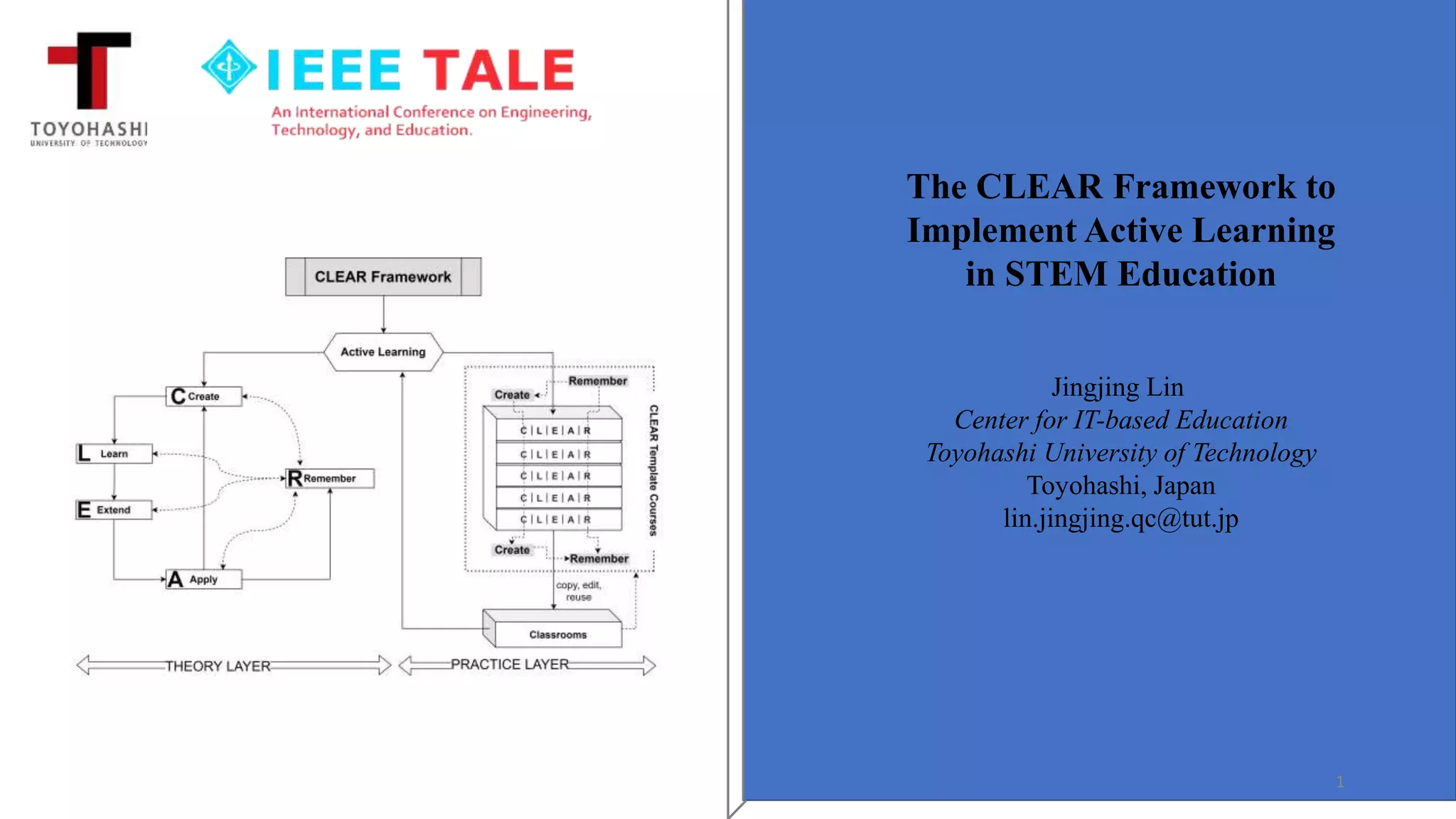
The document outlines the CLEAR (Create, Learn, Extend, Apply, and Remember) framework for active learning in STEM education. The framework is based on Bloom's taxonomy and promotes starting with higher-order cognitive activities like creating before remembering materials. It provides both a theoretical model and practical guidelines for implementing active learning through template courses. Ongoing work is validating the effectiveness of the CLEAR model through literature reviews, expert interviews, and controlled experiments.