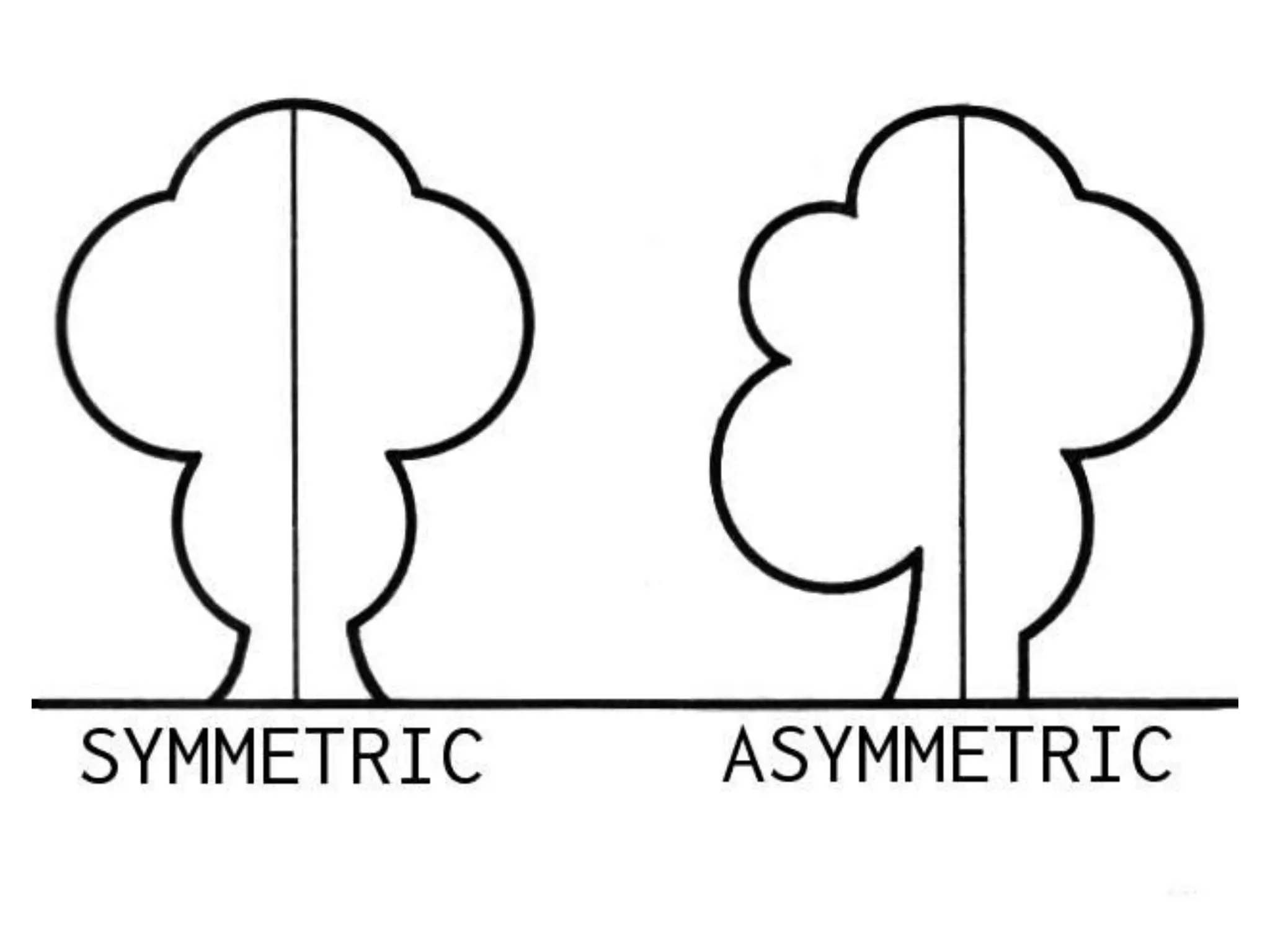
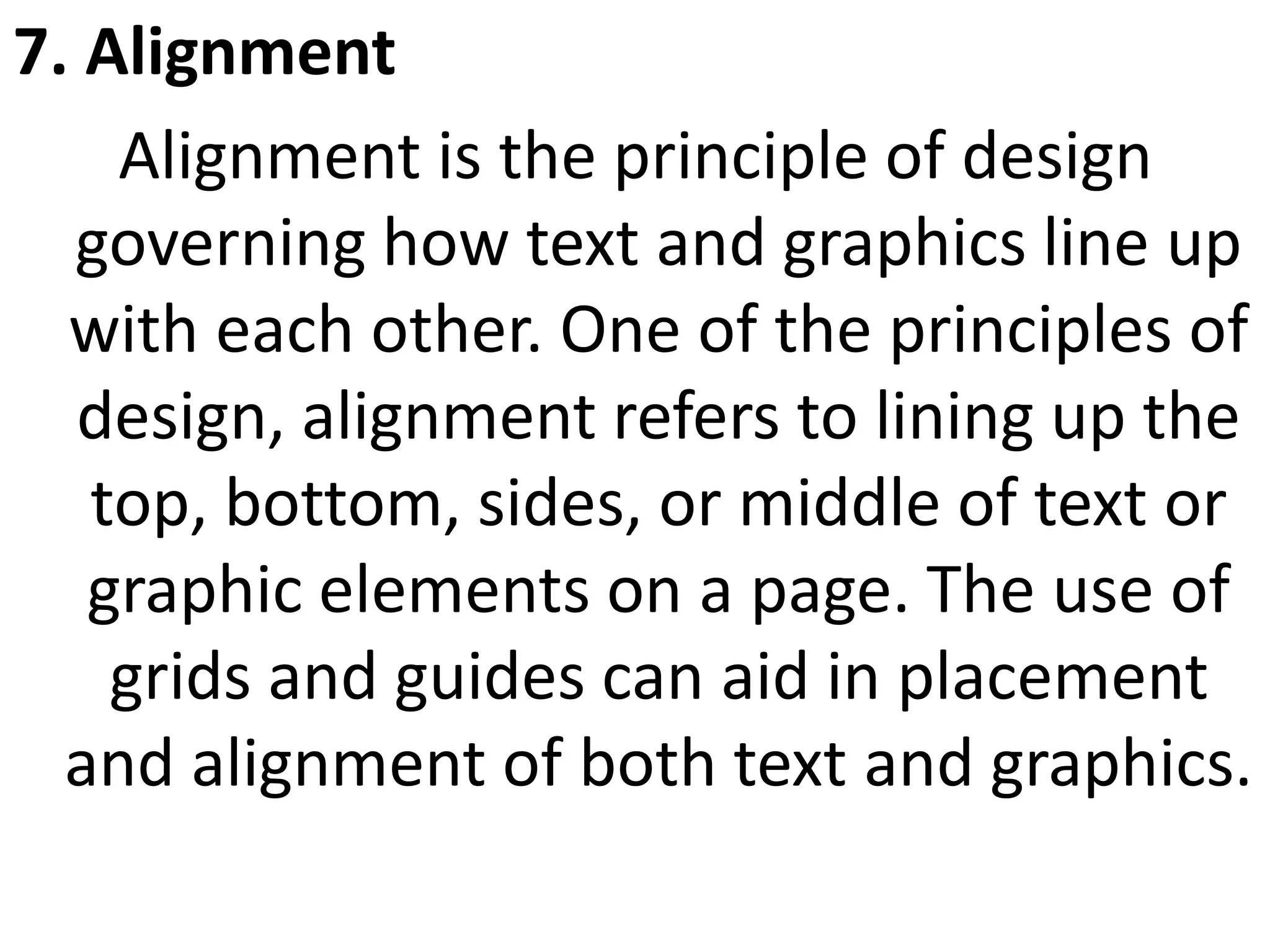
The document discusses basic web design principles and elements. The 7 principles are balance, movement, repetition/rhythm, emphasis, contrast, unity, and alignment. The 7 elements are line, color, shape, size, value, texture, and space. Color has three characteristics: hue, value, and intensity. Balance, repetition, emphasis and contrast are used to create visual interest and structure on a page.