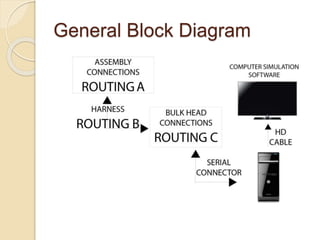
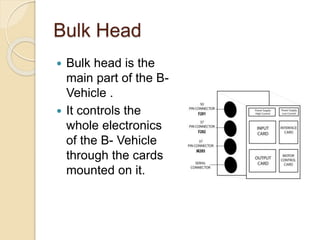
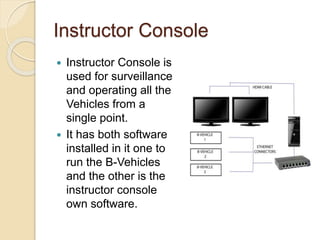
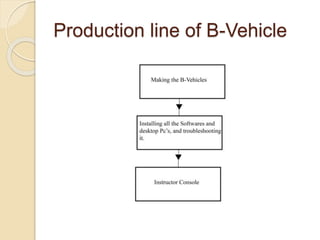
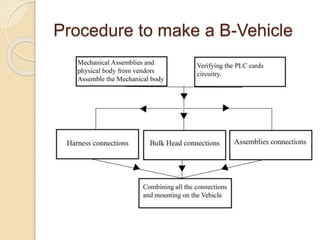
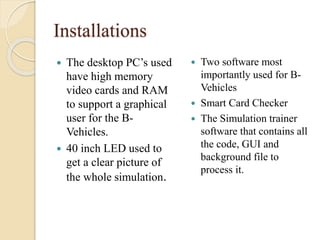
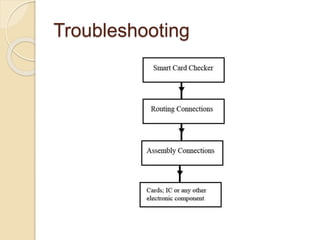
Huzaifa Asghar Ali completed an 8-week internship at DCC Tech where he worked on the B-Vehicle Simulator project. He helped build 12 B-Vehicles from scratch which simulate vehicles and will be deployed soon. He also worked on their bus ticketing system. The B-Vehicles use a bulk head to control electronics through mounted cards and have mechanical assemblies like dashboards. Troubleshooting methods include checking the smart card checker, routing connections, assembly connections, and replacing cards if needed. Recommendations include using a more advanced motherboard, improving the software graphics and training, and making the simulator structure and steering wheel size match original vehicles.