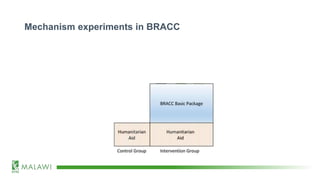
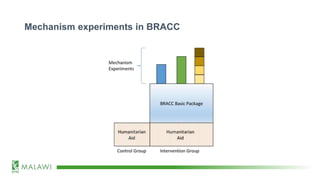
The document discusses existing and proposed mechanism experiments under the BRACC program in Malawi, focusing on the impact and demand for funeral and health insurance, as well as weather index insurance. The experiments utilize randomized control trials and qualitative investigations to understand behavior and quantify mechanisms in the theory of change. Proposed mechanisms also explore the effects of predictability in humanitarian assistance and various dimensions influencing insurance demand and consumption behaviors.



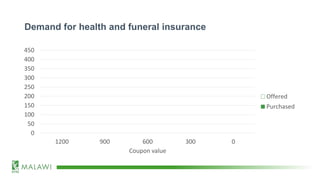
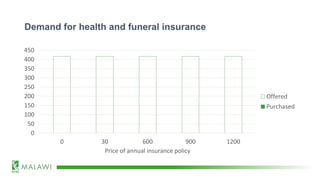
![Demand for health and funeral insurance
[CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE]
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
0 30 600 900 1200
Price of annual insurance policy
Offered
Purchased](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanismexperimentsjanduchoslav12feb2020-200221175251/85/Mechanism-Experiments_presented-by-Jan-Duchoslav_BRACC-resilience-learning-event_12-Feb-2020-9-320.jpg)
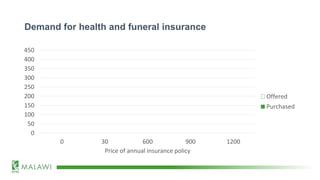
![Demand for health and funeral insurance
[CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE]
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
0 30 600 900 1200
Price of annual insurance policy
Offered
Purchased](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanismexperimentsjanduchoslav12feb2020-200221175251/85/Mechanism-Experiments_presented-by-Jan-Duchoslav_BRACC-resilience-learning-event_12-Feb-2020-10-320.jpg)
![Demand for health and funeral insurance
[CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE]
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
0 30 600 900 1200
Price of annual insurance policy
Offered
Purchased](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanismexperimentsjanduchoslav12feb2020-200221175251/85/Mechanism-Experiments_presented-by-Jan-Duchoslav_BRACC-resilience-learning-event_12-Feb-2020-11-320.jpg)
![Demand for health and funeral insurance
[CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE]
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
0 30 600 900 1200
Price of annual insurance policy
Offered
Purchased](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanismexperimentsjanduchoslav12feb2020-200221175251/85/Mechanism-Experiments_presented-by-Jan-Duchoslav_BRACC-resilience-learning-event_12-Feb-2020-12-320.jpg)
![Demand for health and funeral insurance
[CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE]
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
0 30 600 900 1200
Price of annual insurance policy
Offered
Purchased](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanismexperimentsjanduchoslav12feb2020-200221175251/85/Mechanism-Experiments_presented-by-Jan-Duchoslav_BRACC-resilience-learning-event_12-Feb-2020-13-320.jpg)

