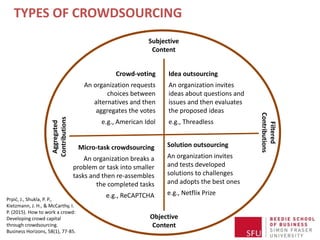
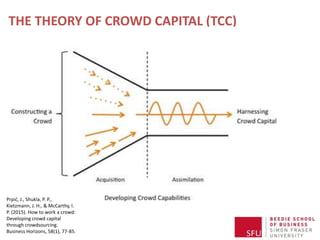
The document discusses how to effectively engage crowds for organizational purposes through crowdsourcing, defining it as utilizing information technologies to outsource business responsibilities. It outlines different types of crowdsourcing, including crowd-voting, idea crowdsourcing, micro-task crowdsourcing, and crowdsourcing solutions, while introducing the theory of crowd capital as a framework for managing and maximizing crowd contributions. Key steps for successful crowdsourcing include determining the purpose, defining the participant population, setting rules, and identifying necessary technologies.