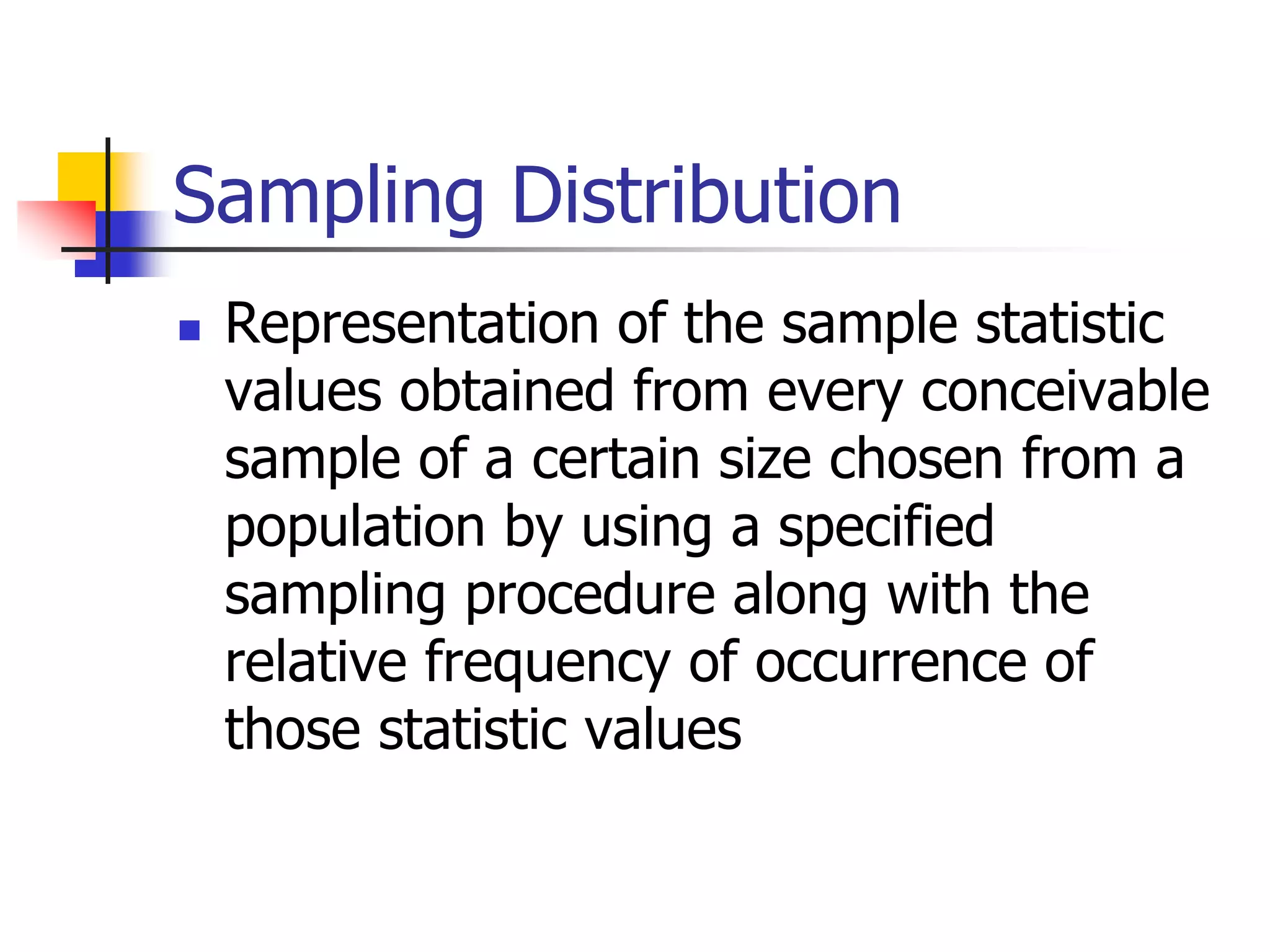
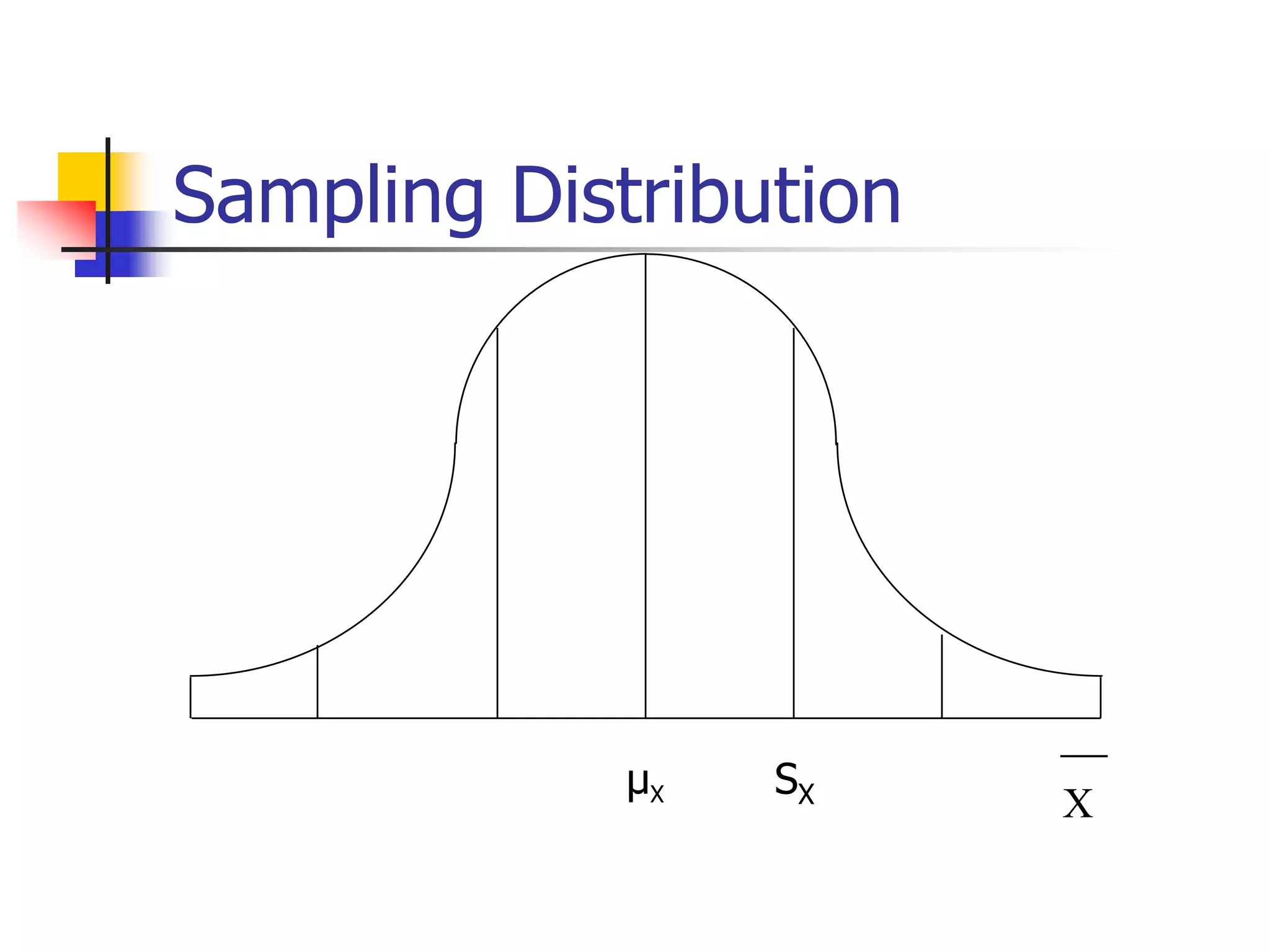
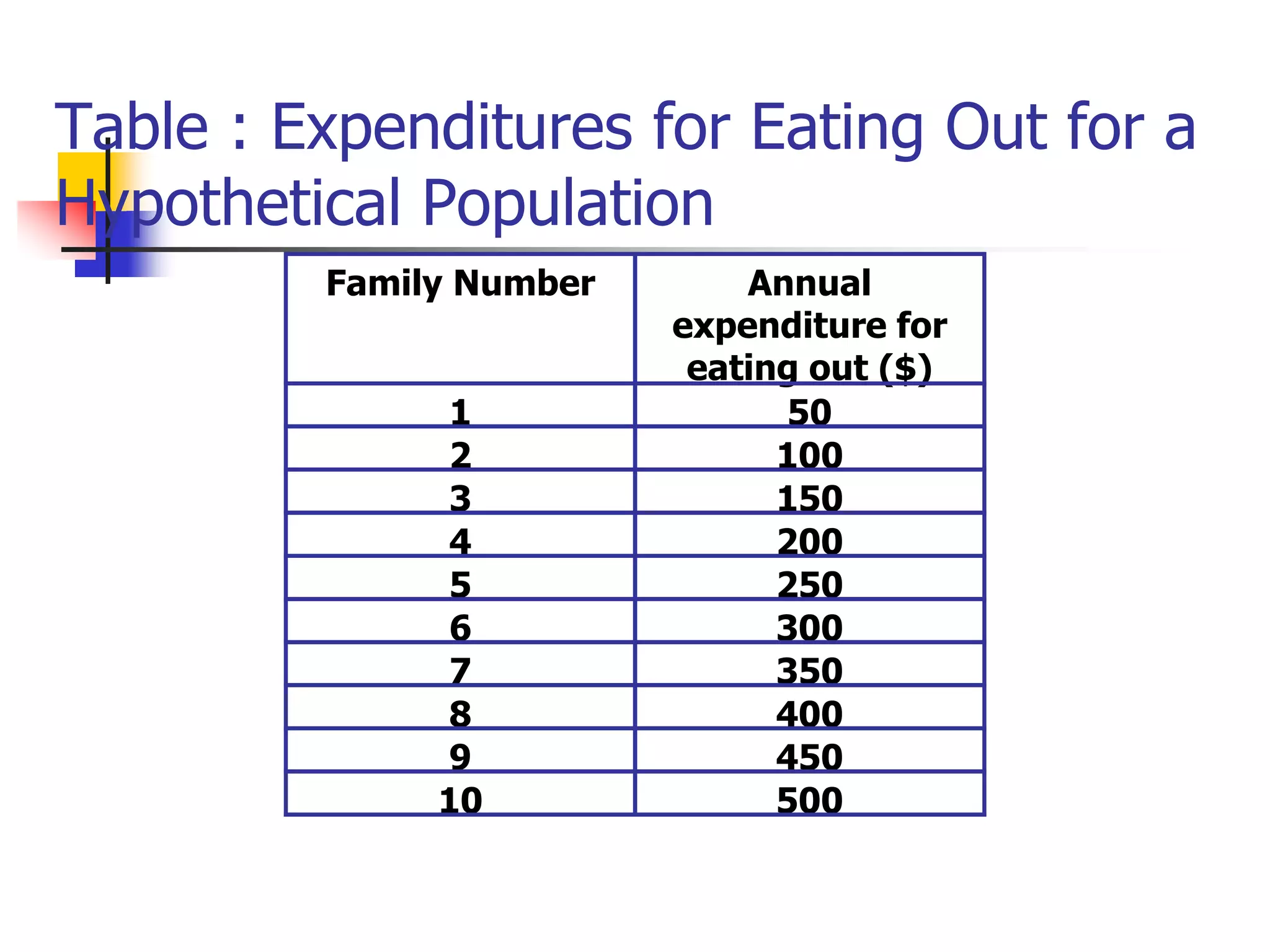
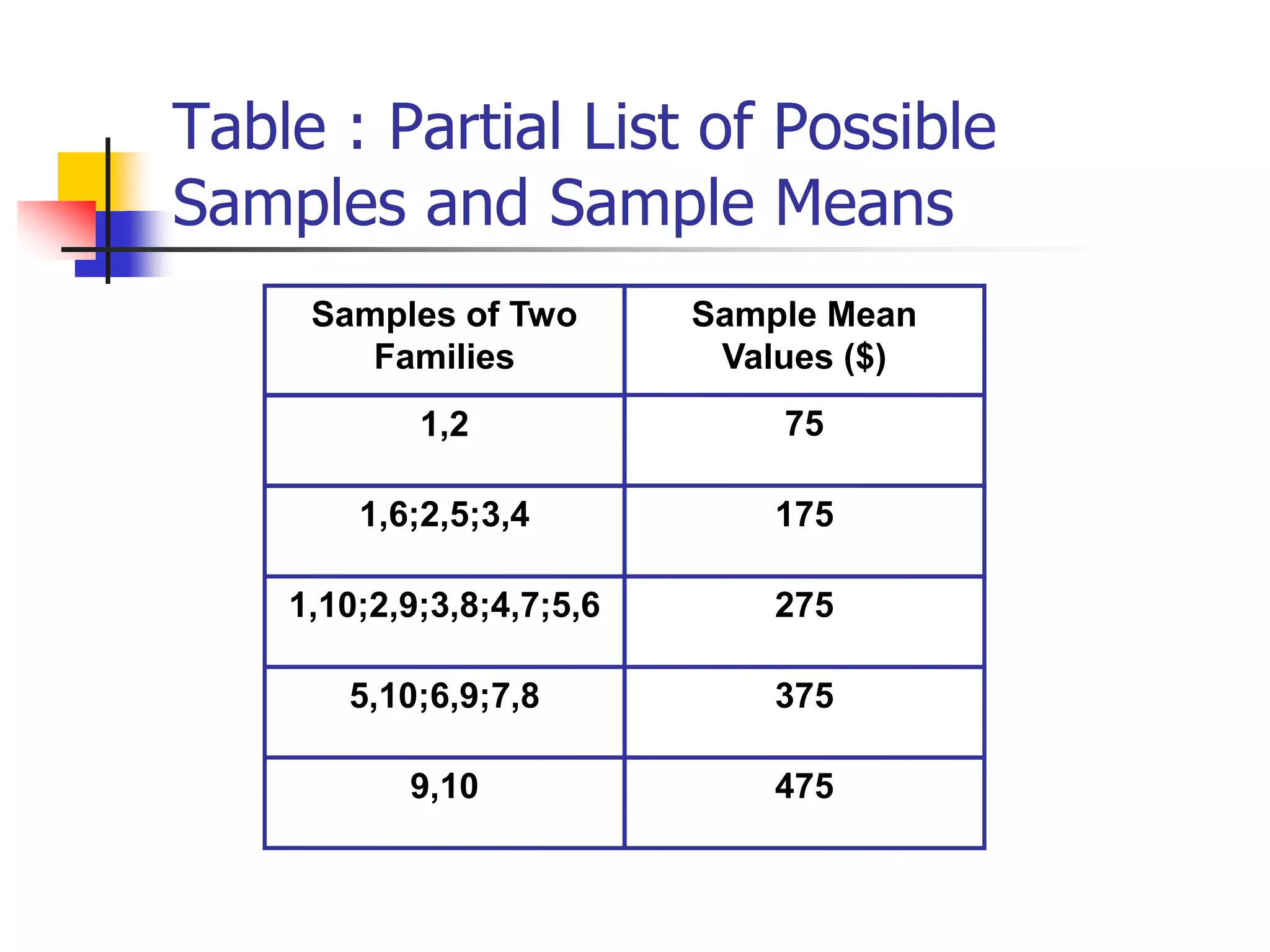
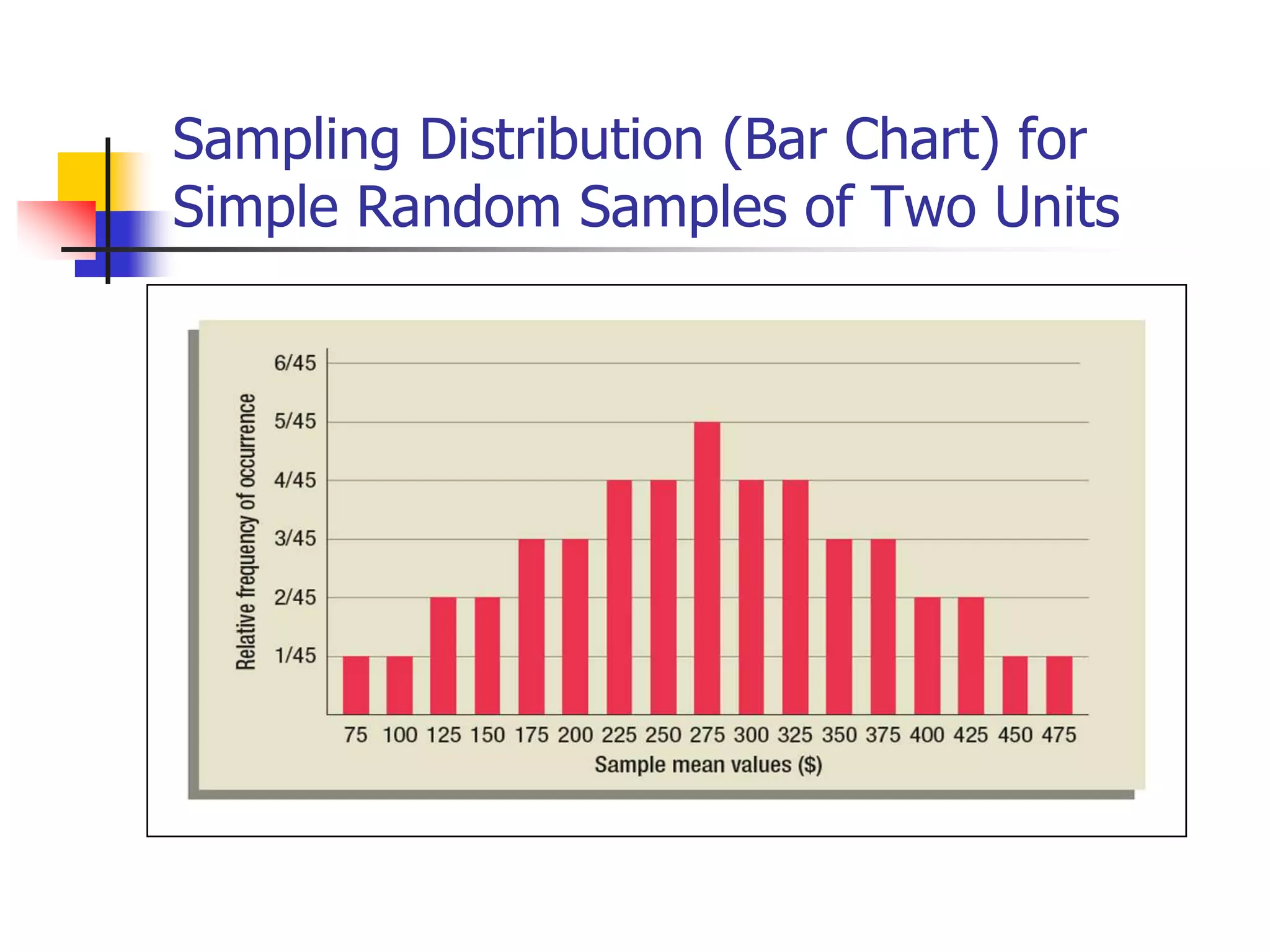
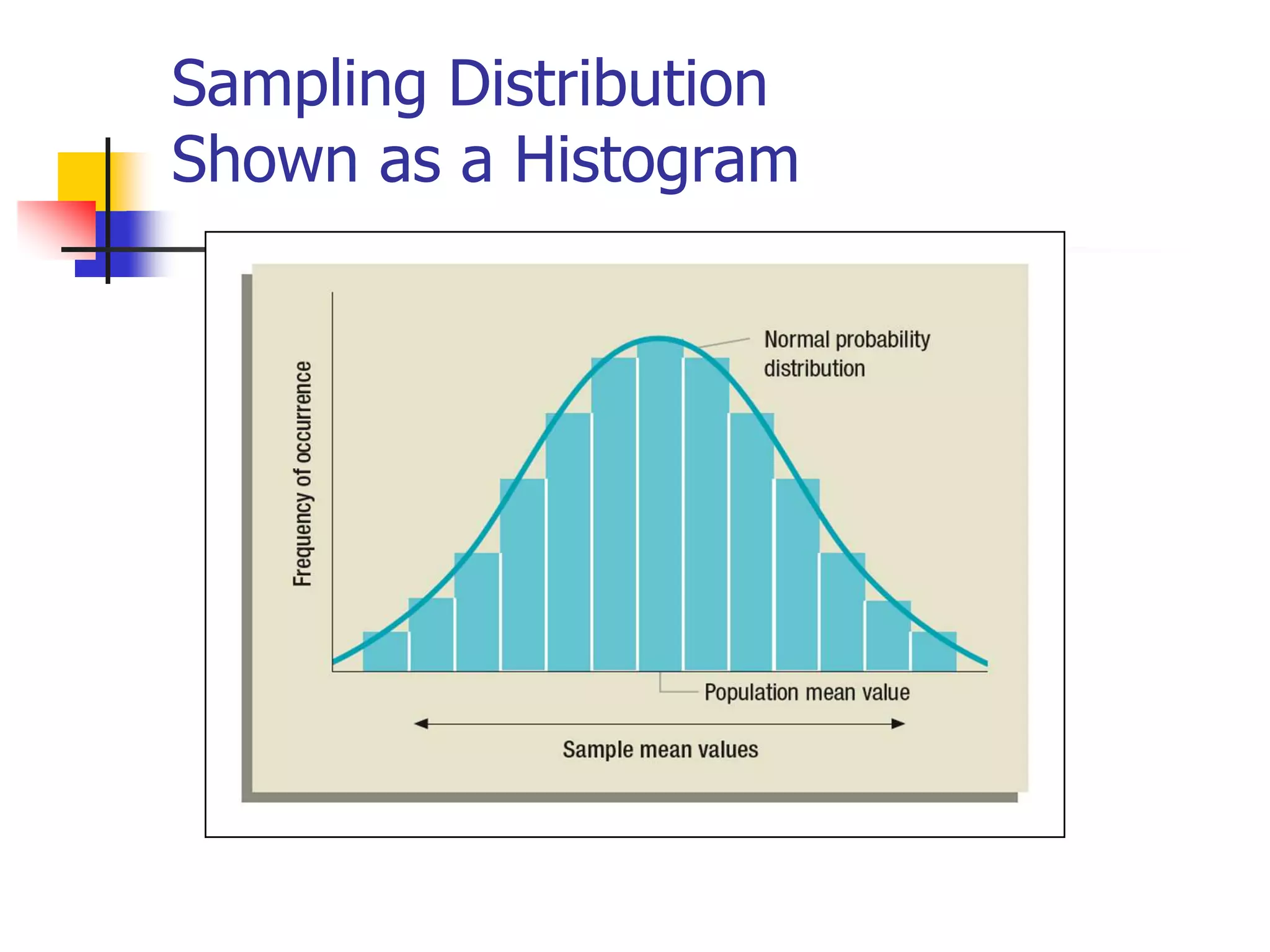
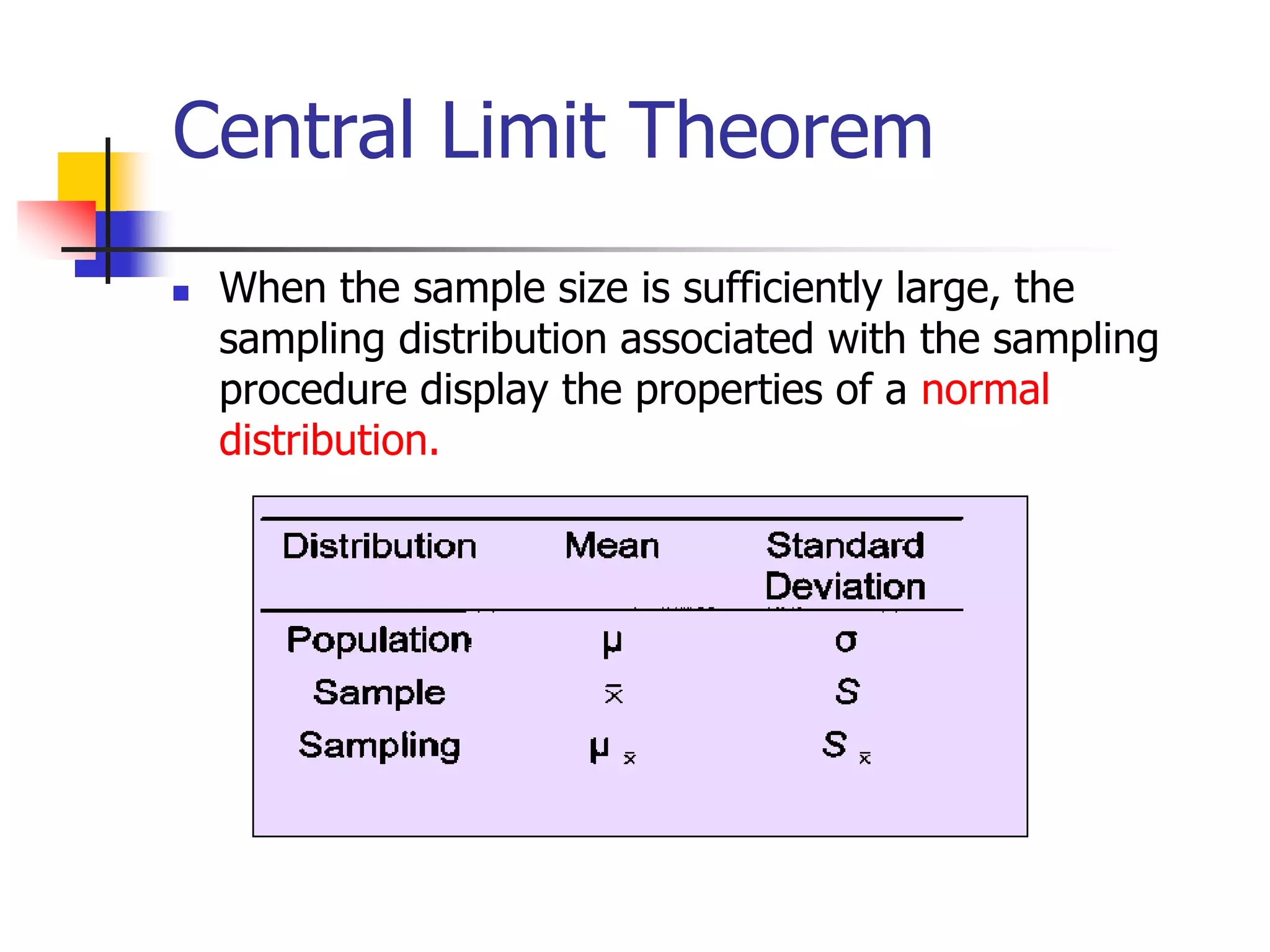
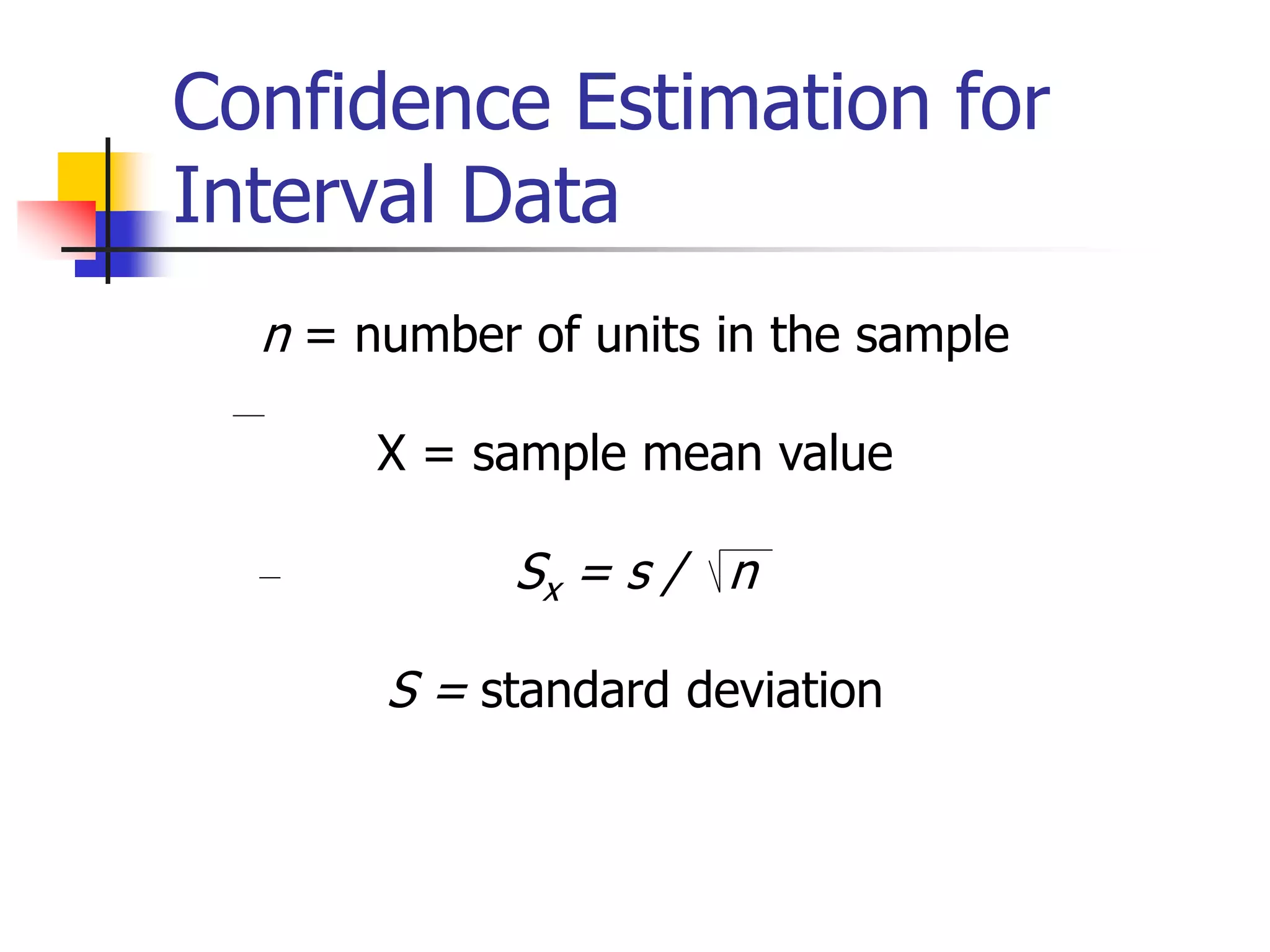
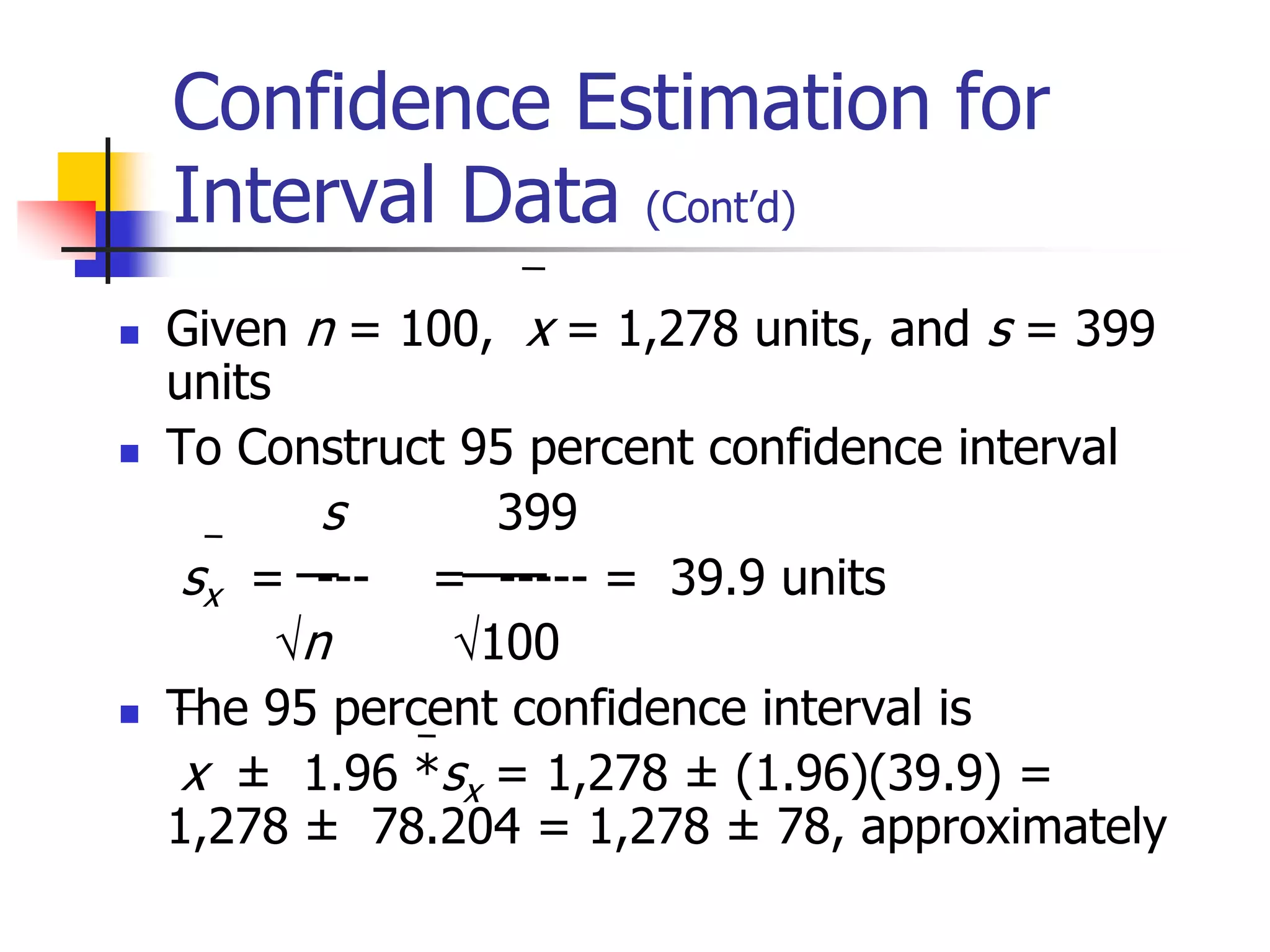
This document discusses sampling distributions and how they are used to represent sample statistic values from all possible samples of a given size from a population. It provides examples of sampling distributions from hypothetical population data on family expenditures for eating out. The central limit theorem is introduced, which states that as sample size increases, the sampling distribution will take the form of a normal distribution. The document then discusses how confidence intervals can be constructed from sample data to estimate population parameters, providing an example using data on annual sales units.