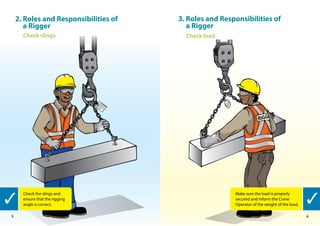
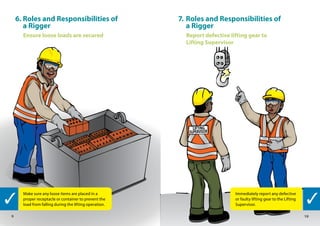
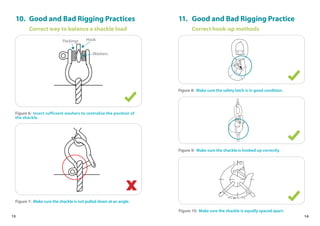
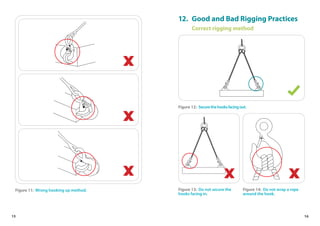
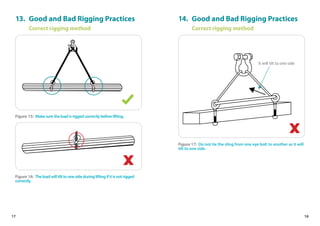
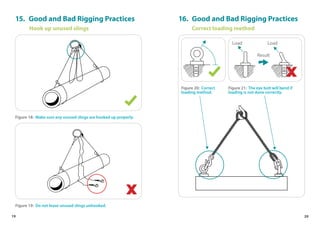
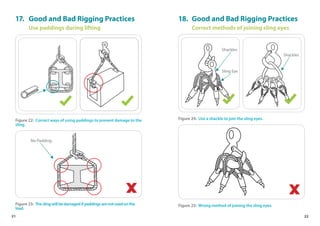
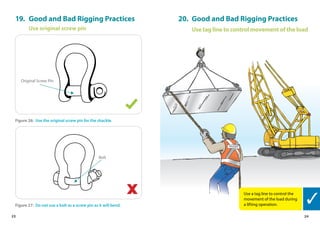
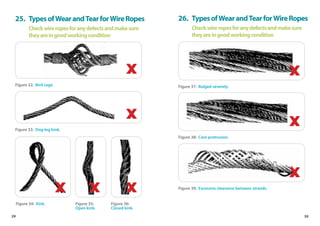
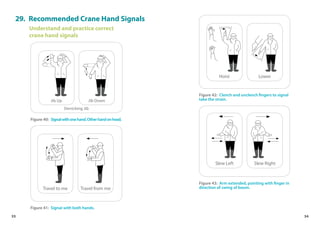
This handbook provides guidance on worker safety for riggers and signalmen. It outlines proper attire and safety equipment, roles and responsibilities, good and bad rigging practices, inspection of lifting equipment, crane hand signals, and communication best practices. The handbook was produced by the National Crane Safety Taskforce and Workplace Safety and Health Council to educate riggers and signalmen on safe lifting operations.