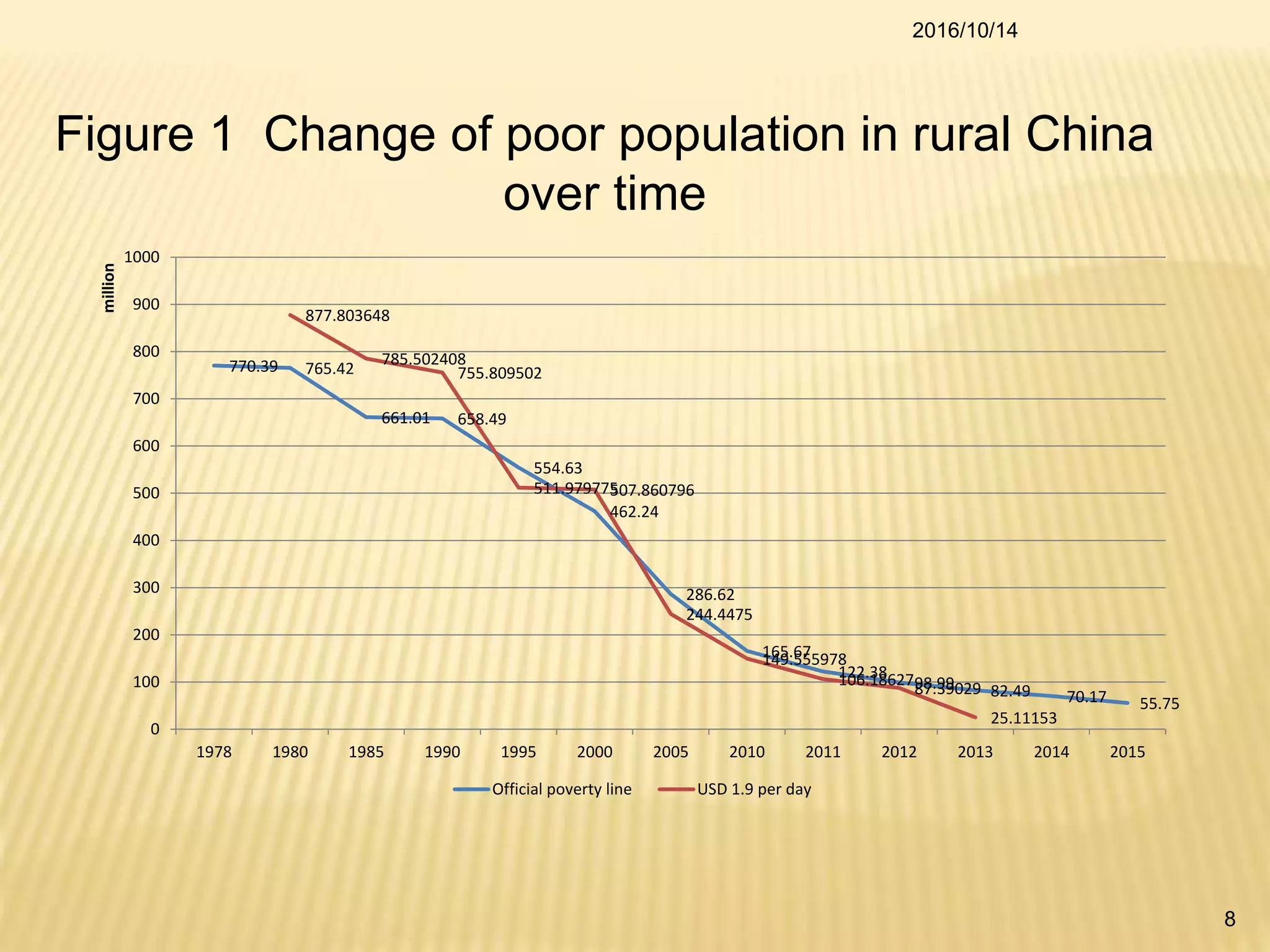
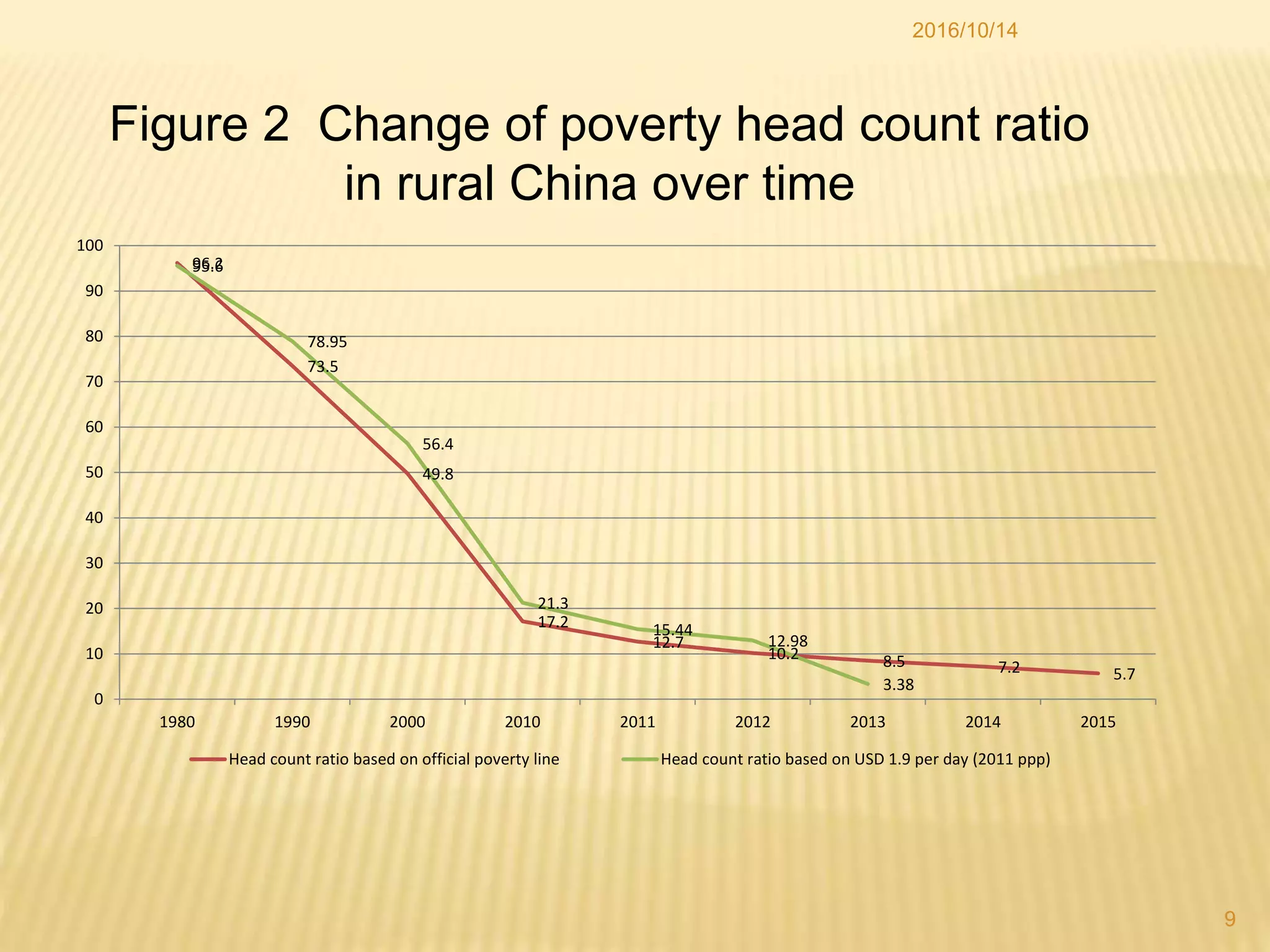
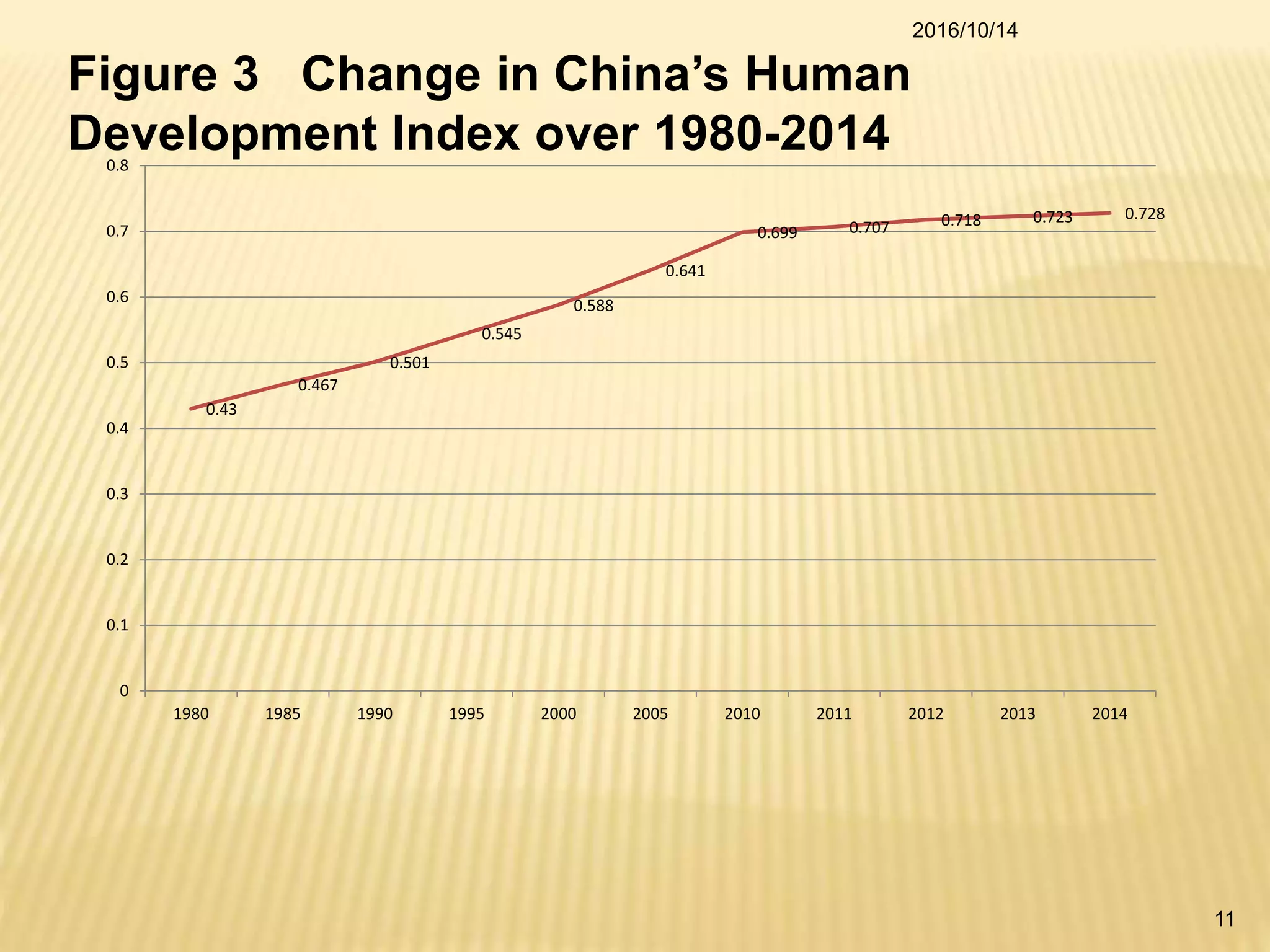
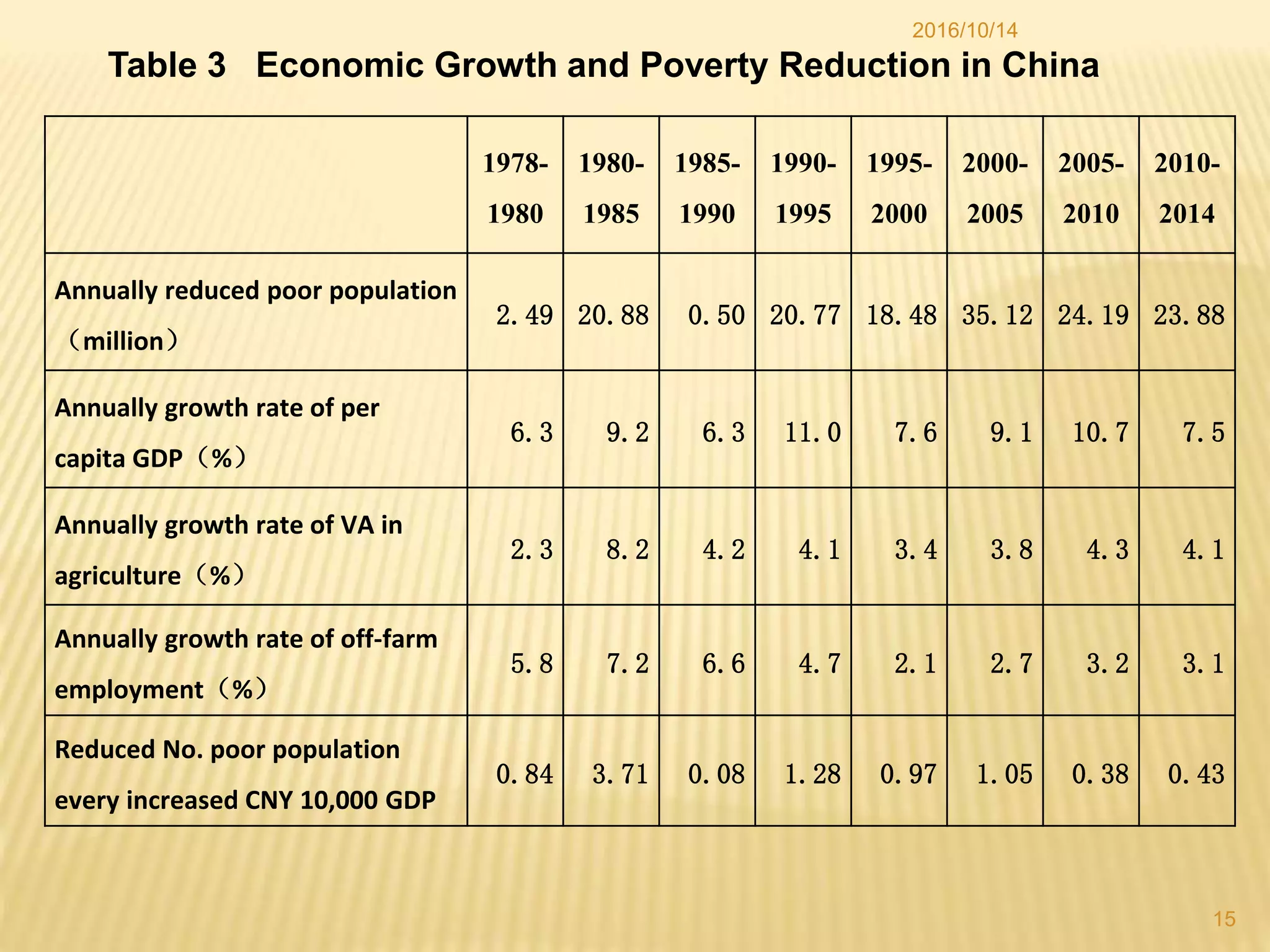
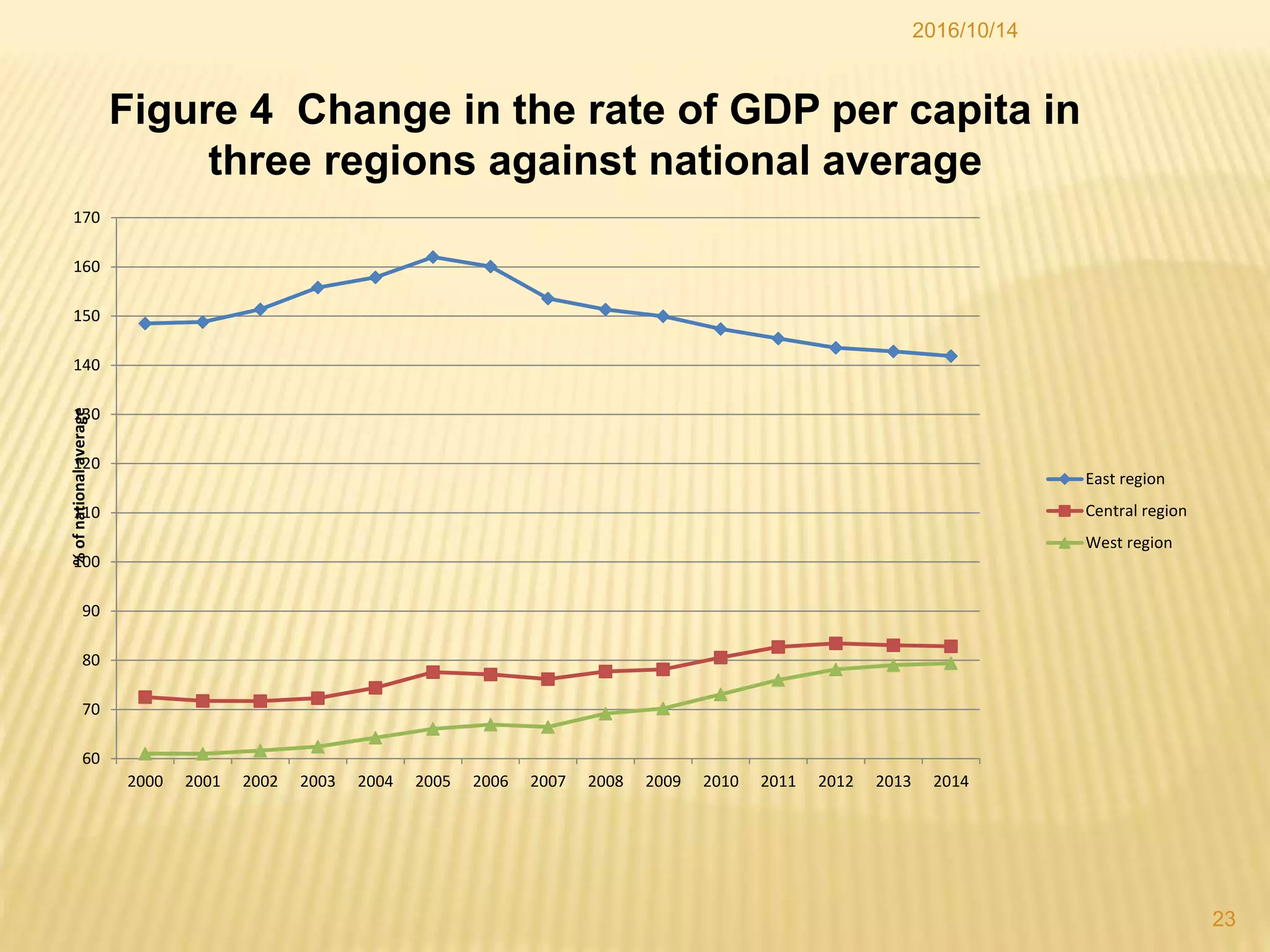
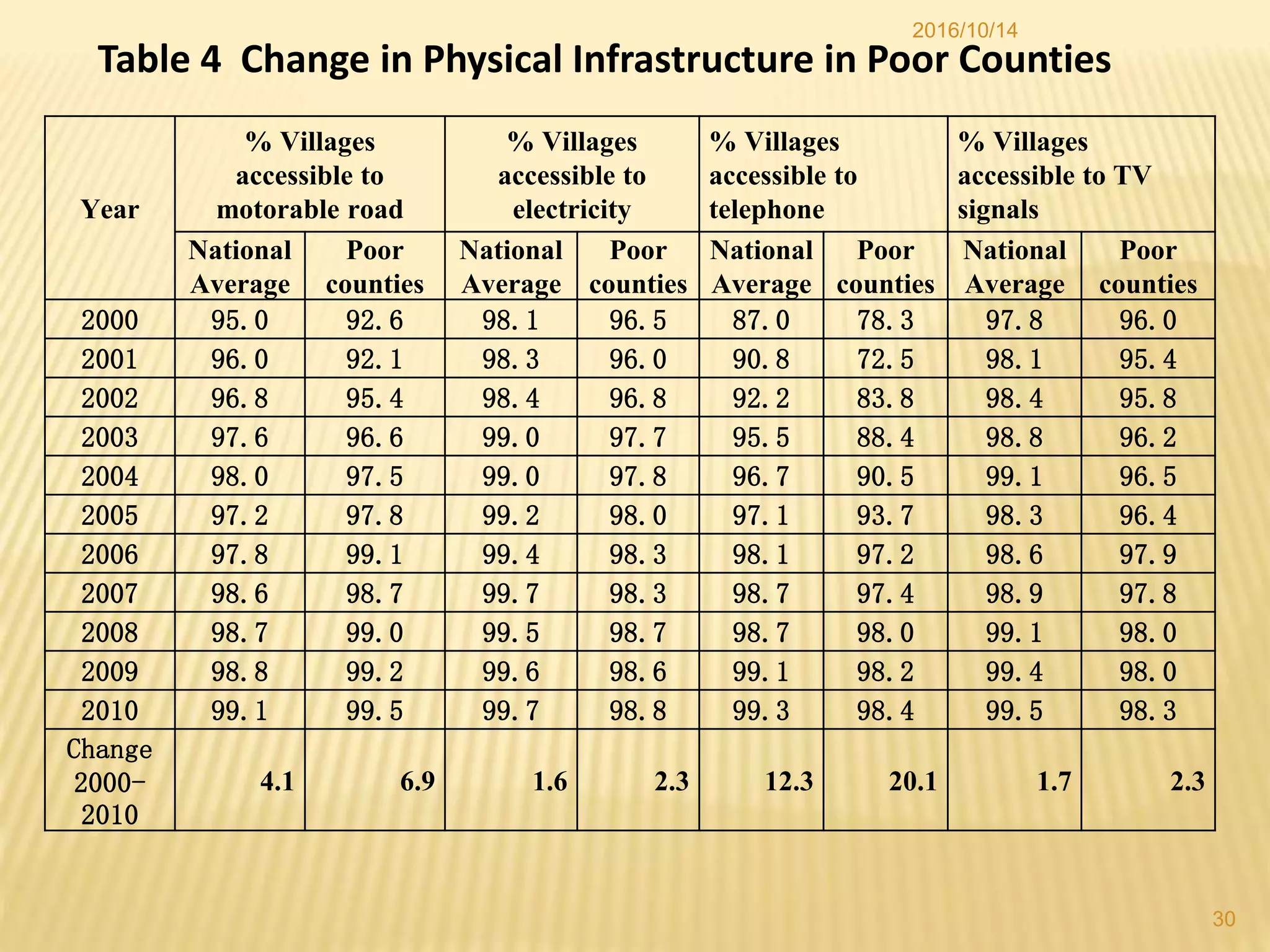
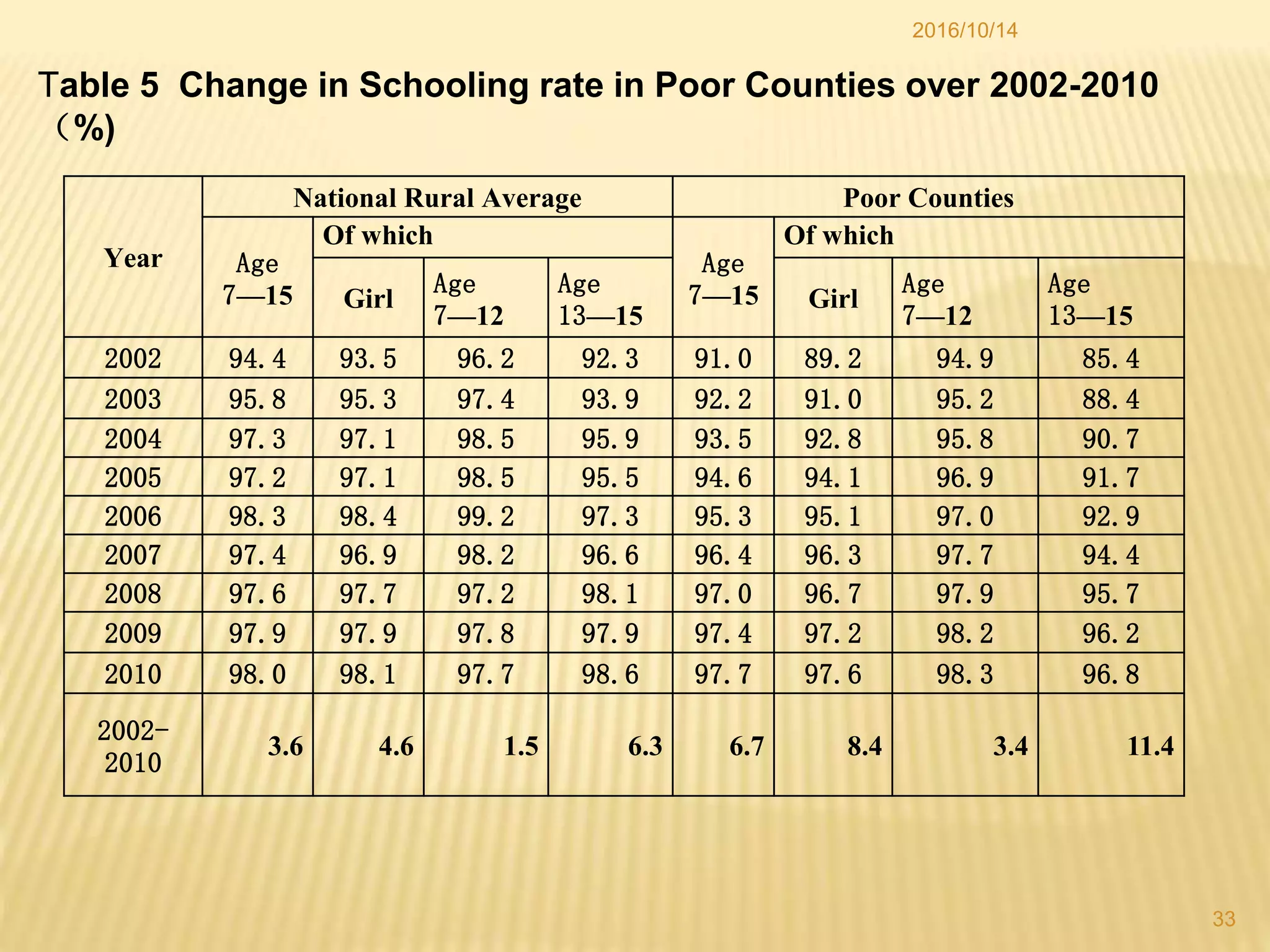
China has made significant progress in reducing rural poverty through sustained economic growth, pro-poor development policies, and targeted poverty reduction programs. Key factors in China's success include maintaining high GDP growth rates, with a particular focus on agricultural development; improving access to education, healthcare, and infrastructure in poor regions; and implementing comprehensive poverty alleviation programs. China has lifted over 700 million people out of poverty since 1978 and now has less than 5% of its population living below the international poverty line.