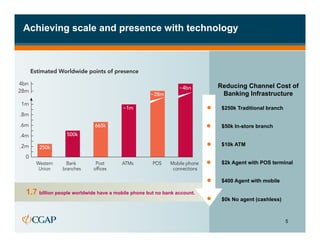
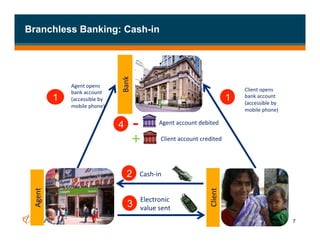
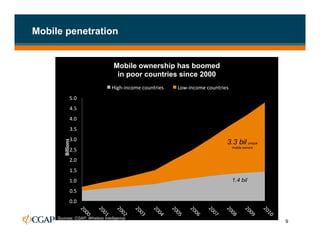
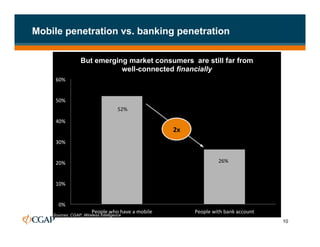
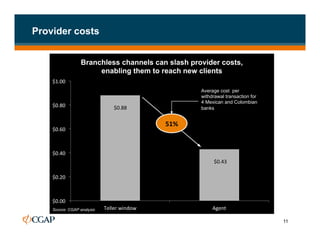
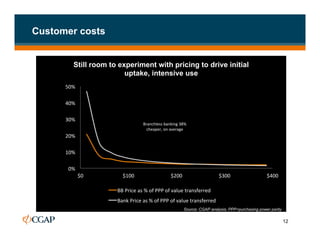
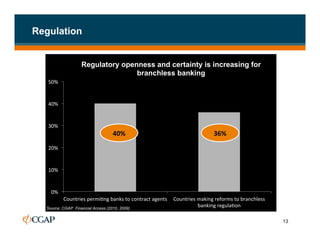
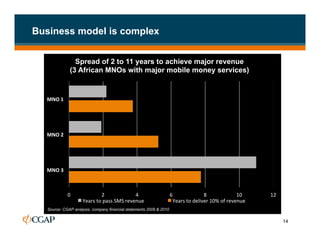
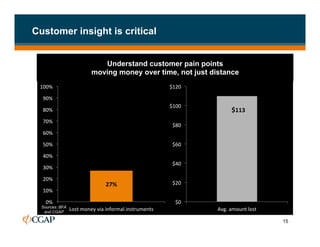
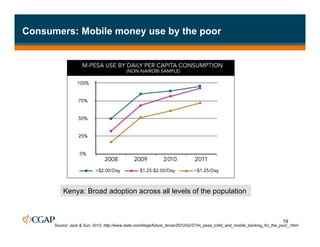
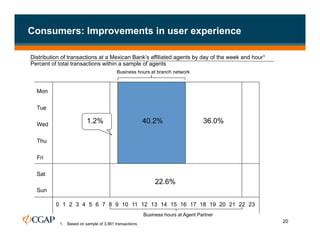
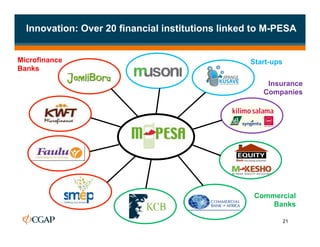
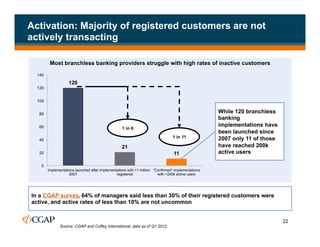
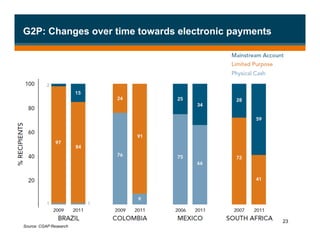
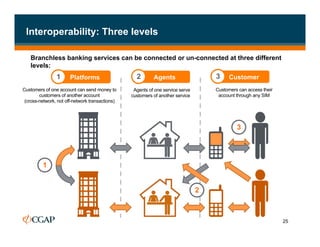
The document discusses branchless banking as a means to expand financial inclusion by leveraging technology to provide services outside traditional bank branches. It highlights the challenges that limit access to banking, such as high costs and low literacy, and presents solutions like agent networks and mobile banking to increase penetration. Key areas of focus include improving customer engagement, regulatory developments, and innovations in service delivery.