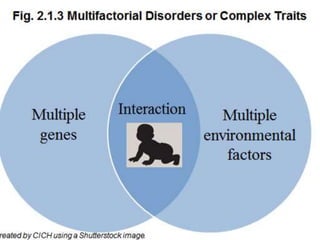
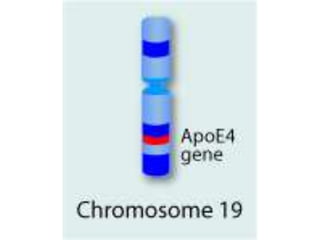
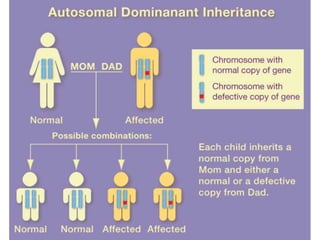
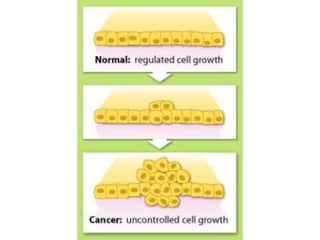
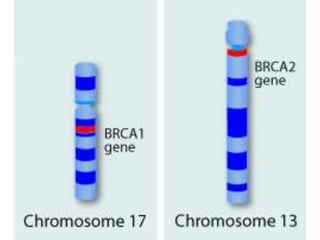
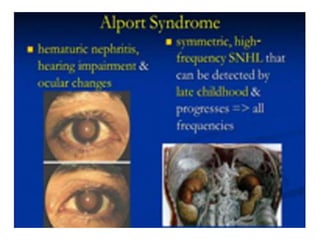
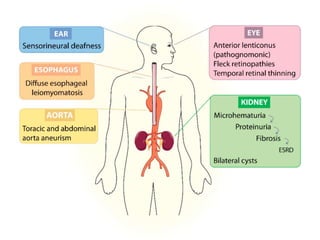
Multifactorial disorders result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Alzheimer's disease is caused by plaques and tangles in the brain that damage cells. The ApoE4 gene increases Alzheimer's risk. Breast and ovarian cancers are sometimes caused by mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 tumor suppressor genes, which increase cancer risk if inherited. Williams syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by distinctive facial features, developmental delays, and medical problems. Alport syndrome is a genetic kidney disease caused by mutations in collagen genes and presents with hematuria, kidney failure, and eye and hearing issues. It has no cure and treatment focuses on slowing disease progression.