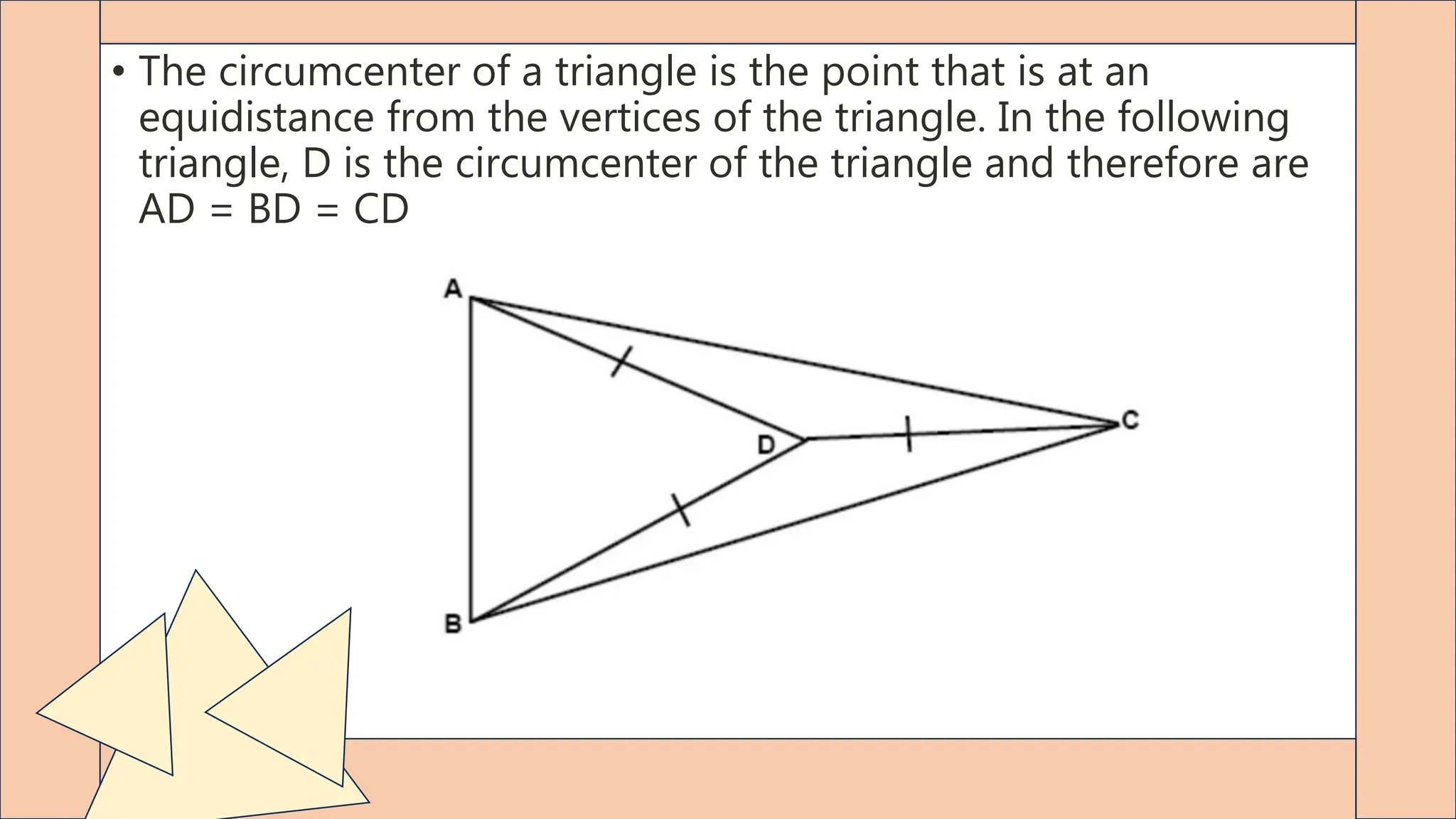
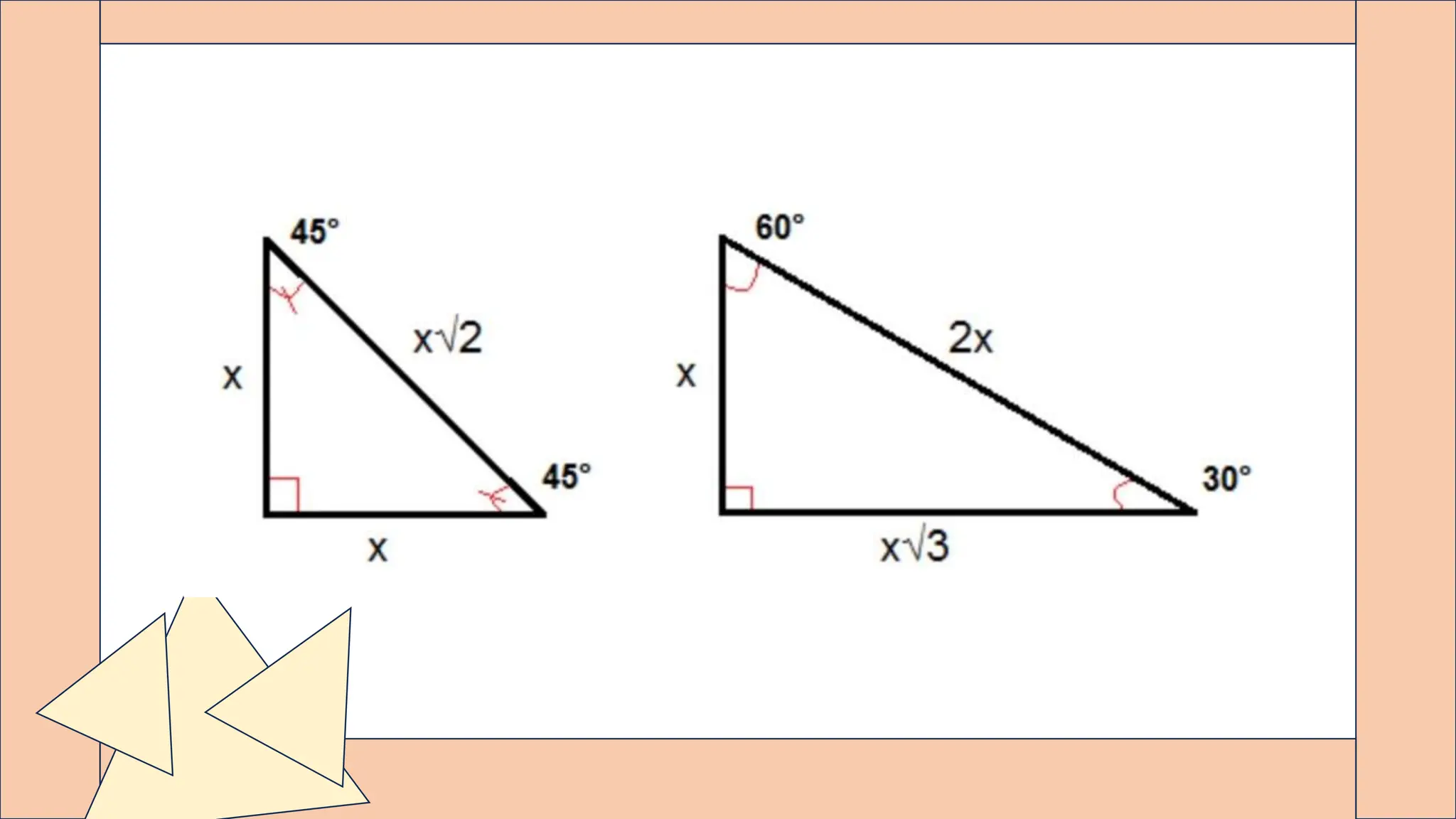
This document provides an overview of key geometry concepts including points, lines, planes, angles, parallel lines, triangles, trigonometry, quadrilaterals, and polygons. It defines a point as having no size, a line as extending infinitely in two directions with length but no width, and parallel lines as two lines that never intersect. The document also discusses the circumcenter of a triangle, using the Pythagorean theorem to determine right triangles, Pythagorean triples, special right triangles, and the formula to find the sum of interior angles in any polygon based on the number of sides.