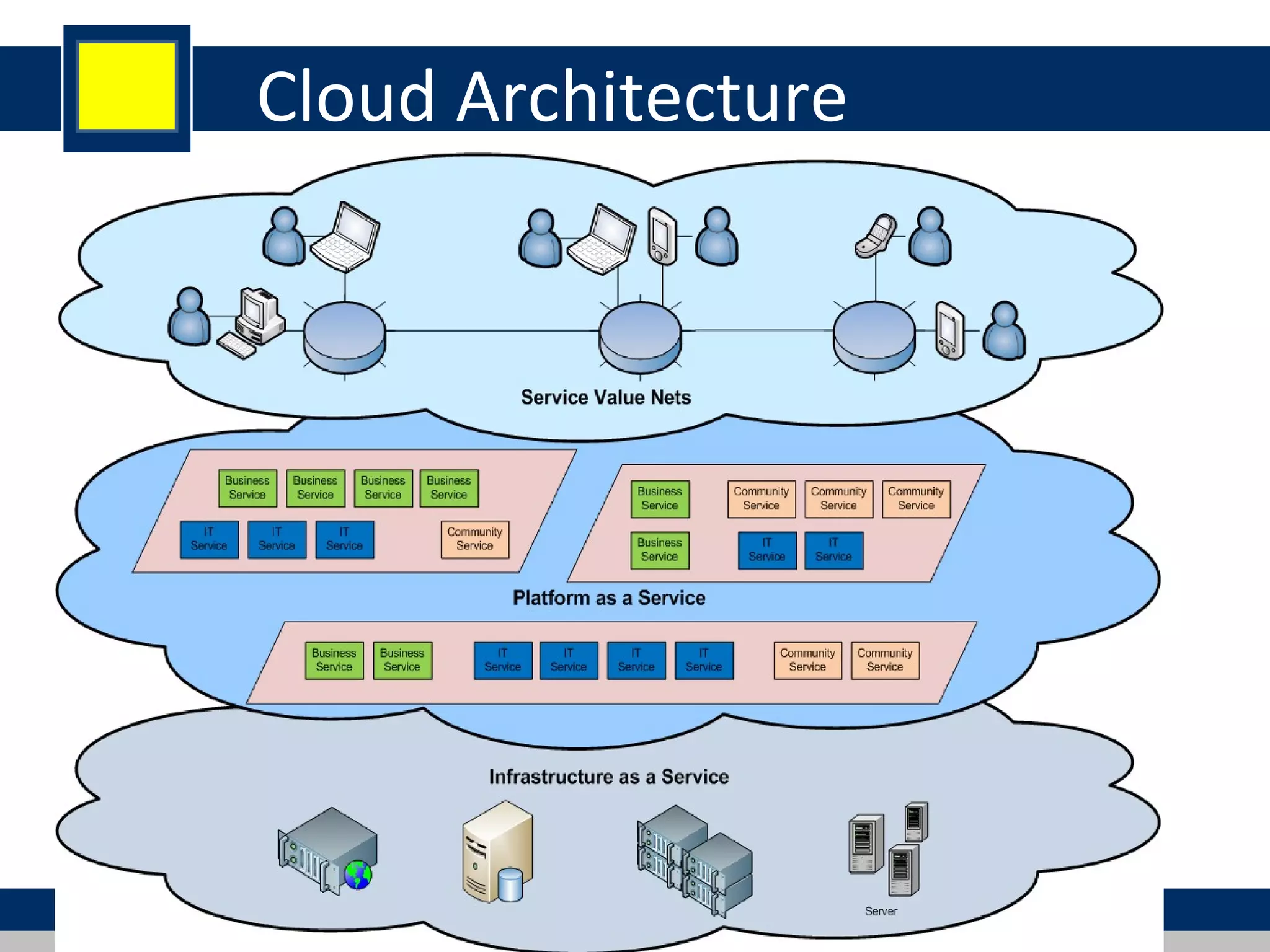
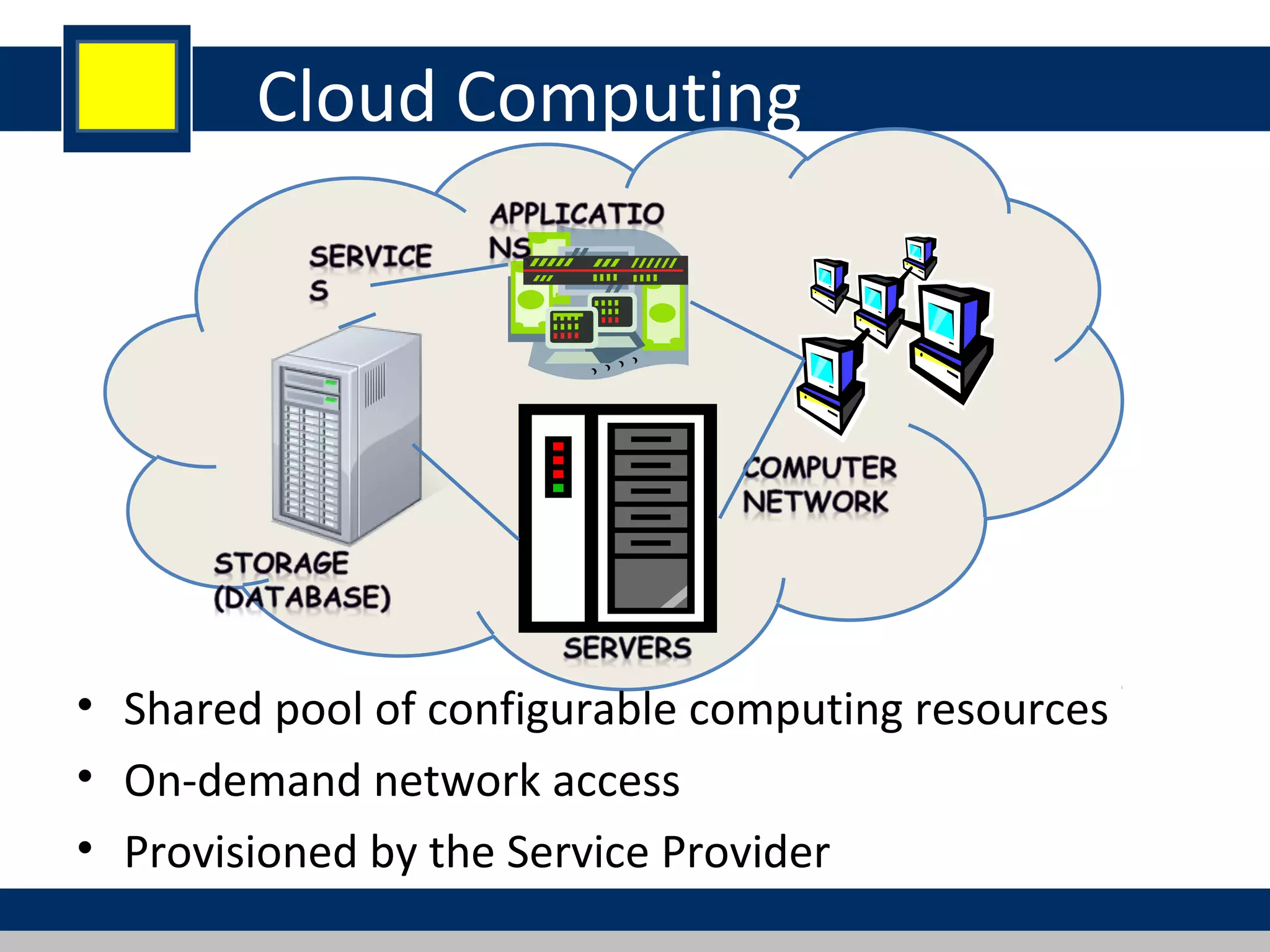
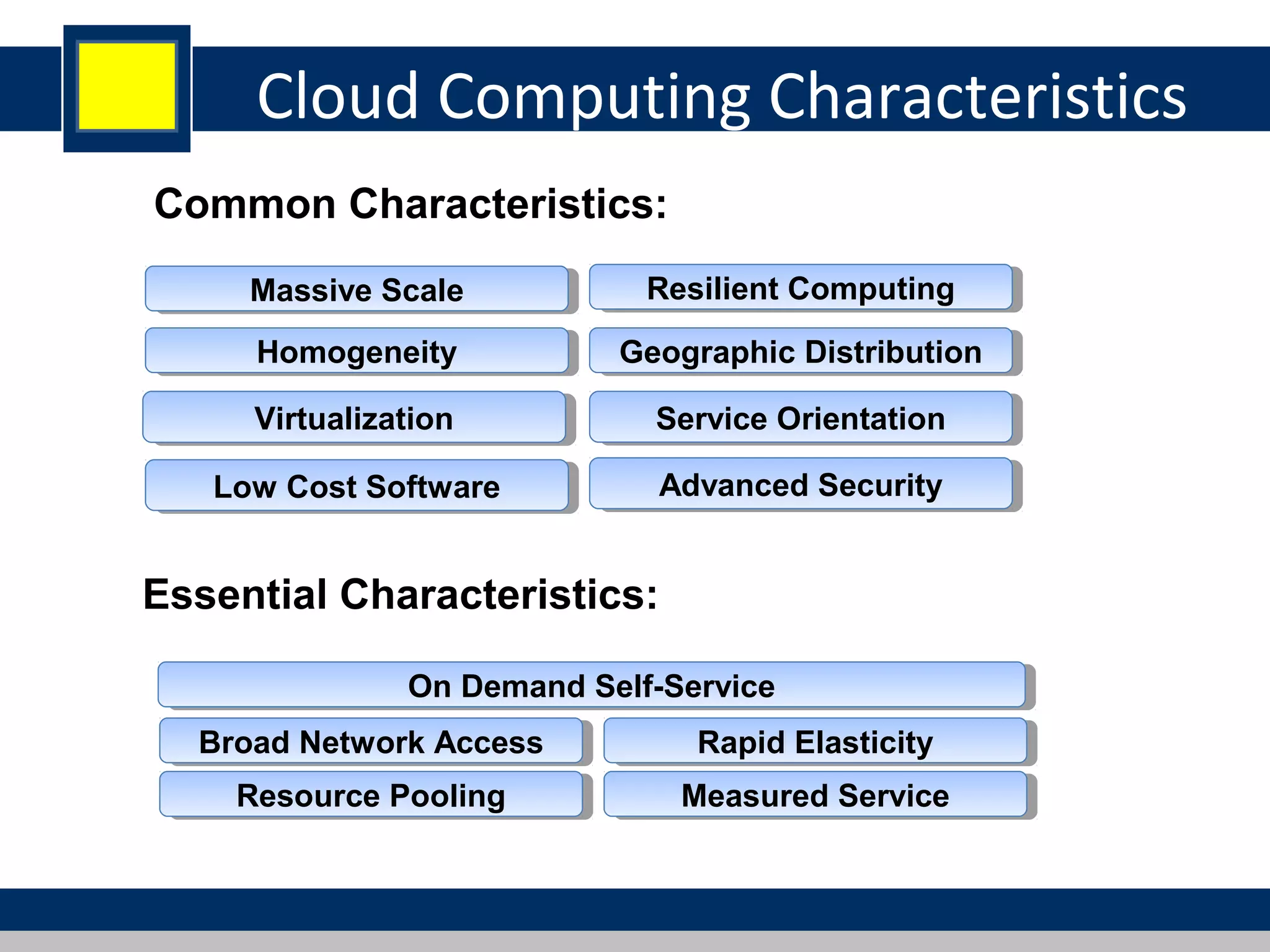
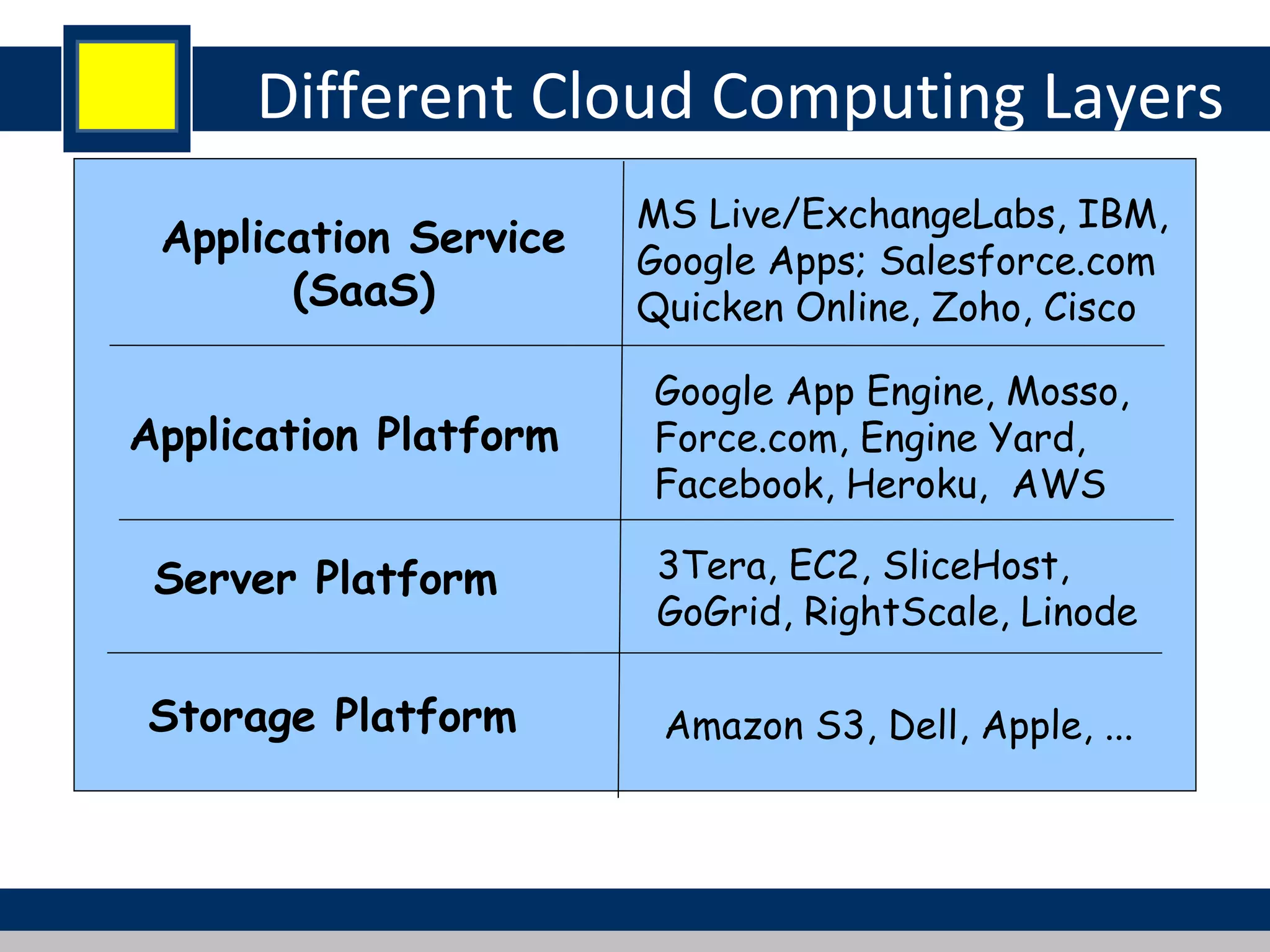
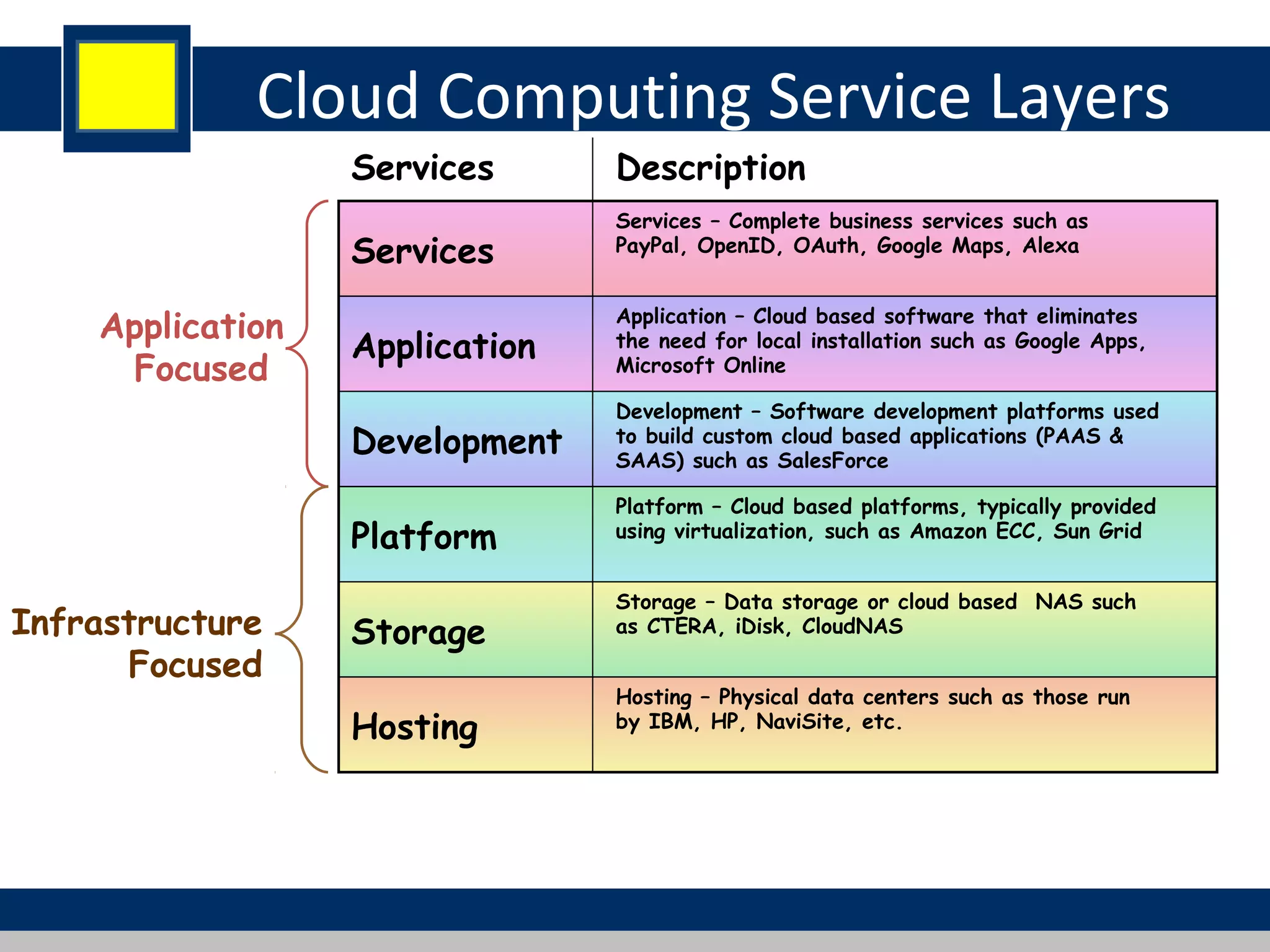
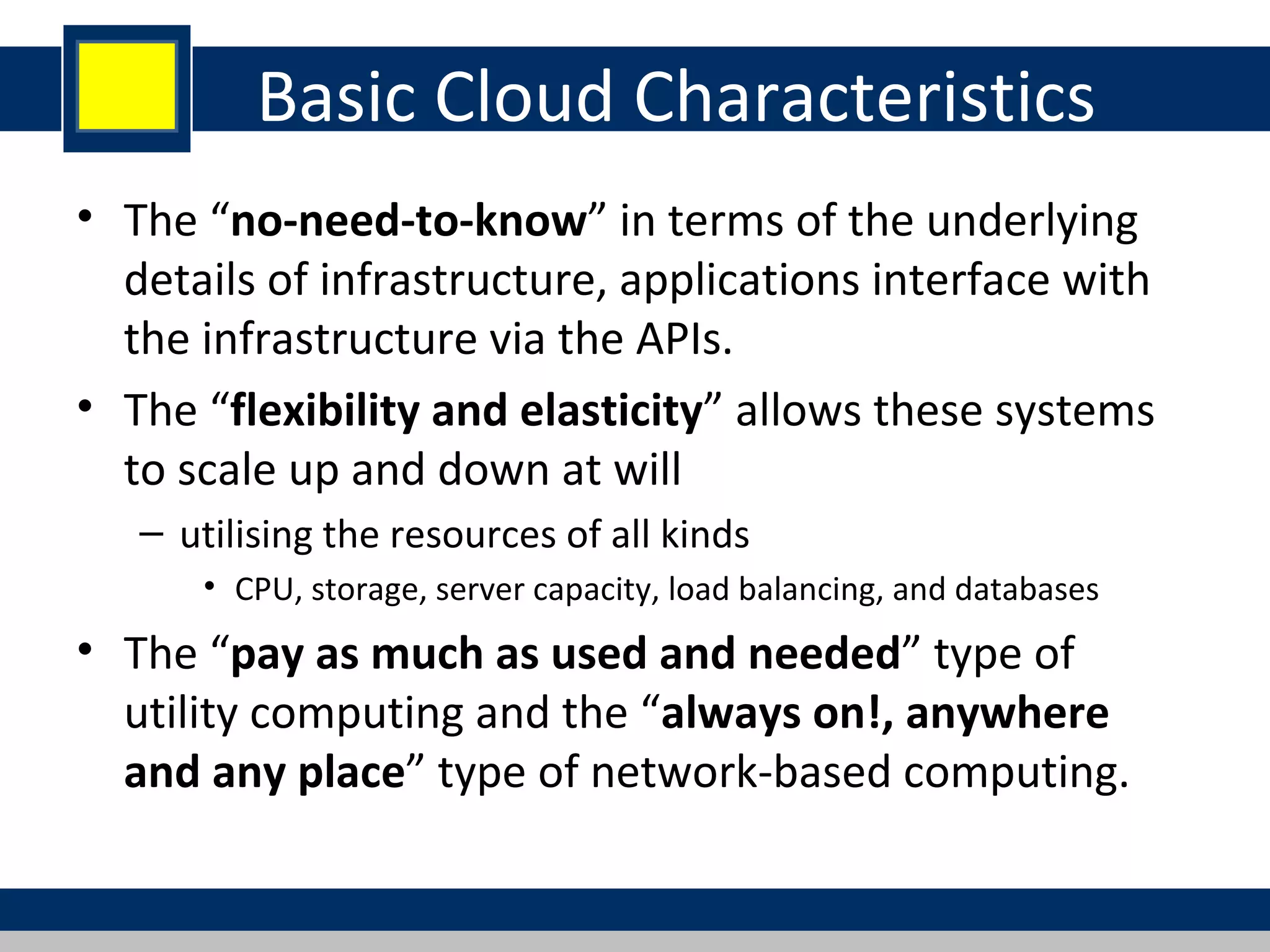
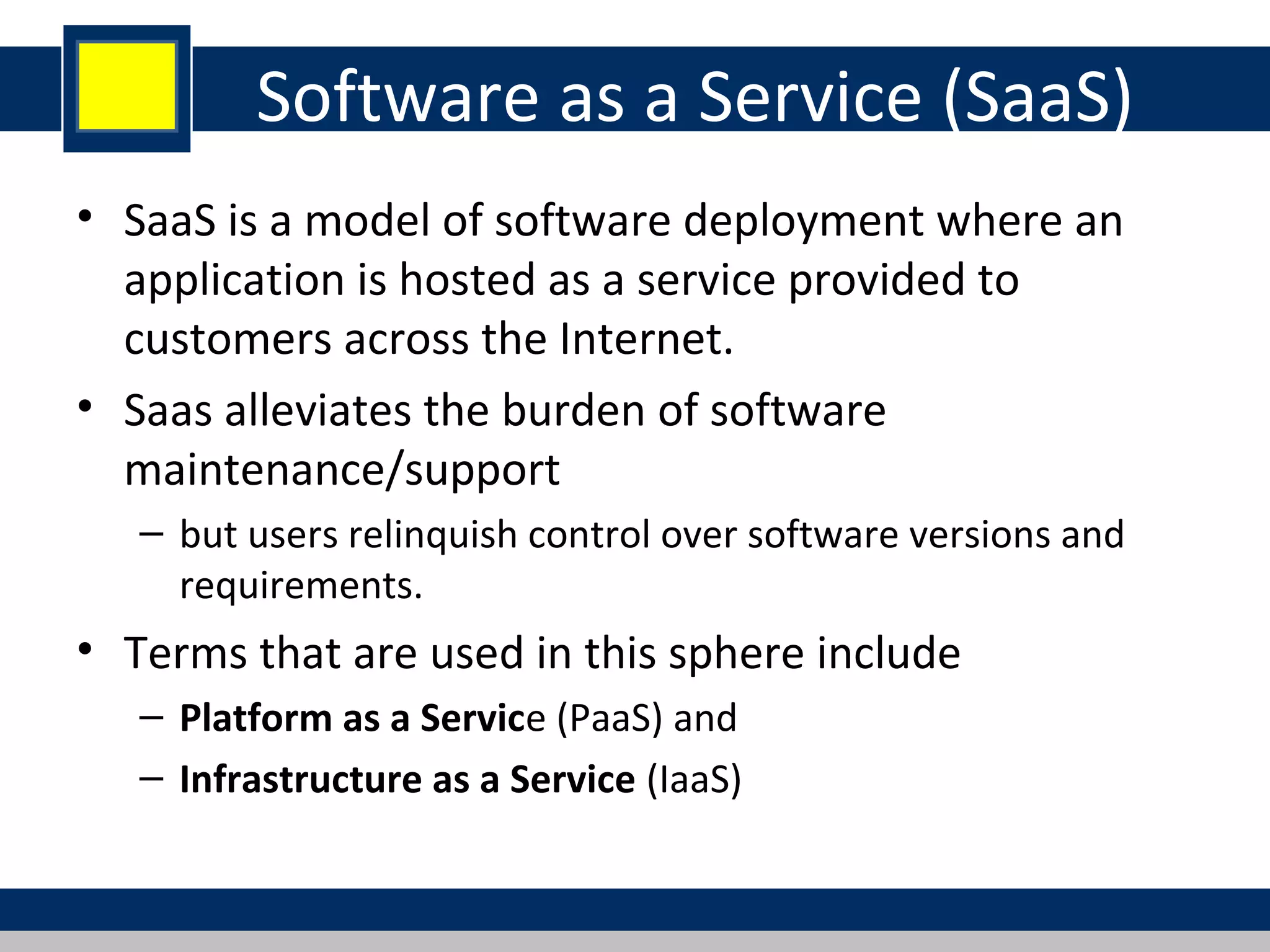
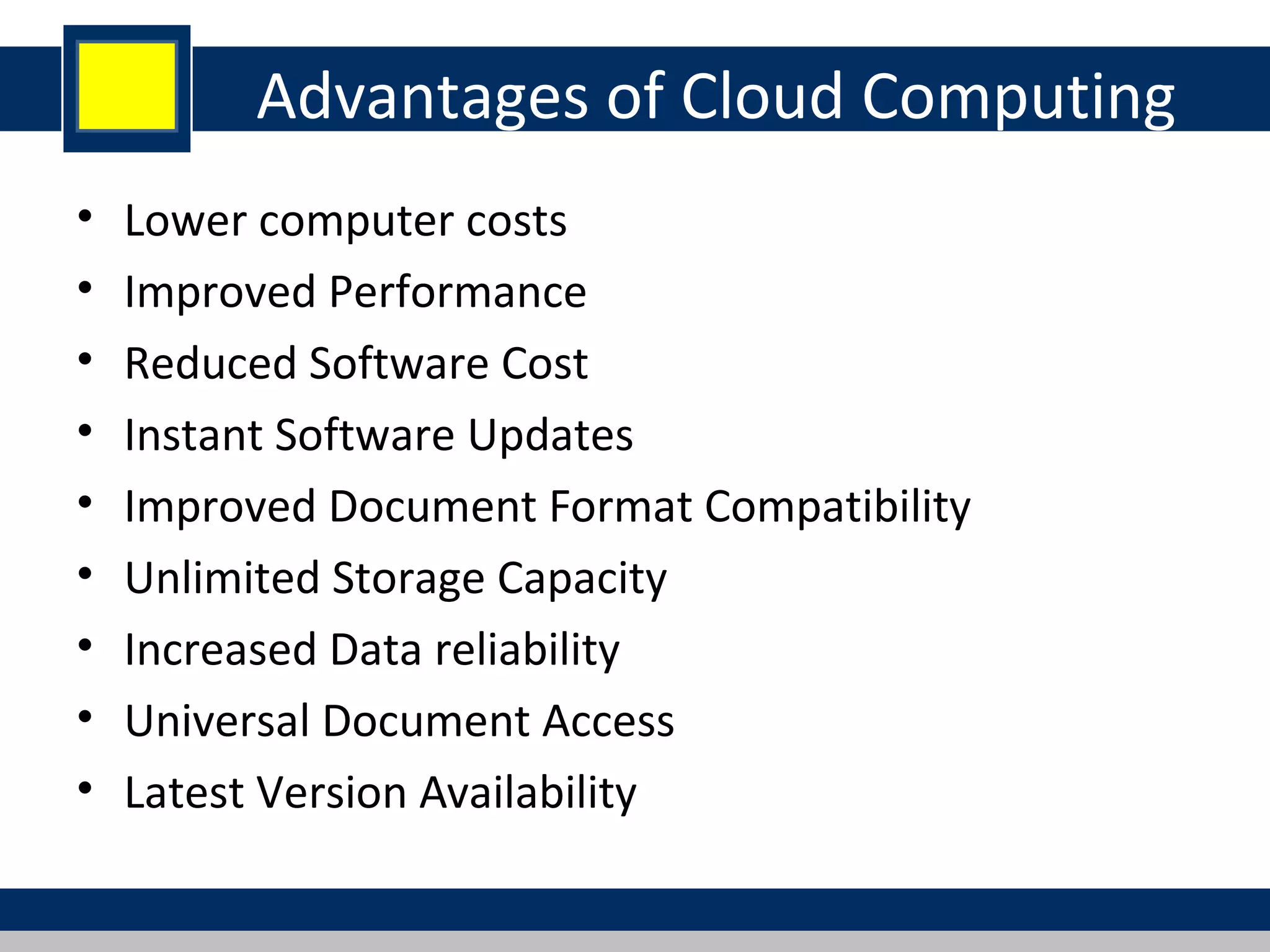
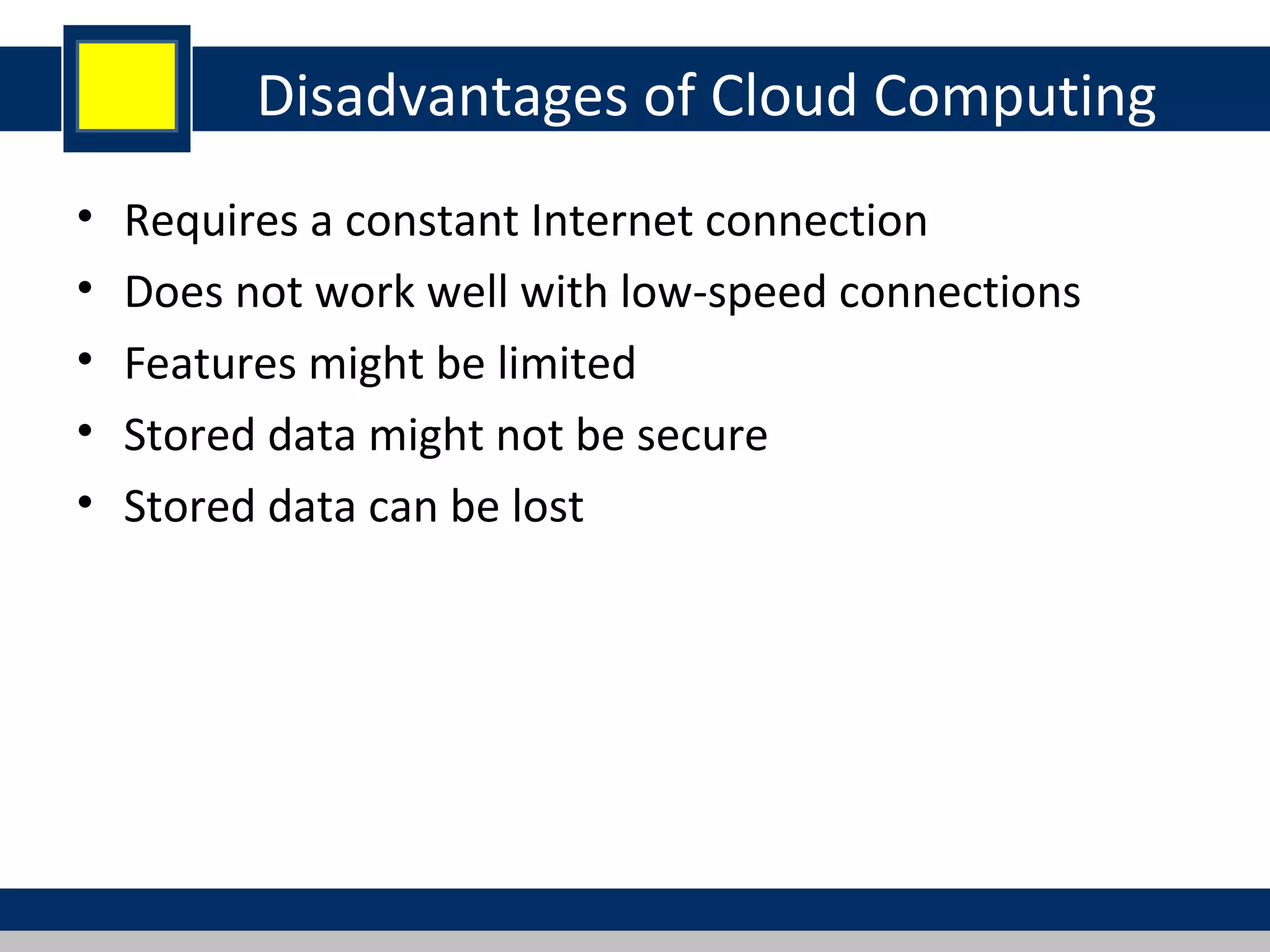
Cloud computing refers to network-based computing that provides on-demand hardware, software, and networking services over the internet, allowing users to access resources anytime and anywhere. It includes various service models such as Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), all designed to minimize the complexity of infrastructure management. While cloud computing offers significant advantages like lower costs and improved performance, it also presents challenges such as dependency on internet connectivity and potential data security issues.