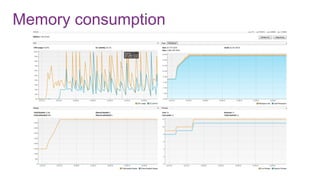
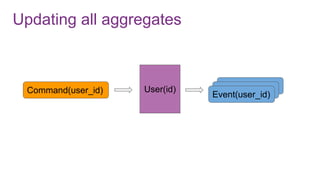
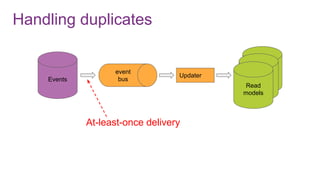
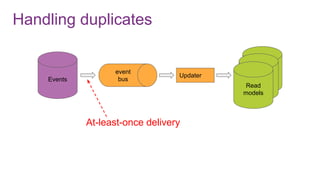
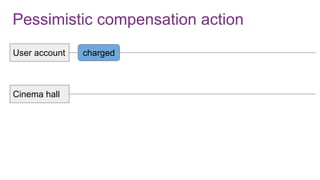
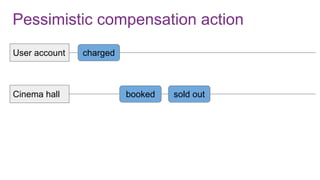
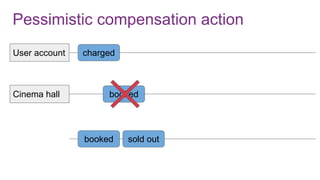
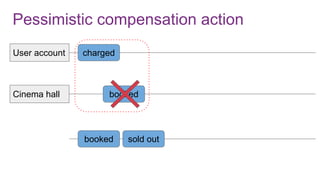
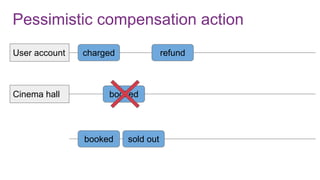
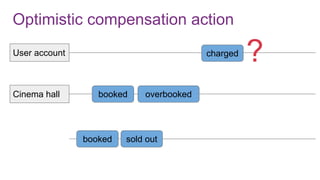
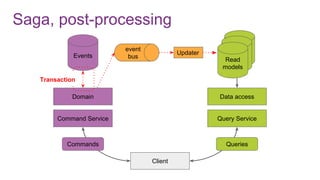
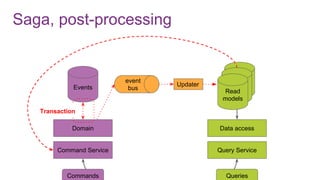
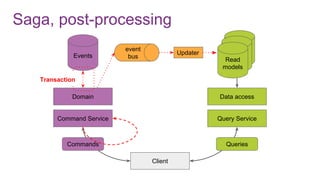
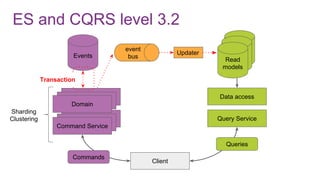
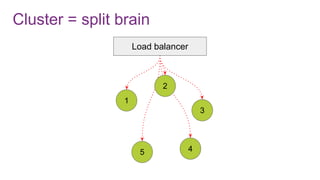
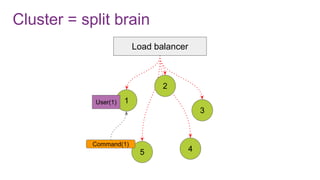
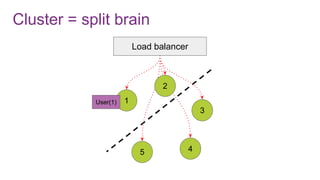
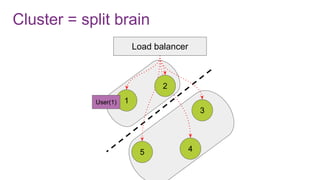
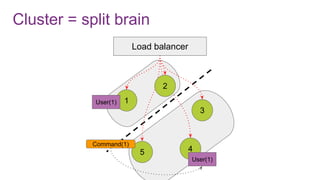
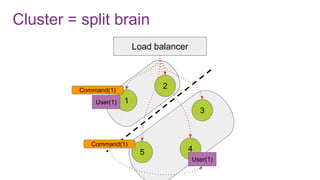
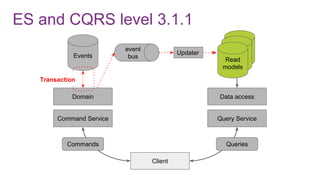
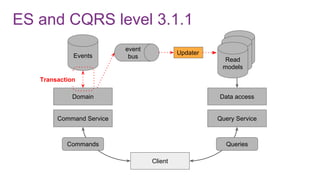
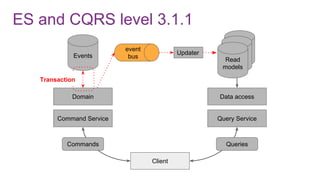
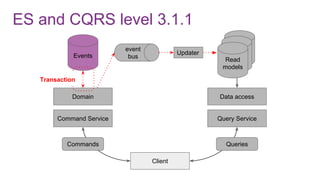
The document discusses the risks and considerations surrounding event sourcing in software architecture, including performance, scalability, and eventual consistency challenges. It explores different levels of event sourcing and CQRS implementations, along with various alternatives and best practices. The presentation also emphasizes the importance of schema evolution and highlights the complexities of scaling event-driven systems.







![What is Event Sourcing?
DB
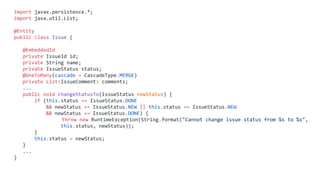
Order {
items=[itemA, itemB]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventsourcing-whatcouldgowrong2-190410152653/85/Andrzej-Ludwikowski-Event-Sourcing-what-could-possibly-go-wrong-Codemotion-Rome-2019-8-320.jpg)
![What is Event Sourcing?
DB
DB
Order {
items=[itemA, itemB]
}
ItemAdded(itemA)
ItemAdded(itemC)
ItemRemoved(itemC)
ItemAdded(itemB)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventsourcing-whatcouldgowrong2-190410152653/85/Andrzej-Ludwikowski-Event-Sourcing-what-could-possibly-go-wrong-Codemotion-Rome-2019-9-320.jpg)






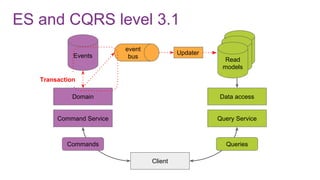
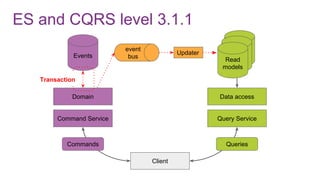
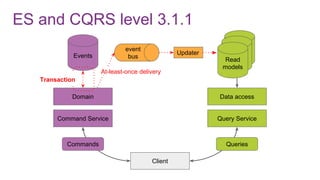
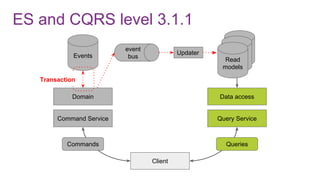




![ES from domain perspective
● commands, events, state
● 2 methods on state
○ process(command: Command): List[Event]
○ apply(event: Event): State](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventsourcing-whatcouldgowrong2-190410152653/85/Andrzej-Ludwikowski-Event-Sourcing-what-could-possibly-go-wrong-Codemotion-Rome-2019-34-320.jpg)

![import org.axonframework.commandhandling.*
import org.axonframework.eventsourcing.*
@Aggregate(repository = "userAggregateRepository")
public class User {
@AggregateIdentifier
private UserId userId;
private String passwordHash;
@CommandHandler
public boolean handle(AuthenticateUserCommand cmd) {
boolean success = this.passwordHash.equals(hashOf(cmd.getPassword()));
if (success) {
apply(new UserAuthenticatedEvent(userId));
}
return success;
}
@EventSourcingHandler
public void on(UserCreatedEvent event) {
this.userId = event.getUserId();
this.passwordHash = event.getPassword();
}
private String hashOf(char[] password) {
return DigestUtils.sha1(String.valueOf(password));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventsourcing-whatcouldgowrong2-190410152653/85/Andrzej-Ludwikowski-Event-Sourcing-what-could-possibly-go-wrong-Codemotion-Rome-2019-37-320.jpg)
![import akka.Done
import com.lightbend.lagom.scaladsl.*
import play.api.libs.json.{Format, Json}
import com.example.auction.utils.JsonFormats._
class UserEntity extends PersistentEntity {
override def initialState = None
override def behavior: Behavior = {
case Some(user) => Actions().onReadOnlyCommand[GetUser.type, Option[User]] {
case (GetUser, ctx, state) => ctx.reply(state)
}.onReadOnlyCommand[CreateUser, Done] {
case (CreateUser(name), ctx, state) => ctx.invalidCommand("User already exists")
}
case None => Actions().onReadOnlyCommand[GetUser.type, Option[User]] {
case (GetUser, ctx, state) => ctx.reply(state)
}.onCommand[CreateUser, Done] {
case (CreateUser(name), ctx, state) => ctx.thenPersist(UserCreated(name))(_ => ctx.reply(Done))
}.onEvent {
case (UserCreated(name), state) => Some(User(name))
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventsourcing-whatcouldgowrong2-190410152653/85/Andrzej-Ludwikowski-Event-Sourcing-what-could-possibly-go-wrong-Codemotion-Rome-2019-38-320.jpg)
![import java.time.Instant
import info.ludwikowski.es.user.domain.UserCommand.*
import info.ludwikowski.es.user.domain.UserEvent.*
import scala.util.{Failure, Success, Try}
final case class User (userId: UserId, name: String, email: Email) {
def applyEvent(userEvent: UserEvent): Try[User] = ??? //pattern matching
def process(userCommand: UserCommand): Try[List[UserEvent]] = ??? //pattern matching
}
object User {
def from(u: UserCreated): User = User(u.userId, u.name, u.email)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventsourcing-whatcouldgowrong2-190410152653/85/Andrzej-Ludwikowski-Event-Sourcing-what-could-possibly-go-wrong-Codemotion-Rome-2019-40-320.jpg)
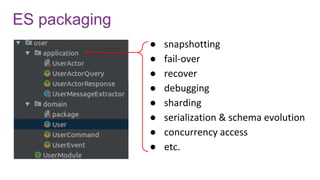
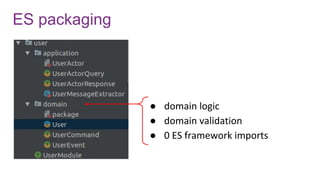










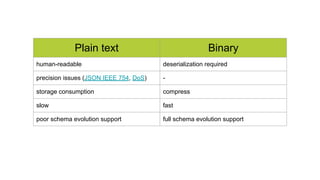





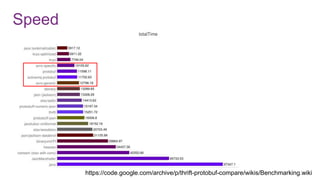
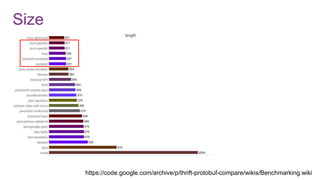
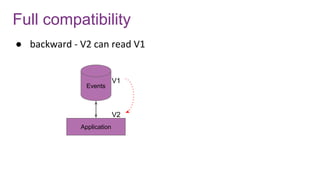
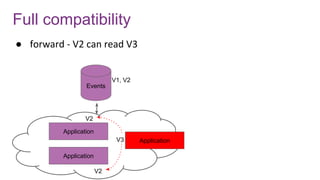




![Avro schema management
package user.domain
UserCreated(
userId: UserId,
operationId: OperationId,
createdAt: Instant,
name: String,
email: Email
) extends UserEvent
{
"type" : "record",
"name" : "UserCreated",
"namespace" :
"info.ludwikowski.es.user.domain",
"fields" : [ {
"name" : "userId",
"type" : "string" }, {
"name" : "operationId",
"type" : "string" }, {
"name" : "createdAt",
"type" : "long" }, {
"name" : "name",
"type" : "string" }, {
"name" : "email",
"type" : "string"
} ]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventsourcing-whatcouldgowrong2-190410152653/85/Andrzej-Ludwikowski-Event-Sourcing-what-could-possibly-go-wrong-Codemotion-Rome-2019-70-320.jpg)
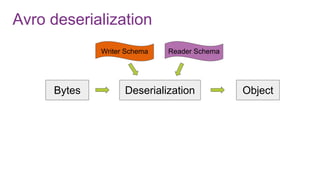

![Avro schema management
package user.domain
UserCreated(
userId: UserId,
operationId: OperationId,
createdAt: Instant,
name: String,
email: Email
) extends UserEvent
{
"type" : "record",
"name" : "UserCreated",
"namespace" :
"info.ludwikowski.es.user.domain",
"fields" : [ {
"name" : "userId",
"type" : "string" }, {
"name" : "operationId",
"type" : "string" }, {
"name" : "createdAt",
"type" : "long" }, {
"name" : "name",
"type" : "string" }, {
"name" : "email",
"type" : "string"
} ]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventsourcing-whatcouldgowrong2-190410152653/85/Andrzej-Ludwikowski-Event-Sourcing-what-could-possibly-go-wrong-Codemotion-Rome-2019-73-320.jpg)
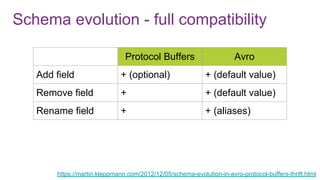
![Protocol Buffers vs. Avro
{
"type" : "record",
"name" : "UserCreated",
"namespace" :
"info.ludwikowski.es.user.domain",
"fields" : [ {
"name" : "userId",
"type" : "string" }, {
"name" : "operationId",
"type" : "string" }, {
"name" : "createdAt",
"type" : "long" }, {
"name" : "name",
"type" : "string" }, {
"name" : "email",
"type" : "string"
} ]
}
message UserCreatedEvent {
string user_id = 1;
string operation_id = 2;
int64 created_at = 3;
string name = 4;
string email = 5;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventsourcing-whatcouldgowrong2-190410152653/85/Andrzej-Ludwikowski-Event-Sourcing-what-could-possibly-go-wrong-Codemotion-Rome-2019-74-320.jpg)