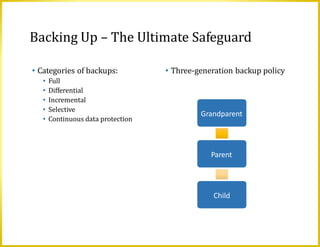
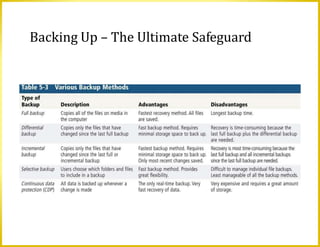
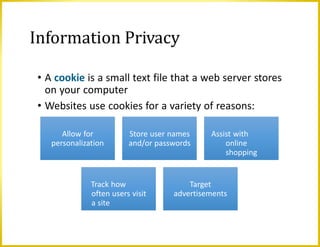
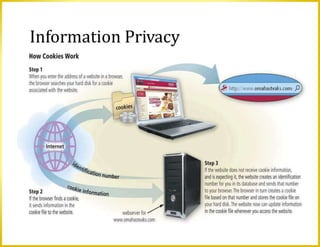
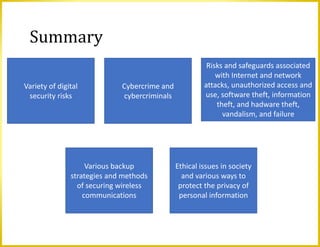
This document discusses a variety of digital security risks including cybercrime, internet and network attacks, unauthorized access and use, software theft, information theft, hardware theft and failure. It describes safeguards such as backups, wireless security, ethics in society and protecting personal information privacy. Issues around intellectual property rights, codes of conduct, information accuracy and green computing are also addressed.