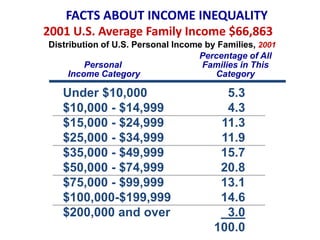
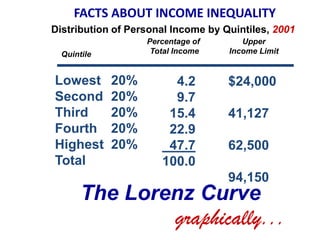
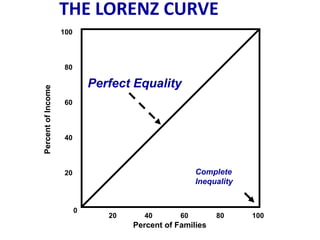
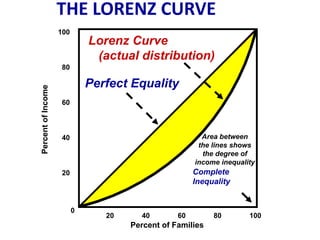
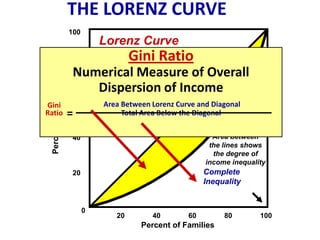
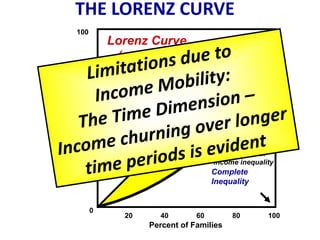
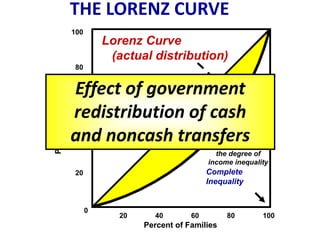
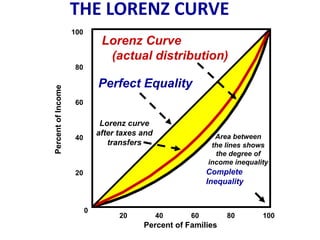
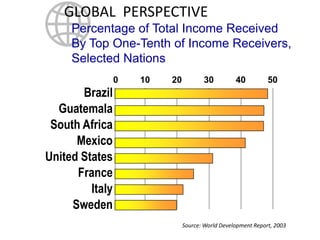
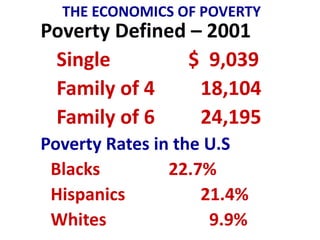
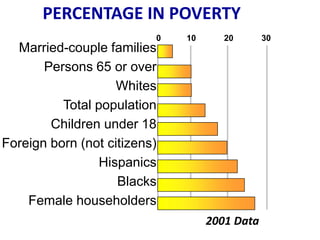
This document discusses income inequality and poverty in the United States. It provides data on income distribution among American families in 2001, showing that the top 20% of families earned 47.7% of all income while the lowest 20% earned only 4.2% of income. It also examines trends in inequality over time and potential causes. Additionally, it defines poverty, provides poverty rates for different demographic groups, and outlines the major public assistance programs that aim to support those in poverty.