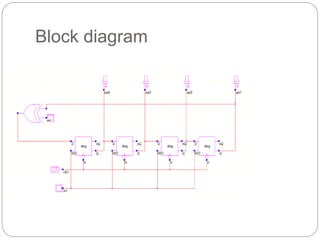
The document discusses Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs), highlighting their structure, operation, and applications. It explains LFSRs as shift registers utilizing D-flip flops and EXOR gates, functioning through feedback mechanisms. Key applications include counters, built-in self-test systems, military uses, and encryption due to their compact and simple design.