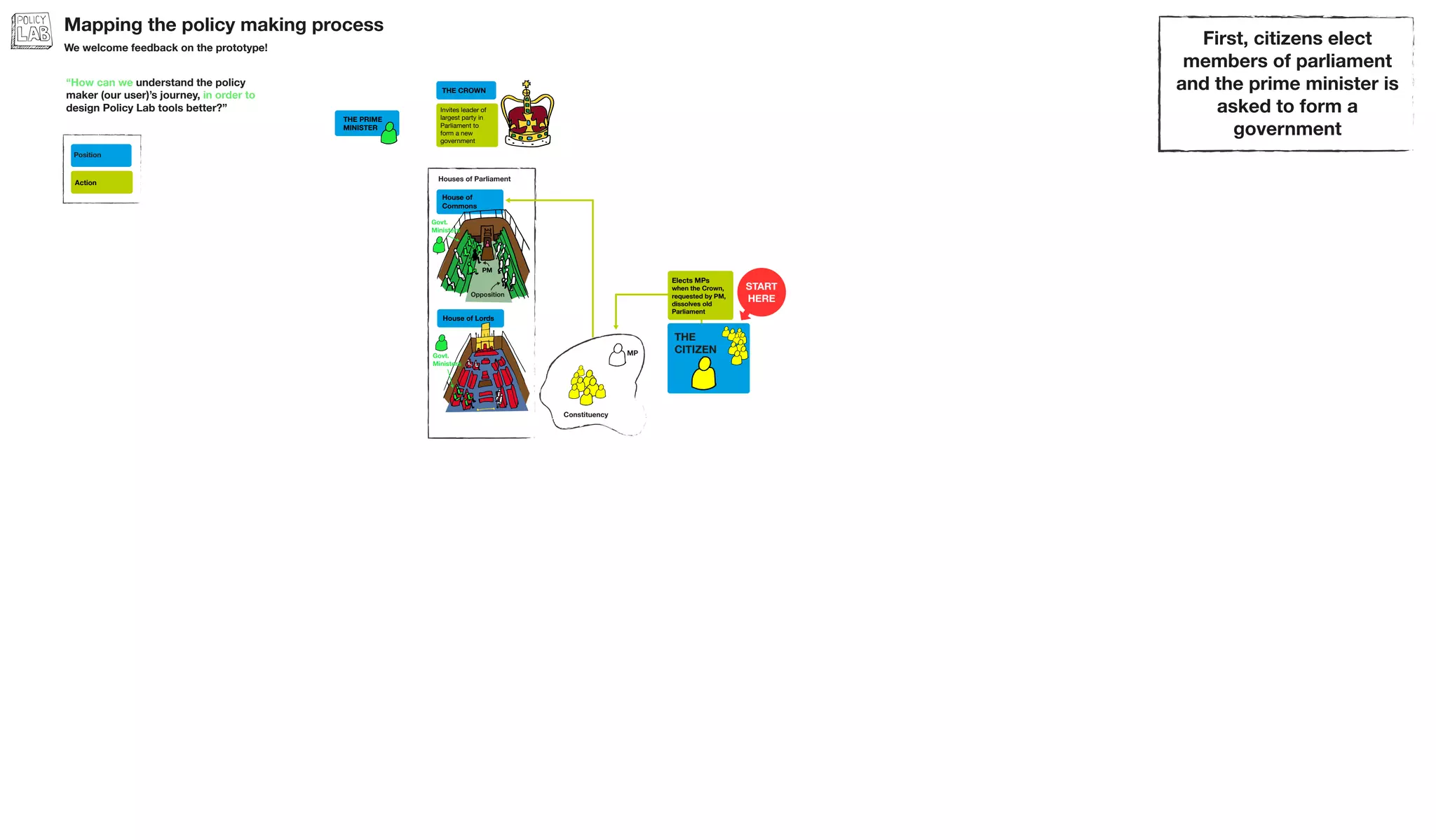
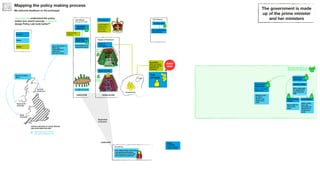
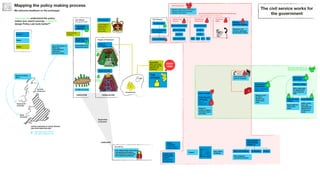
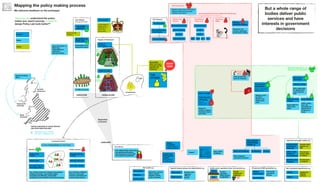
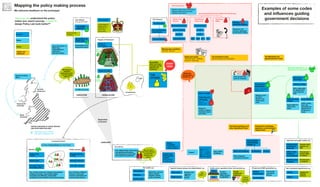
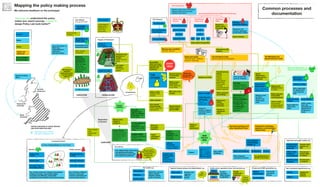
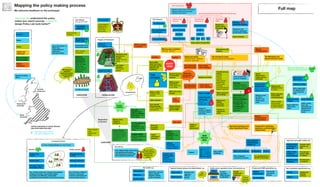
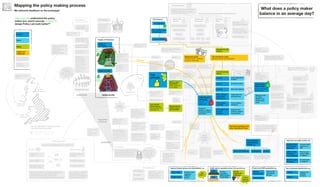
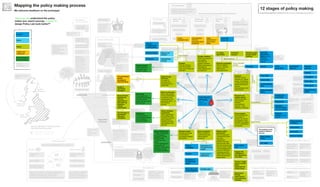
The document outlines the structure and relationships between different parts of the UK government. It shows that citizens elect members of parliament, who then select a prime minister. The prime minister appoints ministers and forms a government. The government is made up of ministers and the civil service. The civil service delivers policy and services. Other public bodies and levels of government also have roles.