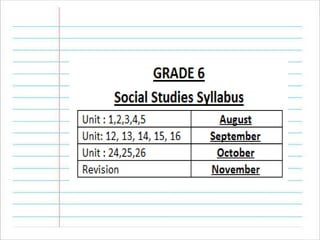
Grade 6 sst august planner
- 3. Title page 15 Aug 21
- 4. Contents: Words Meanings Fill in the blanks Underline true statements Match the column Three Questions Answers Draw Timeline page 2 and 3 (homework) 15 Aug 21
- 5. Words Meanings 1. Civilization society and culture of particular area. 2. Empire Kingdom 3. Constitute be a part of whole 4. Terrain landscape, territory 5. Ancient belonging to past 6. Prosperious bringing wealth and success 7. Ethnicity social behaviour 8. Era time period
- 6. 15 Aug 21 a) A Subcontinent is a distinctive mass of land that makes up a large part of a continent. b) The Indian subcontinent is a region with abundant resources. c) The subcontinent was always able to support large population. d) China is located in the North East of the subcontinent. e) An environment in which different people, cultures, and lifestyles are mixed together, is called a melting pot
- 7. 17 Aug 21 a) Arabian Sea is in the south-west of the subcontinent. b) The subcontinent was always a poor region with no natural resources. c) One of the reasons for studying the ancient history of the subcontinent is to know how we link to the past and how it has affected the modern world. d) ce stands for Common East.
- 8. 16 Aug 21 Q1. Which modern countries make up the subcontinent ? Ans: Subcontinent comprises Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal and Bhutan. Q2. Why was the subcontinent a suitable place for settlement? Ans: Geographically, Subcontinent has its own importance. Favorable climate, fertile land, natural resources are the main reasons for settlement. Q. Why do we study the people of subcontinent from ancient times to present? Ans: It is very important to study history of subcontinent so that we can: a. Understand how people, countries and system have evolved. b. Find out how culture and traditions are developed. c. Plan our future by learning from history.
- 9. Column A Column B CE stands for Common Era BCE stands for before Common Era BC stands for Before Christ West of Pakistan Iran South west of Pakistan Arabian Sea 17 Aug 21
- 10. B o o k p a g e n o . 2 a n d 3
- 12. 17 Aug 21
- 13. Words Meanings Short Questions Answers True and false Fill in the blanks Match the column MCQs Identify the pictures Long Questions Answers 18 Aug 21
- 14. 18 Aug 21 Words Meaning Archaeologist a person who studies human history Flourishing growing and developing strongly Deciphered Unusual language Klin fired brick Red color cooked bricks Downtrodden treated badly by people in power Chariots horse cart Artifact historical object made by human. Descended tp have origin or source Tributaries a river or stream flowing into a larger river or lake
- 15. 19 Aug 21 Q1:What was the first known settlement of the Indus Valley Civilization? Ans:Mehergarh. Q2:Why do we believe that the people of the Indus did not fight any wars? Ans:No weapons and drawing have been found in artifact Q3:What two Questions about this civilization remained unanswered to date? Ans:1. what the writing means and 2. how civilization ended? Q4:What did Aryans learn from local people? Ans:Aryan learnt Farming.
- 16. 1. The Aryans came from the Ural Mountains. True 2. They were basically traders who came to buy and sell goods. False 3. The Aryans introduced chariots and the use of bow and arrow to this region. True 4. The language of the Aryans was Urdu. False 5. The Aryans did not encourage religion. False 20 Aug 21
- 17. 20 Aug 21 a) The people of Harappa were hindu. b) Much of the present day culture in India and Hinduism can be traced back to the Aryans. c) The Aryans came down to the Indus Valley region through the Hindukush Mountains. d) The Ural Mountains are located near modern Western Russia. e) The People of the Indus earned through trade and farming .
- 18. 20 Aug 21 Column A Column B Earliest people in Indus valley Dravidians Harapans were good bricks makers Metals were introduced by Aryans Religious literature of Aryans Vedas Shurdas were Lower caste Brahmin were Highest caste
- 19. 21 Aug 21 a) Anything that gives people reason to believe something (evidence, trust, faith) b) Income from taxes (gift, revenue, budget) c) Worked out the meaning of something written in code or unusual language (help, struggle, decipher) d) To grow or develop strongly (permit, flourish, perish) e) Bring back to life (revive, invite, refuse)
- 20. 21 Aug 21 •The sculpture of the King priest from Mohen jo Daro •Bronze statue referred as Dancing Girl •Writing on the seal which has not been understood
- 21. 22 Aug 21 Q1. How did the Aryans structure society? Ans: Aryan society was divided into social classes. ... This caste system became more complex, dividing Indian society into groups based on rank, wealth or occupation. Castes were family based. The four broad ranks of the caste system in the Indo-Aryan culture, which included 1. Brahmins were priests and scholars 2. Kshatriyas were kings, governors and warriors. 3. Vaishyas were cattle herders, agriculturists, artisans, and merchants 4. Shudras were laborers and service providers.
- 22. Q2. What do you know about earliest people in the Indus Valley? Ans: The earliest people in the Indus valley are known as Dravidians. They move and spread to the southern part India and Sri Lanka. They spoke Dravidian languages. They were very civilized. They were no evidence of weapons found and drawing of battles so we consider that they were peaceful. They traded along the Indus. Taxes were a part of their revenue system. The written language is still deciphered and no one knows how this civilization ended. Some historians suggest that Aryans killed them and some historians suggest that they move from somewhere else.
- 24. 24 Aug 21
- 25. Contents Words Meanings Fill in the blanks MCQs True and false Match the column Questions Answers Label the eight fold path 24 Aug 21
- 26. 24 Aug 21 Words Meanings Astrologer A person who predict future Circumstances Situations Encounter Experience, come across Mediating Thinking deeply Contentment State of happiness Enlightened Spiritually aware
- 27. 24 Aug 21 a) Buddha was born in 565 BCE. b) King Suddhodhana and Queen Maya were Buddha’s parents. c) Siddharth was the prince of Nepal . d) Siddharth realized that humans suffered because of their greed . e) Buddha died in 483 BCE.
- 28. 25 Aug 21 a) Samsara means i. Death ii. Rebirth iii. Popularity b) Good actions that support universal law are called i. Nirvana ii. Dharma iii. Moksha c) The word Buddha means i. The enlightened one ii. The great one iii. The peaceful one d) One of the reasons for the popularity of Buddhism was i. Unpopularity of Buddha ii. Popularity of Hinduism iii. Unpopularity of the caste system
- 29. 25 Aug 21 1. After 29 years Sidharth came out of palace first time. True 2. Prince Sidharth known as Gautam Buddha. True 3. Getting rid of desires is the way to prevent caste system. False 4. Buddha’s and Muslim’s concept about life after death are same. False 5. Buddha was against the caste System. True
- 30. Column A Column B Real name of Buddha Suddhodhana Maya was Queen Sidharth is a prince of Nepal Samara means rebirth Buddha means enlightened 25 Aug 21
- 31. 25 Aug 21 Q1: Define the terms: Karma, Dharma, Nirvana? Ans: Karma: karma means all those action of a person which effect his fate in this life and the next. Dharma: Dharma means the eternal law which the universe follows, good actions which support the universal law are also known as dharma. Nirvana: nirvana means a state of perfect happiness where there is no suffering or desire. Q2. How did Buddhism change people’s lives? Ans: Rejecting the caste system and it preached total equality. This brought the biggest change in people’s live. Every people got their self-respect and dignity.
- 32. Q. Who was Buddha and what did he teach? Ans: The real name of Buddha is Sirdhath. He was a prince of Nepal. He left his kingdom for the search of inner peace. He introduced the new religion as Buddhism. His teachings are: •Every human beings are equal, we are not divided or born into caste. •He guided people to achieve peace and happiness within themselves •He taught people that who perform good actions could reach the higher level of inner peace. 25 Aug21
- 33. Q4.: What were the two questions Buddha searching for? What did he find? Ans: He wanted to know why humankind suffer and how this suffering could relieved. He finally found the answers to his questions that human beings suffered due to their greed. The only way they could reduce this suffering was by getting rid of desires. 25 Aug 21
- 34. F r o m b o o k p a g e n o . 1 4 27 Aug 21
- 36. 27 Aug 21
- 37. Contents •Words meanings •Short Question Answers •Fill in the blanks •True and false •Match the column •MCQs •Label the Map •Long Question Answer •Timeline 27 Aug 21
- 38. Words Meanings Stretched Expanded Prominent Famous Satrapies Ruler Reforms Improve Conquered taken control by military Melting pot of culture a place where a variety of peoples and cultures Invasion conquering Magnificent extremely beautiful Persepolis old Persian city
- 39. 28 Aug 21 Q1: Where was the Persian Empire? Ans: The Persian Empire stretched from Mediterranean sea to parts of Afghanistan and Pakistan. Q2: Who was the founder of Achaemenid Dynasty? Ans: Cyrus the Great was the founder of Achaemenid Dynasty. Q: Who was Darius? Ans: Darius was also known as Darius the Great, he was the third Persian King of the Achaemenid Empire Q4: How Darius divided the Empire into provinces? Ans: Darisu divided the empire into some 20 provinces called satrapies, Every satrapy had their own governor. Q5: Who invaded the Persian Empire? Ans: Alexander the Great, was a king of the Greek kingdom of Macedon. He invaded the Persian empire.
- 40. 29 Aug 21 a)The Persian Empire stretched from the Mediterranean Sea in the west to parts of Pakistan as far east as the region b) Darius established a university at Texila c) The area around Peshawar, Afghanistan, and north- west Pakistan was called Gandhara . d) Darius built a magnificent palace in Persipolis , his capital city. e)Sub continent became a melting pot for different ideas from many civilizations
- 41. 29 Aug 21 1. Achaemenid Dynasty of Persia was founded in eight century BCE. FALSE 2. Daruis was a strict and fair ruler . TRUE 3. Daruis force people to follow his own religion. FALSE 4. The old name of Peshawar is Purushapura. TRUE 5. Persian influences can still be found in Sindh and Panjab. FALSE
- 42. 29 Aug 21 Column A Column B Darius the Great the city of men Purushapura means 521-486 BCE Gandhara includes Sixth century BCE Cyrus the Great Afghanistan and Peshawar Alexander belonged Greek
- 43. 29 Aug 21 1. The Achaemenids were . (Assyrians ,Persians ,Turkish) 2. Zoroaster was a Iranian ______. (king ,magus, prophet) Persian rule started to ____ after a series of wars with the Greeks. (decline ,strengthen ,flourish) 4. Alexander burnt down _____ . (Persia, Persians, Persepolis) 5. The most popular religion of the early Persians was (Buddhism ,Zoroastrianism , Jainism)
- 44. div LABEL: Mediterranean sea, Persepolis, Greece, Hindu Kash (northern India) and Royal Road.
- 45. 30 Aug 21 Q1. How Did Darius rule the Empire? Ans: In history , Durius is known to be a ruler who was strick but fair. He divided his empire into provinces called satrapies so that he could run a fairs efficiently. He introduced many reforms, which led to the strengthening and popularity of the empire. Constructing the Royal road was one of his great achievement. This road started from a pace in Turkey and finally joined the famous Silk Route in northern Pakistan. He was a deeply religious man. He allow the people of the places he conquered to worship as they wish and never force them to follow any religion other than their own.
- 46. 31 Aug 21
- 48. 31 Aug 21
- 49. 1st Sep 21 •Words meanings •Short Questions Answers •Fill in the blanks •True and false •MCQs •Match the column •Long Questions Answers •Map of Alexander Kingdom
- 50. 2nd sep 21 Words Meanings •Territory domain •Succumbed gave way to something over powering •Opponent a person who disagree •Formidable powerful •Verge starting point •Fatigue tired •Revolt rebel •Phalanx military army
- 51. 2nd Aug 21 Q1. Who was Alexander? Ans: Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia. He established the largest empire the ancient world had ever seen. Q2. What was the dream of Alexander? Ans: Alexander inherited his father’s kingdom as well as his dream to conquer the world. He wanted to be known “the king of the world”. Q3. What was the tactic use by the Alexander’s Army to defeat enemies? Ans: The phalanx used the tactic that was orderly formation in which soldiers stand close together; Alexander use this formation to defeat any opponents defense.
- 52. 2nd sep 21 Q4. Who was King Porus? Ans: He was the ancient Indian King. He ruled over Paurava people who lived by the Jehlum and Panjab rivers. Q5. What was happened to the empire after the death of Alexander. Ans: After the death of Alexander, he did not have an adult son to inherit his kingdom so his empire was divided between three of his generals.
- 53. 3rd Sep 21 1. Mecedonia was the small kingdom in the north of Greece. 2. Alexander’s conquests extended from Greece and Egypt in the west to the Persian Empire 3. Alexander was an excellent commander and warrior . 4. After the death of Alexander the Indus valley region came under the rule of Greek General Seleucus 5. Alexander established strong links between the East and the West
- 54. 1. Alexandria Bucephalus is a city Alexander founded in the memory of his father. False 2. King Porus ruled the Hellenic people in Greece. False 3. Aristotle had trained Alexander in military warfare and his father King Philip had educated him. False 4. After Alexander’s death, his kingdom was divided among his three generals. True 5. Alexander conquered the Persians. True
- 55. 4 sep 21 1. Father of Alexander Philip was died by (killing, illness) 2. Persians ruled a large territory to the ____( South, East) 3. Alexander was only __ when he became commander. (18, 25) 4. Alexander spread __ ideas and culture. (Greek, Persian) 5. The dream of Alexander was ___ (Fulfilled, Unfulfilled) 6. Alexander was tutored by ( Aristotle, King Philip) 7. King Porus had formidable army of __( Horses, Elephants)
- 56. Column A Column B Hellenizing means Spreading ancient Greek Culture Bucephalus was horse of Alexander. Alexander died at the age of 32 Alexander became a king at the age of 20 Greek General Sleucus ruled Indus valley King Porus ruled Paurava people 4 sep 21
- 57. 4 sep 21
- 58. 5 Sep 21 Q1. How did Alexander the Great defeat the King Porus? Ans: Alexander defeated the King Porus with a clever attack.The armies had taken up their positions at the opposite ends of the river. Alexander made his soldiers cross the river from two places during the thunderstorm at night and attacked the both wings of Porus army instead of meeting them from the front. Porus own elephants stamp their own men due to this panic attack. King Porus was defeated after a heroic fight. After theVictory, Alexander asked the King Porus that “how he wished to be treated, Porus replied "Treat me as a king would treat another king".This attitude impressedAlexander, Alexander indeed treated him like a king allowed King Porus to continue to govern his territory.