exercises 2 supplementary.pdf
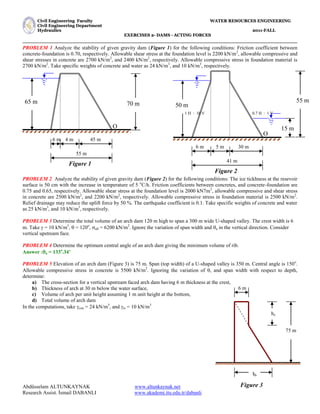
- 1. C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g F Fa ac cu ul lt ty y W WA AT TE ER R R RE ES SO OU UR RC CE ES S E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g D De ep pa ar rt tm me en nt t H Hy yd dr ra au ul li ic cs s 2 20 01 11 1- -F FA AL LL L E EX XE ER RC CI IS SE ES S 2 2- - D DA AM MS S - - A AC CT TI IN NG G F FO OR RC CE ES S Abdüsselam ALTUNKAYNAK www.altunkaynak.net Research Assist. İsmail DABANLI www.akademi.itu.edu.tr/dabanli PROBLEM 1 Analyze the stability of given gravity dam (Figure 1) for the following conditions: Friction coefficient between concrete-foundation is 0.70, respectively. Allowable shear stress at the foundation level is 2200 kN/m2 , allowable compressive and shear stresses in concrete are 2700 kN/m2 , and 2400 kN/m2 , respectively. Allowable compressive stress in foundation material is 2700 kN/m2 . Take specific weights of concrete and water as 24 kN/m3 , and 10 kN/m3 , respectively. PROBLEM 2 Analyze the stability of given gravity dam (Figure 2) for the following conditions: The ice tickhness at the resevoir surface is 50 cm with the increase in temperature of 5 o C/h. Friction coefficients between concretes, and concrete-foundation are 0.75 and 0.65, respectively. Allowable shear stress at the foundation level is 2000 kN7m2 , allowable compressive and shear stress in concrete are 2500 kN/m2 , and 2200 kN/m2 , respectively. Allowable compressive stress in foundation material is 2500 kN/m2 . Relief drainage may reduce the uplift force by 50 %. The earthquake coefficient is 0.1. Take specific weights of concrete and water as 25 kN/m3 , and 10 kN/m3 , respectively. PROBLEM 3 Determine the total volume of an arch dam 120 m high to span a 300 m wide U-shaped valley. The crest width is 6 m. Take = 10 kN/m3 , = 120o , all = 6200 kN/m2 . Ignore the variation of span width and a in the vertical direction. Consider vertical upstream face. PROBLEM 4 Determine the optimum central angle of an arch dam giving the minimum volume of rib. Answer :a = 133o .34’ PROBLEM 5 Elevation of an arch dam (Figure 3) is 75 m. Span (top width) of a U-shaped valley is 350 m. Central angle is 150o . Allowable compressive stress in concrete is 5500 kN/m2 . Ignoring the variation of , and span width with respect to depth, determine: a) The cross-section for a vertical upstream faced arch dam having 6 m thickness at the crest, b) Thickness of arch at 30 m below the water surface, c) Volume of arch per unit height assuming 1 m unit height at the bottom, d) Total volume of arch dam In the computations, take con = 24 kN/m3 , and w = 10 kN/m3 hx 6 m tb 75 m 70 m 6 m 4 m 45 m 55 m O 65 m Figure 1 Figure 3 Figure 2 55 m 6 m 5 m 30 m 41 m O 50 m 0.7 H : 1 V 1 H : 10 V 15 m
- 2. C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g F Fa ac cu ul lt ty y W WA AT TE ER R R RE ES SO OU UR RC CE ES S E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g D De ep pa ar rt tm me en nt t H Hy yd dr ra au ul li ic cs s 2 20 01 11 1- -F FA AL LL L E EX XE ER RC CI IS SE ES S 2 2- - D DA AM MS S - - A AC CT TI IN NG G F FO OR RC CE ES S Abdüsselam ALTUNKAYNAK www.altunkaynak.net Research Assist. İsmail DABANLI www.akademi.itu.edu.tr/dabanli SOLUTION 1 Forces and loads acting the dam: Fwh: Hydrostatic force produced by water in the reservoir and tail water in the downstream Fwv: Water load produced by water weight Fu : Uplift force produced by groundwater W : The weight of the dam (W1, W2, W3) Free body diagram is shown in figure 4 The value of the forces, total vertical and total horizontal forces, and moments: W1 = 6 * ½ * 70 * 24 = 5040 kN XW1 = 1/3 * 6 + 4 + 45 = 51.00 m W1 * XW1 = 257040 kNm W2 = 4 * 70 * 24 = 6720 kN XW2 = ½ * 4 + 45 = 47.00 m W2 * XW2 =315840 kNm W3 = 45 * ½ * 70 * 24 = 37800 kN XW3 = 2/3 * 45 = 30.00 m W3 * XW3=1134000 kNm Fwv = 6 * ½ * 65 * 10 = 1950 kN Xwv = 2/3 * 6 + 4 + 45 = 53.00 m Fwv * XFv =103350 kNm Fwh = 65 * ½ * 65 * 10 = 21125 kN XFwh = 1/3 * 65 = 21.67 m Fwh * XFh =457779 kNm Fu = 65 * ½ * 55 * 10 = 17875 Kn XFu = 2/3 * 55 = 36.67 m Fu * XFu =655476 kNm MO = 457779 + 655476 = 1113255 kNm/m Mr = 257040 + 315840 + 1134000 + 103350 = 1810230 kNm/m V = W1 + W2 + W3 + Fwv - Fu = 33635 kN/m H = Fwh = 21125 kN/m FORCE (kN/m) MOMENT (kN/m/m) MOMENT ARM ABOUT O(m) 70 m 6 m 4 m 45 m 55 m O 65 m W1 W2 W3 Fwv Fwh Fu xm Figure 4
- 3. C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g F Fa ac cu ul lt ty y W WA AT TE ER R R RE ES SO OU UR RC CE ES S E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g D De ep pa ar rt tm me en nt t H Hy yd dr ra au ul li ic cs s 2 20 01 11 1- -F FA AL LL L E EX XE ER RC CI IS SE ES S 2 2- - D DA AM MS S - - A AC CT TI IN NG G F FO OR RC CE ES S Abdüsselam ALTUNKAYNAK www.altunkaynak.net Research Assist. İsmail DABANLI www.akademi.itu.edu.tr/dabanli Stability Check For the Whole Dam: 1. Overturning (F.S0): The dam must be safe against overturning for all loading conditions. F.S0 should be greater than 2.0 for usual loading, and than1.5 for unusual or severe loading. F.S0 = O r M M = 1113255 1810230 = 1.626 > 1.5 O.K. 2. Sliding (F.SS): The dam must be safe against sliding over any horizontal plane. F.SS should be greater than 1.5 for usual loading and than 1.0 for unusual or severe loading. F.SS = H V f = 21125 33635 7 . 0 = 1.11 > 1.0 O.K 3. Shear and sliding together (F.SSS): The dam must be also checked for shear and sliding together. F.SSS should be greater 5.0 for usual loading and 3.0 unusual and severe loading. F.SSS = H A V f S 5 . 0 = 21125 2200 55 5 . 0 33635 7 . 0 = 3.98 > 3.0 O.K. 4. Stress (max/min): The contact stress between the foundation and the dam must be greater than zero and all points or the dam will be unsafe against overturning. Maximum base pressure (max) should be less than the allowable compressive stress and minimum base pressure (min) should be greater than zero. V M M X O r = 33635 1113255 1810230 = 20.72 m e = 72 . 20 2 55 = 6.78 (eccentricity) M = V * e = 33635 * 6.78 = 228045.3 kNm/m (the net moment about the centerline of the base) C = 2 55 = 27.5 m I = 12 1 553 = 13864.58 m3 ( the moment of interia) I C M B V min max/ = 58 . 13864 5 . 27 3 . 228045 55 33635 max = 1063.87 kN/m2 < 2700 kN/m2 O.K. max = 159.22 kN/m2 > 0.00 kN/m2 O.K.
- 4. C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g F Fa ac cu ul lt ty y W WA AT TE ER R R RE ES SO OU UR RC CE ES S E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g D De ep pa ar rt tm me en nt t H Hy yd dr ra au ul li ic cs s 2 20 01 11 1- -F FA AL LL L E EX XE ER RC CI IS SE ES S 2 2- - D DA AM MS S - - A AC CT TI IN NG G F FO OR RC CE ES S Abdüsselam ALTUNKAYNAK www.altunkaynak.net Research Assist. İsmail DABANLI www.akademi.itu.edu.tr/dabanli SOLUTION 2 Forces and loads acting the dam: Fi : Ice Load (for cold climates and Fi1, and Fi2 for reservoir and tail water in the downstream, respectively) Fw: Water force produced by earthquake (Fw1, and Fw2 for reservoir and tail water in the downstream, respectively) Fwh: Hydrostatic force produced by water in the reservoir and tail water in the downstream (Fwh1, and Fwh2) Fwv: Water load produced by water weight (Fwv1, and Fwv2 for reservoir and tail water in the downstream, respectively) Fu : Uplift force produced by groundwater (since the tail water in the downstream, the diagram of uplift force will be in trapezoidal shape) W : The weight of the dam (W1, W2, W3…Wn) Fd : Earthquake forces (Fdh1 and Fdv1: horizontally and vertically) Free body diagram is shown in figure 4 Shear and sliding check due to ice force at the reservoir surface: Average shear stress: 5 90 = 18 kN/m2 << 2200 O.K. Sliding check: 90 25 5 5 75 . 0 = 5.21 >> 1.00 O.K. 55 m 6 m 5 m 30 m 41 m 50 m W1 W2 W3 Fwv1 Fwh1 Fu xm Fw1 Fi1 Fdv Fdh Figure 5 O 15 m Fwv2 Fwh2 Fw2 Fi2
- 5. C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g F Fa ac cu ul lt ty y W WA AT TE ER R R RE ES SO OU UR RC CE ES S E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g D De ep pa ar rt tm me en nt t H Hy yd dr ra au ul li ic cs s 2 20 01 11 1- -F FA AL LL L E EX XE ER RC CI IS SE ES S 2 2- - D DA AM MS S - - A AC CT TI IN NG G F FO OR RC CE ES S Abdüsselam ALTUNKAYNAK www.altunkaynak.net Research Assist. İsmail DABANLI www.akademi.itu.edu.tr/dabanli The value of the forces, total vertical and total horizontal forces, and moments: W1 = 50 * 6.0 * 0.5 *25 = 3750 kN 37.00 m 138750 kNm W2 = 55 * 5.0 * 1.0 *25 = 6875 kN 32.50 m 223438 kNm W3 = 50 * 30 * 0.5 * 25 = 18750 kN 20.00 m 375000 kNm Fwv1 = 50 * 6 * 0.5 * 10 = 1500 kN 39.00 m 58500 kNm Fwv2 = 15 * 9 * 0.5 * 10 = 675 kN 3.00 m 2025 kNm Fwh1 = 55 * 55 * 0.5*10 = 15125 kN 17.00 m 257125 kNm Fwh2 = 15 * 15 * 0.5*10 = 1125 kN 5.00 m 5625 kNm Fu =[(50+15)/2]*41*10*0.5= 6663 kN 23.30 m 168295 kNm FW1 = 0.726*C*k**h1 2 FW1 = 0.726*0.65*0.1*10*502 = 1180 kN 17.00 m 20056 kNm FW2 = 0.726*0.46*0.1*10*152 = 75 kN 5.00 m 375 kNm Fi1 = 90 kN 50.00 m 4500 kNm Fi2 = 90 kN 15.00 m 1350 kNm Fdv = k *W=0.1* 29375 =2937.5 kN 30.10 m 88419 kNm Fdh = k * W=0.1*29375 =2937.5 kN 20.64 m 60630 kNm Stability Check For the Whole Dam (When vertical Fd (Fdv) is considered): MO = 257125+168295+20056+4500+88419 = 538395 kNm/m Mr = 138750+223438+375000+58500+2025+5625+375+1350 = 805063 kNm/m V = W1 + W2 + W3 + Fwv1 + Fwv2- Fu -Fdv = 21950 kN/m H = Fwh1- Fwh2 + FW1 - FW2 + Fi1 - Fi2 = 15105 kN/m 1. Overturning (F.S0): The dam must be safe against overturning for all loading conditions. F.S0 should be greater than 2.0 for usual loading, and than1.5 for unusual or severe loading. F.S0 = O r M M = 538395 805063 = 1.495 < 1.5 NOT O.K. 2. Sliding (F.SS): The dam must be safe against sliding over any horizontal plane. F.SS should be greater than 1.5 for usual loading and than 1.0 for unusual or severe loading. F.SS = H V f = 15105 21950 65 . 0 = 0.94 < 1.0 NOT O.K. FORCE (kN/m) MOMENT (kN/m/m) MOMENT ARM ABOUT O(m)
- 6. C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g F Fa ac cu ul lt ty y W WA AT TE ER R R RE ES SO OU UR RC CE ES S E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g D De ep pa ar rt tm me en nt t H Hy yd dr ra au ul li ic cs s 2 20 01 11 1- -F FA AL LL L E EX XE ER RC CI IS SE ES S 2 2- - D DA AM MS S - - A AC CT TI IN NG G F FO OR RC CE ES S Abdüsselam ALTUNKAYNAK www.altunkaynak.net Research Assist. İsmail DABANLI www.akademi.itu.edu.tr/dabanli 3. Shear and sliding together (F.SSS): The dam must be also checked for shear and sliding together. F.SSS should be greater 5.0 for usual loading and 3.0 unusual and severe loading. F.SSS = H A V f S 5 . 0 = 15105 2200 41 5 . 0 21950 65 . 0 = 3.93 > 3.0 O.K. 4. Stress (max/min): The contact stress between the foundation and the dam must be greater than zero and all points or the dam will be unsafe against overturning. Maximum base pressure (max) should be less than the allowable compressive stress and minimum base pressure (min) should be greater than zero. V M M X O r = 21950 538395 805063 = 12.15 m e = 15 . 12 2 41 = 8.35 (eccentricity) M = V * e = 21950 * 8.35 = 183307 kNm/m (the net moment about the centerline of the base) C = 2 41 = 20.5 m I = 12 1 413 = 5743.42 m4 ( the moment of interia) I C M B V min max/ = 42 . 5743 5 . 20 183307 41 21950 max = 1189.64 kN/m2 < 2700 kN/m2 O.K. max = -118.91 kN/m2 < 0.00 kN/m2 NOT O.K. Stability Check For the Whole Dam (When horizontal Fd (Fdh) is considered): MO = 257125+168295+20056+4500+60630 = 510606.0 kNm/m Mr = 138750+223438+375000+58500+2025+5625+375+1350 = 805063.0 kNm/m V = W1 + W2 + W3 + Fwv1 + Fwv2 - Fu = 19012.5 kN/m H = Fwh1- Fwh2 + FW1 - FW2 + Fi1 - Fi2 + Fdh = 18042.5 kN/m
- 7. C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g F Fa ac cu ul lt ty y W WA AT TE ER R R RE ES SO OU UR RC CE ES S E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g D De ep pa ar rt tm me en nt t H Hy yd dr ra au ul li ic cs s 2 20 01 11 1- -F FA AL LL L E EX XE ER RC CI IS SE ES S 2 2- - D DA AM MS S - - A AC CT TI IN NG G F FO OR RC CE ES S Abdüsselam ALTUNKAYNAK www.altunkaynak.net Research Assist. İsmail DABANLI www.akademi.itu.edu.tr/dabanli 1. Overturning (F.S0): The dam must be safe against overturning for all loading conditions. F.S0 should be greater than 2.0 for usual loading, and than1.5 for unusual or severe loading. F.S0 = O r M M = 510606 805063 = 1.58 > 1.5 O.K. 2. Sliding (F.SS): The dam must be safe against sliding over any horizontal plane. F.SS should be greater than 1.5 for usual loading and than 1.0 for unusual or severe loading. F.SS = H V f = 5 . 18042 5 . 19012 65 . 0 = 0.65 < 1.0 NOT O.K. 3. Shear and sliding together (F.SSS): The dam must be also checked for shear and sliding together. F.SSS should be greater 5.0 for usual loading and 3.0 unusual and severe loading. F.SSS = H A V f S 5 . 0 = 5 . 18042 2200 41 5 . 0 5 . 19012 65 . 0 = 3.19 > 3.0 O.K. 4. Stress (max/min): The contact stress between the foundation and the dam must be greater than zero and all points or the dam will be unsafe against overturning. Maximum base pressure (max) should be less than the allowable compressive stress and minimum base pressure (min) should be greater than zero. V M M X O r = 5 . 19012 510606 805063 = 15.49 m e = 49 . 15 2 41 = 5.0 (eccentricity) M = V * e = 19012.5 * 5.0 = 95299.25 kNm/m (the net moment about the centerline of the base) C = 2 41 = 20.5 m I = 12 1 413 = 5743.42 m4 ( the moment of interia) I C M B V min max/ = 42 . 5743 5 . 20 25 . 95299 41 5 . 19012 max = 803.87 kN/m2 < 2700 kN/m2 O.K. max = 123.57 kN/m2 > 0.00 kN/m2 O.K.
- 8. C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g F Fa ac cu ul lt ty y W WA AT TE ER R R RE ES SO OU UR RC CE ES S E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g D De ep pa ar rt tm me en nt t H Hy yd dr ra au ul li ic cs s 2 20 01 11 1- -F FA AL LL L E EX XE ER RC CI IS SE ES S 2 2- - D DA AM MS S - - A AC CT TI IN NG G F FO OR RC CE ES S Abdüsselam ALTUNKAYNAK www.altunkaynak.net Research Assist. İsmail DABANLI www.akademi.itu.edu.tr/dabanli SOLUTION 3 2 2 Sin B r = 2 120 2 300 Sin = 173 m Thickness at the base: tb = all r h = 6200 173 120 10 = 33.5 m 173 10 6200 6 h = 21.5 m L = r * = 120 180 173 = 362 m VT = L h h t b h b b 2 = 362 5 . 21 120 2 5 . 33 6 5 . 21 6 = 750924 m3 SOLUTION 4 The optimum central angle for a minimum volume of arch rib can be determined by differentiating the equation written below with respect to and equating to zero. V = all r h 2 V’ = Continue 120o 6 m 300 m 120o 6 m 300 m h*=21.5 m 6 m tb = 33.5 m 120 m Figure 6 Figure 7
- 9. C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g F Fa ac cu ul lt ty y W WA AT TE ER R R RE ES SO OU UR RC CE ES S E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G C Ci iv vi il l E En ng gi in ne ee er ri in ng g D De ep pa ar rt tm me en nt t H Hy yd dr ra au ul li ic cs s 2 20 01 11 1- -F FA AL LL L E EX XE ER RC CI IS SE ES S 2 2- - D DA AM MS S - - A AC CT TI IN NG G F FO OR RC CE ES S Abdüsselam ALTUNKAYNAK www.altunkaynak.net Research Assist. İsmail DABANLI www.akademi.itu.edu.tr/dabanli SOLUTION 5 a) 2 2 Sin B r = 2 150 2 350 Sin = 181 m Thickness at the base: tb = all r h = 5500 181 75 10 = 24.7 m 181 10 5500 6 h = 18.23 m b) t30 = 5500 181 30 10 = 9.87 m c) V = all r h 2 = 150 180 5500 181 75 10 2 = 11695.65 m3 /m d) L = r * = 150 180 181 = 474 m VT = L h h t b h b b 2 = 474 23 . 18 75 2 7 . 24 6 23 . 18 6 = 464899 m3 hx=18.23 m 6 m tb=24.7 m 75 m Figure 8