Form 3 Science Notes Chapter 6 Land and Its Resources
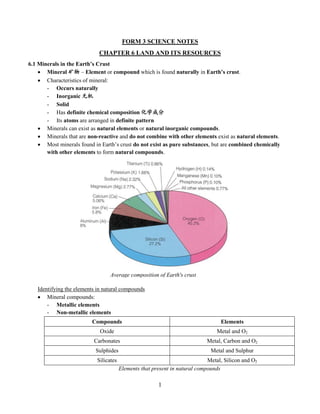
- 1. 1 FORM 3 SCIENCE NOTES CHAPTER 6 LAND AND ITS RESOURCES 6.1 Minerals in the Earth’s Crust Mineral 矿物 – Element or compound which is found naturally in Earth’s crust. Characteristics of mineral: - Occurs naturally - Inorganic 无机 - Solid - Has definite chemical composition 化学成分 - Its atoms are arranged in definite pattern Minerals can exist as natural elements or natural inorganic compounds. Minerals that are non-reactive and do not combine with other elements exist as natural elements. Most minerals found in Earth’s crust do not exist as pure substances, but are combined chemically with other elements to form natural compounds. Identifying the elements in natural compounds Mineral compounds: - Metallic elements - Non-metallic elements Compounds Elements Oxide Metal and O2 Carbonates Metal, Carbon and O2 Sulphides Metal and Sulphur Silicates Metal, Silicon and O2 Elements that present in natural compounds Average composition of Earth's crust
- 2. 2 Properties of minerals Hardness of minerals - Refers to its resistance to scratches - Can be determined by scratching it against an object such as nail, coin or fingernail - Hardness is measured on Mohs’ scale (The higher the number, the harder the mineral) Hardness Mineral Hardness Mineral 1 Talcum (Talc) 6 Feldspar (Orthoclase) 2 Gypsum 7 Quartzite (Quartz) 3 Calcite 8 Topaz 4 Fluorite 9 Corundum 5 Apatite 10 Diamond Mohs’ scale Solubility of minerals in water - Most minerals do not dissolve or are insoluble in water - Oxides, sulphides and carbonates of potassium and sodium dissolve in water - All other metal oxides, metal sulphides and metal carbonate do not dissolve in water Effect of heat on minerals - Unstable minerals break down when heated strongly - Most metal carbonates are unstable and break down into metal oxides and carbon dioxide - Potassium dioxide and sodium carbonate are stable Metal carbonate -----> Metal oxide + Carbon dioxide Copper carbonate -----> Copper oxide + Carbon dioxide
- 3. 3 - Most metal oxides are very stable minerals and do not break down when heated. - Result – Change of colour - Sulphur dioxide bleaches acidifies potassium manganate (VII) solution (Purple Colourless) 6.2 Reaction between Metals and Non-metals Metal and non-metal elements Mineral ores that exist as metal oxides include: - Bauxite 矾土 (Aluminium oxide) - Haematite 赤铁矿 (Iron oxide) - Cassiterite 锡石 (Tin oxide) Most metals are active and combine with non-metals such as O2 and S to form stable compounds in Earth’s crust. Reaction of metals with oxygen Oxidation 氧化 – Reaction of metals with O2 in air to form metal oxides. Reactive metals (Magnesium, Aluminium) react very quickly with O2. Less reactive metals (Lead, Copper) react very slowly with O2. Some metals such as gold, silver and platinum do not react with O2. Reaction of metals with sulphur Sulphur 硫 (S) is found in abundance 丰富 near volcanoes. It is a reactive non-metal. Large number of ores in Earth’s crust are sulphur compounds: - Galena 方铅矿 (Lead sulphide) - Sphalerite 闪锌矿 or zinc blende (Zinc sulphide) - Pyrite 黄铁矿 (Iron sulphide) Silver oxide -----> Silver + Oxygen Metal sulphide -----> Metal oxide + Sulphur dioxide Zinc sulphide -----> Zinc oxide + Sulphur dioxide Metal + Oxygen -----> Metal oxide Metal + Sulphur -----> Metal sulphide
- 4. 4 6.3 Silicon Compounds Silicon 硅 (Si) is the second most abundant element in Earth’s crust. Silicon does not exist as element in natural state and combine with other elements in silicon compounds. Properties of silica and silicates Silica (Silicon dioxide) - Consists of silicon and O2 - Examples: Quartz 石英, Sand 砂, Flint 燧石 Silicates - Consists of silicon, O2 and a metal - Examples: Clay 粘土, Asbestos 石棉, Gemstones 宝石, Mica 云母 Stability of silica and silicates can be determined by testing their properties: - Solubility in water - Reaction with hydrochloric acid - Effects of heat Silica and silicates are stable because both compounds do not: - Dissolve in water with exception of sodium silicate 硅酸钠 - React with dilute acid - Change in form when heated. Acidic silica dissolves in alkalis to form silicates. Silicates do not react with alkalis. Use of silicon compounds in everyday life Quartz (Watch, Microchips in silicon wafer) Sand (Glassware, Concrete pillars) Glass fibres (Fibre optic cables) China clay / Kaolin (Cement, Ceramic vases) Gemstones (Jade, Ruby) Mica (Microwave oven, Electric iron) Silicon
- 5. 5 6.4 Calcium Compounds Calcium 钙 (Ca) is a reactive element and does not exist in pure form in nature. Calcium is found naturally occurring calcium compounds such as calcium carbonate that consists of calcium, O2 and carbon. Natural calcium carbonate exists in many forms. (Calcite 方解石, marble 大理石, limestone 石灰石, coral reefs, shells, teeth and bones of animals) Reaction of calcium carbonate: - Reacts with dilute acids to release CO2. H2O and salt is formed. - It is insoluble in water. - When it is heated strongly, it breaks down into calcium oxide and CO2 is released. Formation of calcium oxide and calcium hydroxide Calcium carbonate breaks down to form calcium oxide 氧化钙 when heated strongly. When a little water is added to calcium oxide, it changes to calcium hydroxide 氢氧化钙. Calcium hydroxide is slightly soluble in water. It dissolves in water to form calcium hydroxide solution. Calcium carbonate + Dilute hydrochloric acid -----> Calcium chloride (Salt) + water + Carbon dioxide Calcium oxide (Quicklime) + Water -----> Calcium hydroxide (Slaked lime) + Heat energy Calcium carbonate -----> Calcium oxide (Quicklime) + Carbon dioxide Calcium hydroxide (Slaked lime) -----> Calcium hydroxide solution (Lime water) + Heat energy Calcium
- 6. 6 Use of calcium compounds Calcium carbonate - Prepare quicklime - Make cement using clay and water Calcium oxide (Quicklime) - Prepare slaked lime - Dry alkaline gases (Ammonia gas) Calcium hydroxide (Slaked lime) - Prepare lime water - Reduce acidity of soil Calcium hydroxide solution (Lime water) - Test for presence of CO2 6.5 Natural Fuel Resources and Their Importance Formation of natural fuel resources Coal - Soft black sedimentary rock 沉积岩 - Composed of carbon, often mixed with sulphur and nitrogen - Formed from plants that grew in swampy areas millions of years ago Petroleum (Crude oil) - Thick, sticky black oil - Mixture of hydrocarbons 碳氢化合物 of different boiling points - This property enables the hydrocarbons to be separated by distillation Natural gas - Consists of hydrocarbons, mainly methane gas 沼气 - Found trapped together with petroleum below seabed between layer of non-porous rocks 无孔的 岩石. Formation of petroleum and natural gas - Formed from decaying organic matter such as phytoplankton 浮游植物 and the remains of small plants and animals millions of years ago. Formation of coal
- 7. 7 Fractional distillation of petroleum Fractional distillation 分馏 – Separation of liquids with different boiling points through evaporation and condensation. Condensed liquid: Distillate / Petroleum fraction Takes place in large fractionating towers in oil refineries 炼油厂 Formation of natural gas and petroleum Boiling point increase Viscosity 粘性 increase Amount of soot increase Combustibility decrease Fractional distillation
- 8. 8 The contributions of petroleum and natural gas to the economic development of Malaysia Provides employment for many Malaysians. Contribute to development of towns (Kertih and Bintulu) Important in transportation, mining industry, manufacturing industry, agricultural industry, infrastructure and construction. Petrochemical 石化 industry produces plastics, detergents and cosmetics. These contribute to country’s revenue 收入 and economic progress. Efficient ways of using natural fuel resources Energy efficiency includes efficiency in power generation, the transmission and distribution of electricity and the end-uses of energy. Better road facilities and more efficient public transportation Reduce wastage and recycle materials Switch off lights and electrical appliances not in use Use automatic switches to control electrical appliances, fans, lights and air conditioners Building that make use of solar energy will reduce use of petroleum energy Educate public on the true situation of energy sources and the need to use energy efficiently Oil refinery