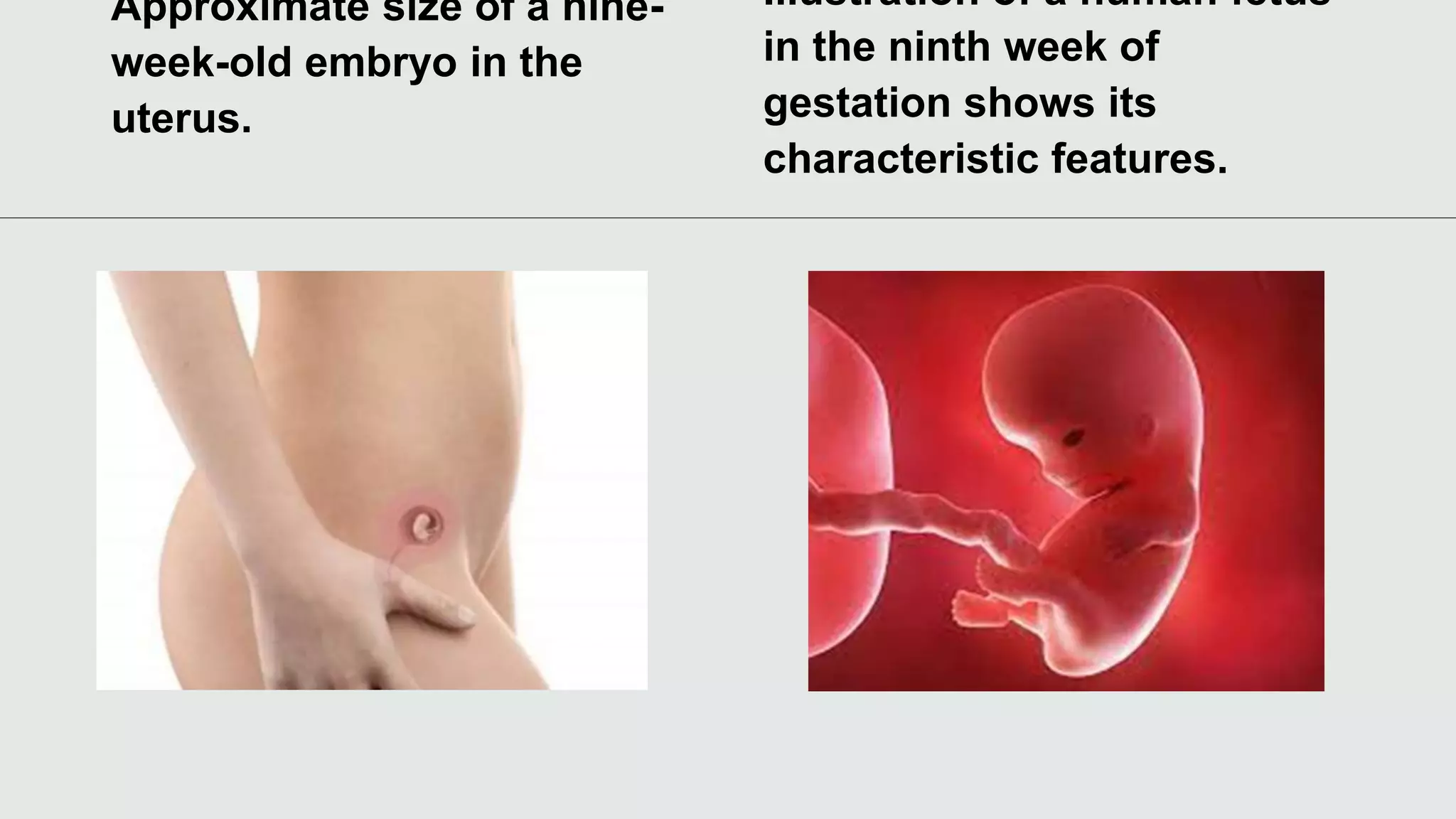
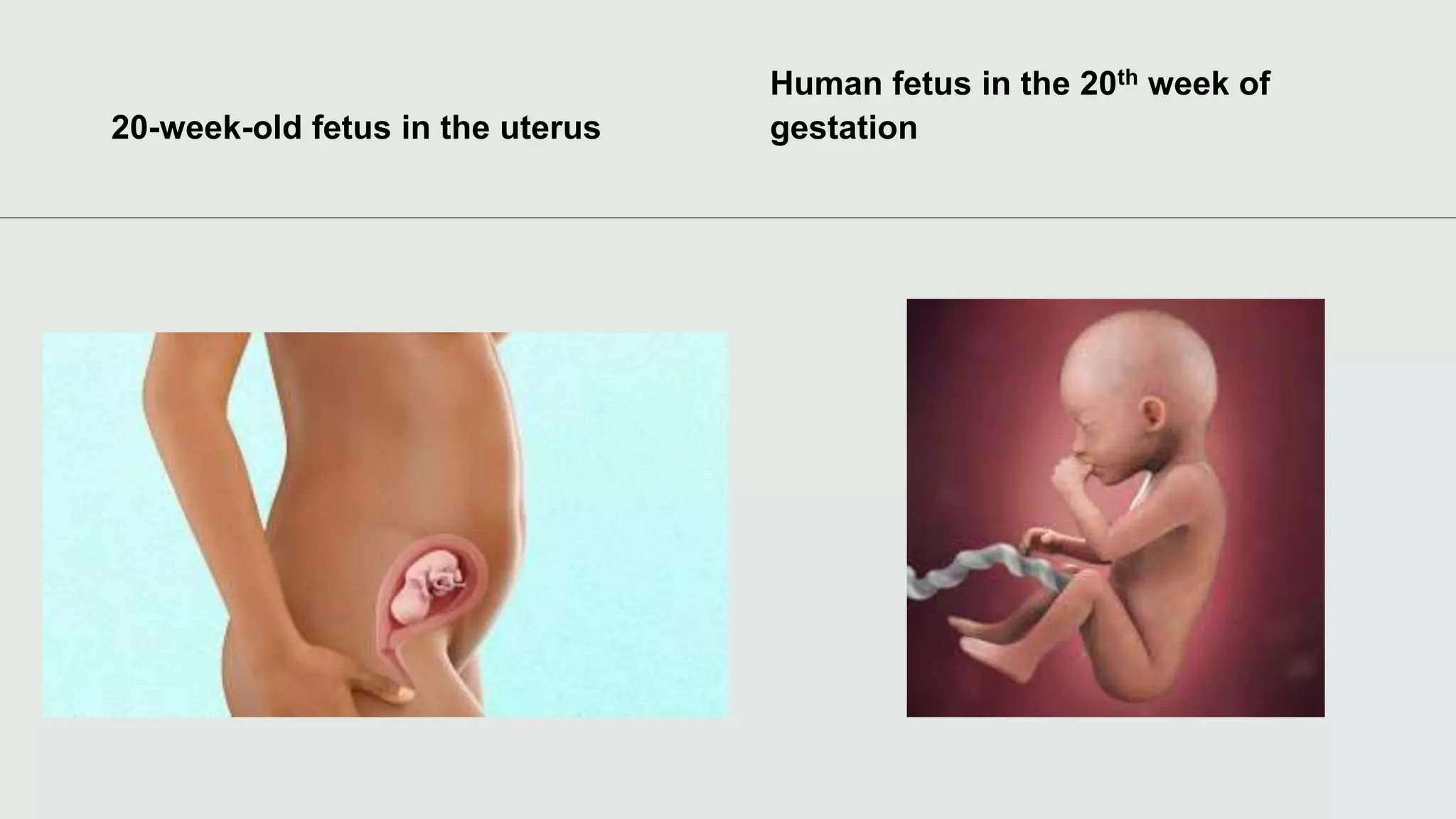
The document describes the stages of fetal development from 9 weeks of gestation through birth. It notes that by 9 weeks, external features are evident and the fetus can move its limbs. From 10-12 weeks, the size doubles and features are more refined. By 13-16 weeks, the head becomes proportional and facial expressions can be observed. Various organs reach their sizes by 17-20 weeks and lanugo hair covers the body. Birth typically occurs between 36-40 weeks when contractions begin to dilate the cervix, the fetus is expelled, and the placenta is delivered. A C-section may be needed if vaginal birth poses risks.