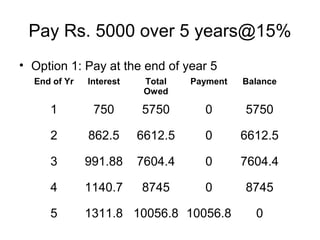
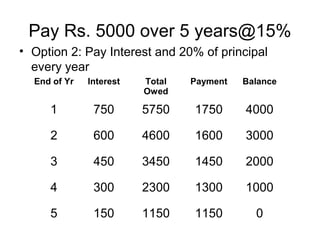
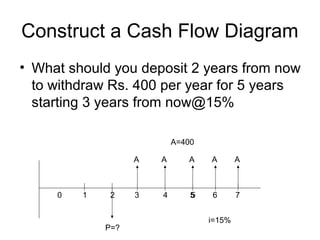
This document discusses time value of money concepts like interest, interest rates, equivalence, and cash flow diagrams. It provides examples of calculating interest on loans and investments over time at different interest rates. It also discusses equivalence and retirement planning examples comparing investing small amounts each year versus delaying investments. Constructing cash flow diagrams is introduced as a way to visualize money flows over time under different scenarios.







![In Class Exercise
• Your friend tells you that he has just
repaid a loan he got 3 years ago at 10%
per year. You learn that he has just paid
Rs. 200. How much did he borrow?
• P = F/[(1+i)^n]
– P= 200/(1.10^3)
– P= Rs. 150](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-151111183154-lva1-app6891/85/1-interest-and-equivalence-11-320.jpg)

