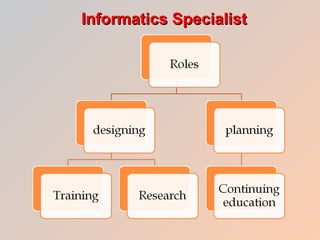
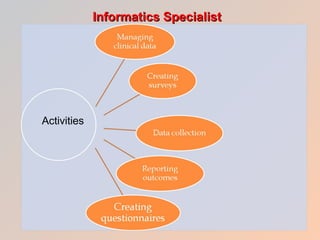
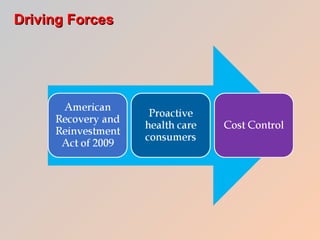
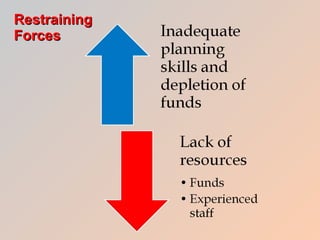
The document discusses how health care informatics and computerized physician order entry (CPOE) systems can improve patient care by decreasing medication errors and reducing health care costs. CPOE systems work to prevent errors from incorrect data entry, transcription errors, and clinical errors. They also aim to reduce reimbursement problems from billing errors. The role of informatics specialists is to support electronic medical records and network environments while maintaining professional ethics. CPOE systems allow physicians to correctly order medications, dosages, and check for contraindications, thereby preventing errors and improving patient care.